12th Grade > Chemistry
ALCOHOLS PHENOLS AND ETHERS MCQs
Total Questions : 28
| Page 3 of 3 pages
Answer: Option C. -> 2−methylpropan−2−ol
:
C
Lucas reagent is Anhydrous ZnCl2+conc.HCl and it gives turbidity immediately with tertiary alcohols.
(CH3)3C−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→(CH3)3C−Cl+H2O
3∘reactsimmediately
(CH3)2CH−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→(CH3)2CH−Cl+H2O
2∘reactsafter5min.
CH3CH2CH2−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→CH3CH2CH2−Cl+H2O
1∘reactsonlyonheating.
:
C
Lucas reagent is Anhydrous ZnCl2+conc.HCl and it gives turbidity immediately with tertiary alcohols.
(CH3)3C−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→(CH3)3C−Cl+H2O
3∘reactsimmediately
(CH3)2CH−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→(CH3)2CH−Cl+H2O
2∘reactsafter5min.
CH3CH2CH2−OH+HCIAnhyd.ZnCl2+HCl−−−−−−−−−−−−→CH3CH2CH2−Cl+H2O
1∘reactsonlyonheating.
Answer: Option D. -> Electrophilic substitution reaction- Phenol > Benzene > p-nitrophenol
:
D
a) The acidic character of alcohols is due to the polar nature
of O–H bond. An electron-releasing group(–CH3,–C2H5) increases electron density on oxygen tending to decreasethe polarity of O-H bond. This decreases the acid strength.
Acidic strength- Tertiary alcohol < Secondaryalcohol < Primary alcohol
b) Alcohols have high boiling point due to hydrogen bonding. Aldehyde & ethers have high boiling points than alkanes due to polar-nature of C-O bond.
Boiling point order-n-Butane < ethoxyethane < pentanal < pentan-1-ol
c) Relative ease of dehydration of alcohols- Primary < Seconadary < Tertiary.
Greater the no. of alkyl groups, more stable is the carbocation due to positive inductive effect.
d) In phenol, presence of O-H group strongly activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic substitution reaction. Chloro group is weakly deactivating due to electronegative chlorine but o & p-director.
Due to nitro group, p-nitrophenol is strongly deactivating towardselectrophilic substitution reaction.
:
D
a) The acidic character of alcohols is due to the polar nature
of O–H bond. An electron-releasing group(–CH3,–C2H5) increases electron density on oxygen tending to decreasethe polarity of O-H bond. This decreases the acid strength.
Acidic strength- Tertiary alcohol < Secondaryalcohol < Primary alcohol
b) Alcohols have high boiling point due to hydrogen bonding. Aldehyde & ethers have high boiling points than alkanes due to polar-nature of C-O bond.
Boiling point order-n-Butane < ethoxyethane < pentanal < pentan-1-ol
c) Relative ease of dehydration of alcohols- Primary < Seconadary < Tertiary.
Greater the no. of alkyl groups, more stable is the carbocation due to positive inductive effect.
d) In phenol, presence of O-H group strongly activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic substitution reaction. Chloro group is weakly deactivating due to electronegative chlorine but o & p-director.
Due to nitro group, p-nitrophenol is strongly deactivating towardselectrophilic substitution reaction.
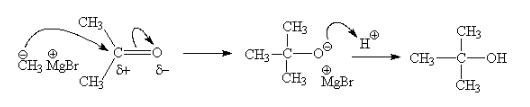
Answer: Option C. -> 2-Iodo-2-methylpropane and ethanol
:
C
In step 2 of the reaction, the departure of leaving group (HO–C2H5) creates a more stable carbocation [(CH3)3C+], and the reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
:
C
In step 2 of the reaction, the departure of leaving group (HO–C2H5) creates a more stable carbocation [(CH3)3C+], and the reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
Answer: Option A. -> Carbon-Oxygen linkage bond length is shorter in phenol than in methanol
:
A
The carbon– oxygen bond length (136 pm) in phenol is slightly less than that in methanol. This is due to
(i) partial double bond character on account of the conjugation of unshared electron pair of oxygen with the aromatic ring and
(ii) sp2 hybridised state of carbon to which oxygen is attached.
Ethers are Lewis bases due to presence of lone pairs on oxygen atom. Bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle (109∘−28'). It is due to the repulsion betweenthe unshared electron pairs of oxygen. Hydroboration-Oxidation of alkenes is in accordance with Anti-Markownikoff’s rule. The addition of borane to the double bond takes place in such a manner that the boron atom gets attached to the sp2 carboncarrying greater number of hydrogen atoms.
:
A
The carbon– oxygen bond length (136 pm) in phenol is slightly less than that in methanol. This is due to
(i) partial double bond character on account of the conjugation of unshared electron pair of oxygen with the aromatic ring and
(ii) sp2 hybridised state of carbon to which oxygen is attached.
Ethers are Lewis bases due to presence of lone pairs on oxygen atom. Bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle (109∘−28'). It is due to the repulsion betweenthe unshared electron pairs of oxygen. Hydroboration-Oxidation of alkenes is in accordance with Anti-Markownikoff’s rule. The addition of borane to the double bond takes place in such a manner that the boron atom gets attached to the sp2 carboncarrying greater number of hydrogen atoms.
Answer: Option A. -> Phenol
:
A
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, was first isolated in the early 19th century from coal tar.
:
A
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, was first isolated in the early 19th century from coal tar.
Answer: Option B. -> OH group in phenol is weakly deactivating towards electrophilic
substitution reaction.
:
B
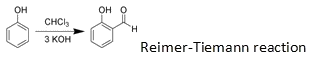
The presence of –OH group in phenols strongly activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic substitution and directs the incoming group to ortho and para positions due to resonance effect.
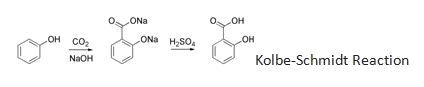
:
B
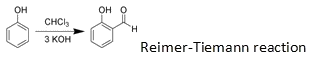
The presence of –OH group in phenols strongly activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic substitution and directs the incoming group to ortho and para positions due to resonance effect.
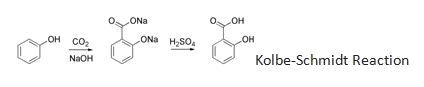
Answer: Option C. -> Ethyl alcohol
:
C
CH3COOH+4HLiAlH4−−−−→CH3CH2OH+H2O
:
C
CH3COOH+4HLiAlH4−−−−→CH3CH2OH+H2O