12th Grade > Physics
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES MCQs
Total Questions : 24
| Page 2 of 3 pages
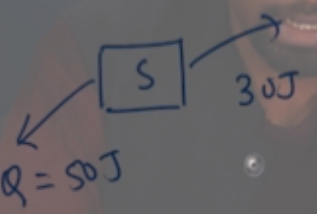
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
A system which exchanges both matter & energy with the surroundings is called an open system by definition.
Open system -matter and energy both can be transferred.
Closed system - Only energy can be transferred.
Isolated - Neither energy nor matter can be transferred.
:
B
A system which exchanges both matter & energy with the surroundings is called an open system by definition.
Open system -matter and energy both can be transferred.
Closed system - Only energy can be transferred.
Isolated - Neither energy nor matter can be transferred.
Answer: Option B. -> -80 J
:
B
Take a minute and try to get this on your own. Then move on the next video for the explanation.
:
B
Take a minute and try to get this on your own. Then move on the next video for the explanation.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Fundamental properties which determine the state of a system are referred to as state variables or state functions or thermodynamic parameters. The change in the state properties depends only on the initial and final states of the system, but is independent of the manner in which the change has been brought about. In other words, the state properties do ont depend upon the path taken.
:
A
Fundamental properties which determine the state of a system are referred to as state variables or state functions or thermodynamic parameters. The change in the state properties depends only on the initial and final states of the system, but is independent of the manner in which the change has been brought about. In other words, the state properties do ont depend upon the path taken.
Answer: Option D. -> TP1≠TP2.
:
D
Just like a single macroscopic pressure being undefined for a gas which is not in equilibrium, a single macroscopic temperature is also undefined. So the temperature at P1andP2 need not necessarily be the same, and most likely wouldn't be the same.
:
D
Just like a single macroscopic pressure being undefined for a gas which is not in equilibrium, a single macroscopic temperature is also undefined. So the temperature at P1andP2 need not necessarily be the same, and most likely wouldn't be the same.
Answer: Option C. -> 70 m
:
C
Accoding to Boyle's law (P1V1)bottom = (P2V2)top
(10 + h) × 43πr13 = 10 × 43πr23 but r2=2r1
∴ (10 + h)r13 = 10 × 8 r13 ∴ 10 + h = 80 ∴ h = 70 m
:
C
Accoding to Boyle's law (P1V1)bottom = (P2V2)top
(10 + h) × 43πr13 = 10 × 43πr23 but r2=2r1
∴ (10 + h)r13 = 10 × 8 r13 ∴ 10 + h = 80 ∴ h = 70 m
Answer: Option D. -> 2 ×105Nm2
:
D
Energy = 300 J/litre = 300 ×103J/m3
P= 23E=2×300×1033 = 2 ×105N/m2
:
D
Energy = 300 J/litre = 300 ×103J/m3
P= 23E=2×300×1033 = 2 ×105N/m2
Answer: Option D. -> 30R
:
D
As we know 1 mol of any ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.4 liters.
Hence number of moles of gas μ=44.822.4 = 2
Since the volume of cylinder is fixed,
Hence (△Q)V = μ(CV)△T=2×32R×10 = 30R(∵(CV)mono=3R2))
:
D
As we know 1 mol of any ideal gas at STP occupies a volume of 22.4 liters.
Hence number of moles of gas μ=44.822.4 = 2
Since the volume of cylinder is fixed,
Hence (△Q)V = μ(CV)△T=2×32R×10 = 30R(∵(CV)mono=3R2))
Answer: Option C. -> 5RT4V
:
C
The pressure exerted by a gas is given by
P=nRTV
= massmolecularweight×RTV
Pressure exerted by oxygen P1=832RTV=14RTV
Pressure exerted by oxygen P2=1428RTV=12RTV
Pressure exerted by carbon dioxide
P3=2244RTV=12RTV
From Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure exerted by the mixture is given by
P=P1+P2+P3
=14RTV+12RTV+12RTV
= 5RT4V,
which is choice (c)
:
C
The pressure exerted by a gas is given by
P=nRTV
= massmolecularweight×RTV
Pressure exerted by oxygen P1=832RTV=14RTV
Pressure exerted by oxygen P2=1428RTV=12RTV
Pressure exerted by carbon dioxide
P3=2244RTV=12RTV
From Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure exerted by the mixture is given by
P=P1+P2+P3
=14RTV+12RTV+12RTV
= 5RT4V,
which is choice (c)
Answer: Option B. -> 22 gm
:
B
Vander wal's gas equation for μ mole of real gas
(P + μ2αV2)(V - μb) = μRT ⇒ P = μRTV−μb−μ2V2
on comparing the given equation with this standard equation we get μ=12. Hence μ = mM⇒ mass of gas
m = μM = 12×44 = 22gm
:
B
Vander wal's gas equation for μ mole of real gas
(P + μ2αV2)(V - μb) = μRT ⇒ P = μRTV−μb−μ2V2
on comparing the given equation with this standard equation we get μ=12. Hence μ = mM⇒ mass of gas
m = μM = 12×44 = 22gm
Answer: Option B. -> 1.40
:
B
CO is diatomic gas, for diatomic gas
Cp=72R and Cv=52R⇒γ=CpCv=7R25R2 = 1.4
:
B
CO is diatomic gas, for diatomic gas
Cp=72R and Cv=52R⇒γ=CpCv=7R25R2 = 1.4