12th Grade > Physics
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND INDUCTION MCQs
Electromagnetic Waves, Electromagnetic Induction, Waves On A String
Total Questions : 73
| Page 2 of 8 pages
Answer: Option D. -> between 0 and 2A
:
D
When two waves of amplitude A interfere the maximum amplitude is 2A and minimum is zero. The resultant amplitude in any general case is between 0 and 2A depending upon the phase difference.
:
D
When two waves of amplitude A interfere the maximum amplitude is 2A and minimum is zero. The resultant amplitude in any general case is between 0 and 2A depending upon the phase difference.
Answer: Option C. -> The total energy is in form of kinetic energy
:
C
When the string is such that the net displacement because of both the pulses is not zero. The total energy is distributed in kinetic and potential energy. When string has no displacement, there is no potential energy. Potential energy basically arises due to stretching of string which would be zero in such case and as we know all energy is conserved. The total energy is only kinetic!
:
C
When the string is such that the net displacement because of both the pulses is not zero. The total energy is distributed in kinetic and potential energy. When string has no displacement, there is no potential energy. Potential energy basically arises due to stretching of string which would be zero in such case and as we know all energy is conserved. The total energy is only kinetic!
Answer: Option D. -> The pulses will pass through each other without any change in their shapes after the overlap.
:
D
The shapes of wave pulses after the overlap are identical to their original shapes.
After overlap each pulse travels just as it did before.
:
D
The shapes of wave pulses after the overlap are identical to their original shapes.
After overlap each pulse travels just as it did before.
Question 15. Doing the Mexican wave' in a sports stadium is when people stand and sit in a continuuous order. So as to make a wave [as looked from outside] people don't leave their respective seat and just move up and down. The wave, transverse in nature appears to be moving. Is this example of a real physical wave?
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
A wave or a 'real' physics wave transports both momentum and energy which of course this wave doesn't do. [we are not talking about sports enthusiasm] This is not a real physics wave!
:
B
A wave or a 'real' physics wave transports both momentum and energy which of course this wave doesn't do. [we are not talking about sports enthusiasm] This is not a real physics wave!
Answer: Option A. -> 12
:
A
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B.A transverse wave travels on A with speed vA and on B with speed vB.The ratio (vAvB) is
v = √Tμ; as T is constant, v ∝ 1√μ
But μ = masslength = πr2ρ → μ ∝ r2
⇒ v ∝ 1r → vAvB = rBrA = r2r = 12
:
A
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B.A transverse wave travels on A with speed vA and on B with speed vB.The ratio (vAvB) is
v = √Tμ; as T is constant, v ∝ 1√μ
But μ = masslength = πr2ρ → μ ∝ r2
⇒ v ∝ 1r → vAvB = rBrA = r2r = 12
Answer: Option B. -> amplitude A2, frequency ωπ
:
B
y=Asin2(kx−ωt)
This is not ideal equation of wave we don't havesin2θ in ideal equation so let's remove the square.
Use trigonometry
cos2θ=cos2θ−sin2θ
=1−2sin2θ
sin2θ=1−cos2θ2
y=A{1−cos2(kx−wt)2}2
y=A2−A2cos(2kx−2ωt)
y′=(y−A2)=−A2cos(2kx−2ωt)
So amplitude =−A2
angular frequency(ω′)=2ω
frequency(f)=ω2π=2ω2π=ωπ
:
B
y=Asin2(kx−ωt)
This is not ideal equation of wave we don't havesin2θ in ideal equation so let's remove the square.
Use trigonometry
cos2θ=cos2θ−sin2θ
=1−2sin2θ
sin2θ=1−cos2θ2
y=A{1−cos2(kx−wt)2}2
y=A2−A2cos(2kx−2ωt)
y′=(y−A2)=−A2cos(2kx−2ωt)
So amplitude =−A2
angular frequency(ω′)=2ω
frequency(f)=ω2π=2ω2π=ωπ
Question 18. Two waves, each having a frequency of 100 Hz and a wavelength of 2.0 cm, are travelling in the same direction on a string. What is the phase difference between the waves (a) if the second wave was produced 0.015 s later than the first one at the same place, what would be the resultant amplitude? [Given individual amplitudes = 2.0 mm]
Answer: Option D. -> zero
:
D
Phase diagram method can be used here but for that we need to calculate the phase difference.
Δϕ=2πΔtT
Here Δt=0.015s
T1 which is the time period =1f
T=1100
So Δϕ=2π0.0151100=3π=2π+π as 2π is the period, the effective phase difference is π now let's draw
the phase diagram
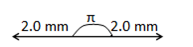
So we can see that net amplitude would be zero.
:
D
Phase diagram method can be used here but for that we need to calculate the phase difference.
Δϕ=2πΔtT
Here Δt=0.015s
T1 which is the time period =1f
T=1100
So Δϕ=2π0.0151100=3π=2π+π as 2π is the period, the effective phase difference is π now let's draw
the phase diagram

So we can see that net amplitude would be zero.
Answer: Option B. -> y=5sin(π3x−4πt)
:
B
here λ=6m
∴k=2π6=π3
ω=2πT=2π0.5=4π
given,amplitude =5m
y=5sin(π3x−4πt)
[the standard equation is y=Asin(kx-ω t)]
:
B
here λ=6m
∴k=2π6=π3
ω=2πT=2π0.5=4π
given,amplitude =5m
y=5sin(π3x−4πt)
[the standard equation is y=Asin(kx-ω t)]
Answer: Option B. -> 2.5× 109 W/m2
:
B
Area through which the energy of beam passes
=(6.328×10−7)=4×10−13m2
∴I=PA=10−34×10−13=2.5×109W/m2
:
B
Area through which the energy of beam passes
=(6.328×10−7)=4×10−13m2
∴I=PA=10−34×10−13=2.5×109W/m2
















