12th Grade > Physics
OPTICS MCQs
Wave Optics, Ray Optics Refraction, Ray Optics Fundamentals, Ray Optics Curved Surface Refraction, Ray Optics Curved Mirrors
Total Questions : 111
| Page 9 of 12 pages
Answer: Option C. -> Carbon disulphide n =1.66
:
C
A lens shows opposite behaviour if μmedium>μlens.e., a convergent lens becomes divergent in nature
:
C
A lens shows opposite behaviour if μmedium>μlens.e., a convergent lens becomes divergent in nature
Answer: Option D. -> Complete image will be formed of decreased intensity
:
D
To form the complete image only two rays are to be passed through the lens. Moreoverthe total amount of light released by the object is not passing through the lens because of the covering. Therefore the intensity of the image will be reduced and theimage formed will befaint, not sharp.
:
D
To form the complete image only two rays are to be passed through the lens. Moreoverthe total amount of light released by the object is not passing through the lens because of the covering. Therefore the intensity of the image will be reduced and theimage formed will befaint, not sharp.
Answer: Option D. -> 2.0
:
D
For spherical surface using n2v−n1u=n2−n1R
n2R−1∞=n−1R ; n=2n−2⇒n=2.
:
D
For spherical surface using n2v−n1u=n2−n1R
n2R−1∞=n−1R ; n=2n−2⇒n=2.
Question 85. A glass hemisphere of radius 0.04 m and R.I. of the material 1.6 is placed centrally over a cross mark on a paper (i) with the flat face; (ii) with the curved face in contact with the paper. In each case the cross mark is viewed directly from above. The position of the images will be
[ISM Dhanbad 1994]
[ISM Dhanbad 1994]
Answer: Option D. -> 3f4
:
D
Let R be the radius of curvature of each surface. Then
1f=(1.5−1)(1R+1R)
∴R=f
For the water lens
1f=(43−1)(−1R−1R)=13(−2R)
or 1f=−23R
Now using 1F=1f1+1f2+1f3 we have
1F=1f+1f+1f
=2f−23f=43f ∴F=3f4
:
D
Let R be the radius of curvature of each surface. Then
1f=(1.5−1)(1R+1R)
∴R=f
For the water lens
1f=(43−1)(−1R−1R)=13(−2R)
or 1f=−23R
Now using 1F=1f1+1f2+1f3 we have
1F=1f+1f+1f
=2f−23f=43f ∴F=3f4
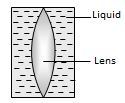
Answer: Option A. -> Should be greater than two times the radius of curvature of the refracting surface
:
A
Applying μ2v−μ1u=μ2−μ1R
1.5v−1−u=(1.5)−1R
Dividing with 1.5 on both the sides.
or 1v+23u=13R
For v to be positive 13R>23u
or u>2R
:
A
Applying μ2v−μ1u=μ2−μ1R
1.5v−1−u=(1.5)−1R
Dividing with 1.5 on both the sides.
or 1v+23u=13R
For v to be positive 13R>23u
or u>2R
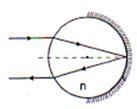
Answer: Option D. -> appear to intersect behind the reflecting surface.
:
D
Remember, as a rule of thumb, that if parallel rays after falling on any kind of reflecting surface get diverged, they can never actually intersect! And this is what happens in a convex mirror, it is a diverging mirror. So, parallel rays will never meet after getting reflected, but, when extended backwards they will appear to meet behind the mirror, you shall see in later modules that this how they from virtual image.
:
D
Remember, as a rule of thumb, that if parallel rays after falling on any kind of reflecting surface get diverged, they can never actually intersect! And this is what happens in a convex mirror, it is a diverging mirror. So, parallel rays will never meet after getting reflected, but, when extended backwards they will appear to meet behind the mirror, you shall see in later modules that this how they from virtual image.