12th Grade > Physics
OPTICS MCQs
Wave Optics, Ray Optics Refraction, Ray Optics Fundamentals, Ray Optics Curved Surface Refraction, Ray Optics Curved Mirrors
Total Questions : 111
| Page 10 of 12 pages
Answer: Option C. -> Concave mirror
:
C
Plane mirror and convex mirror always forms erect images. Image formed by
concave mirror may be erect or inverted depending on position of object.
:
C
Plane mirror and convex mirror always forms erect images. Image formed by
concave mirror may be erect or inverted depending on position of object.
Answer: Option A. -> Is plane
:
A
Lets first of all think about the situation given to us. Two parallel incident rays give us two parallel reflected rays. It means that at both the points the normal must be parallel, only then this is possible. (Think from the point of view of the law of reflection followed by both the rays.)
Now, we know that, for a spherical mirror, the normal at any point passes through the center of curvature. So, if all the normals pass through a point, they are not parallel.
So, we can only have parallel normal in the case of a plane mirror. So our mirror here is a plane mirror.
:
A
Lets first of all think about the situation given to us. Two parallel incident rays give us two parallel reflected rays. It means that at both the points the normal must be parallel, only then this is possible. (Think from the point of view of the law of reflection followed by both the rays.)
Now, we know that, for a spherical mirror, the normal at any point passes through the center of curvature. So, if all the normals pass through a point, they are not parallel.
So, we can only have parallel normal in the case of a plane mirror. So our mirror here is a plane mirror.

Answer: Option D. -> A real, inverted, same-sized image can be formed using a convex mirror
:
D
Convex mirror always forms, virtual, erect and smaller image.
:
D
Convex mirror always forms, virtual, erect and smaller image.
Answer: Option B. -> f&I4
:
B
There will be no changein focal length. f1=f But Intensity I∝A
But Intensity I∝A
I1I=r21r2=14∵r1=r2I1=I4
:
B
There will be no changein focal length. f1=f But Intensity I∝A
But Intensity I∝A
I1I=r21r2=14∵r1=r2I1=I4
Question 95. A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. If the eye is placed 60 cm to the right of the lens at a distance h below the principal axis, then the maximum value of h to see the image will be
Answer: Option A. -> mx(m+1)2
:
A
v−u=−m;v+u=x⇒u=x1+m
1f=1v−1u⇒f=mx(m+1)2
:
A
v−u=−m;v+u=x⇒u=x1+m
1f=1v−1u⇒f=mx(m+1)2
Answer: Option A. -> At one of the foci, virtual and double its size
:
A
1f=1v−1u (Given u=−f2 )
⇒1f=1v+(1f2)⇒1v=1f−2f
⇒1v=−1f and m=vu=ff2 = 2
So virtual at the focus and of double size.
:
A
1f=1v−1u (Given u=−f2 )
⇒1f=1v+(1f2)⇒1v=1f−2f
⇒1v=−1f and m=vu=ff2 = 2
So virtual at the focus and of double size.
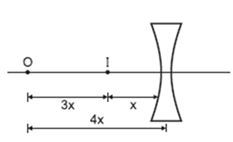
Answer: Option D. -> – 30 cm
:
D
For real image m=-2
∴ M = fu+f⇒−2=fu+f=20u+20⇒ u=-30 cm.
:
D
For real image m=-2
∴ M = fu+f⇒−2=fu+f=20u+20⇒ u=-30 cm.