6th Grade > Mathematics
PRACTICAL GEOMETRY MCQs
:
Construction of circle: 1 Mark
Construction of intersecting lines: 1 Mark
Construction of quadrilateral: 1 Mark
Construction:
1) Draw a circle of radius 4 cm with centre O.
2) Take a point A on the circle. Join OA.
3) Draw a perpendicular to OA at A.
4) Draw a radius OB, making an angle of 120° (180° – 60°) with OA.
5) Draw a perpendicular to OB at point B. Let these perpendiculars intersect at P.
6) PA and PB are the required tangents inclined at angle of 60°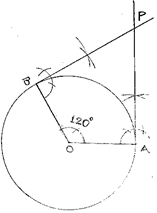
:
(a) 2 Marks
(b) 2 Marks
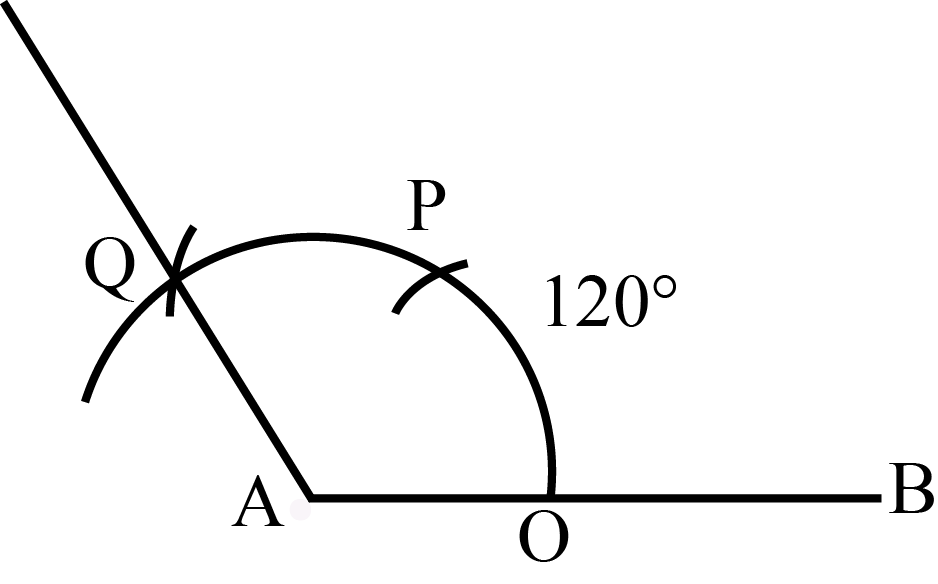
(a) The steps given below should be followed to construct an angle and its bisector:
i) Draw a line l and mark a point 'O' on it.
ii) Mark a point A at 115∘ with the help of protractor. Join OA.
iii) Draw an arc of convenient radius, while taking point O as the centre. Let it intersect both rays of the 115∘ angle at point A and B.
iv) Taking A and B as centres, draw an arc of radius more than 12 AB in the interior of the angle of 115∘. Let those intersect each other at C. Join OC.
OC is the required bisector of the angle of 115∘.
(b) As usual, we will have to use only a straight edge and the compass.
Given ∠A, whose measure is not known.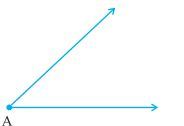
Step 1: Draw a line l and choose a point P on it.
![]()
Step 2: Place the compass at A and draw an arc to cut the rays of ∠A at B and C.
Step 3: Use the same compass setting to draw an arc with P as centre, cutting l in Q
Step 4: Set your compass to the length BC with the same radius.

Step 5: Place the compass pointer at Q and draw the arc to cut the arc drawn earlier in R.
Step 6: Join PR. This gives us ∠P. It has the same measure as ∠A.
This means ∠QPR has the same measure as ∠BAC.
:
Construction of circle: 1 Mark
Construction of chords: 1 Mark
Construction of bisector: 1 Mark
Meeting point: 1 Mark
i) Mark any point C on the sheet. Now, by adjusting the compass up to 3 cm and by putting the pointer of compass, draw the circle. It is the required circle of 3 cm radius.
ii) Take any two chords AB and CD in the circle.
iii) Taking A and B as centres and with radius more than half of AB, draw arcs on both sides of AB, intersecting each other at E, F. Join EF which is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
iv) Taking C and D as centres and with radius more than half of CD, draw arcs on both sides of CD, intersecting each other at G and H . Join GH which is the perpendicular bisector of CD.
Now, we find that EF and GH meet at the centre of circle O.
:
Construction of angle: 1 Mark
Construction of bisector: 1 Mark
Steps: 2 Marks
i) Draw any angle 125∘with O as its centre.
ii) Take points A and B on its two arms. Now taking O and A as centre and radius more than half of AB draw arcs at C and D.
iii) Similarly, draw the arcs at E and F on side OB.
iv) Join CD and EF.
These are the perpendicular bisectors of OA and OB.
:
C
Tracing the line may not give accurate result. Similarly, measuring using a ruler may give wrong results depending upon the angle of viewing. Using a compass and a ruler would be the easiest and most accurate method to copy a given line segment AB.
Draw a line AB. At A, draw an arc of length 3cm using compass such that it intersects AB at O. With the same spread of compass, put the compass pointer at O and make an arc that intersects the previous arc at P. With the same spread again, put the compass pointer at P and draw an arc that intersects the first arc at Q. Join A and Q. Using the protractor, measure ∠QAB. What is the value of ∠QAB.
:
B
There are no corners in a circular floor!
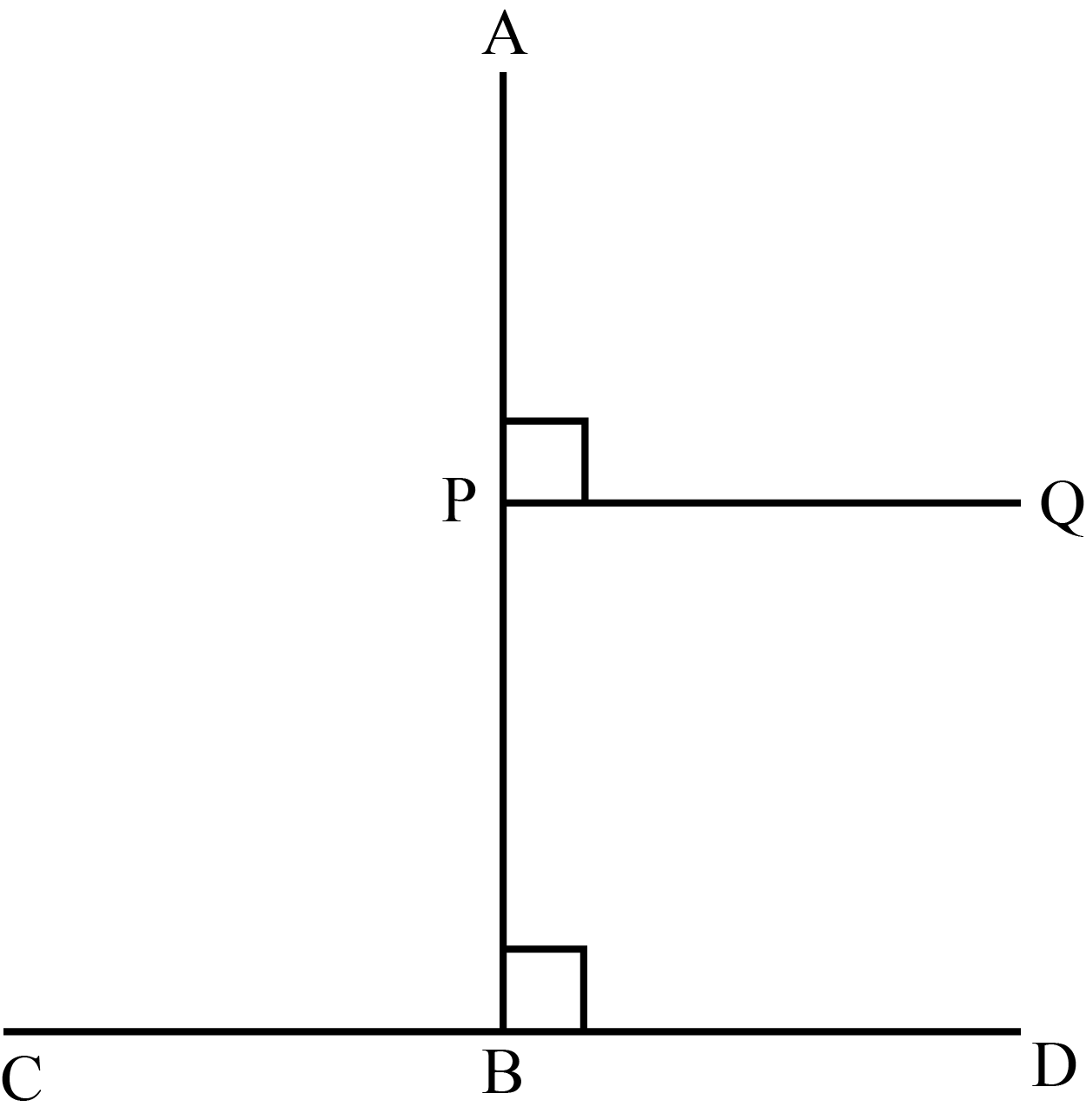
The 2 set squares that you have are both right angled triangles. So, one of the angles is 90∘.
When it is 12:15, the angle included between the hour hand and the minute hand is not 90∘, it is slightly lesser than that because the hour hand moves in clockwise direction as well along with the minute hand.
:
D
We can't draw a 60∘ angle using a set square that has 45∘-45∘-90∘ angles. Using a protractor and compass, and by using a Set Square (30∘-60∘-90∘), we can draw 60∘ angle.