12th Grade > Biology
EVOLUTION MCQs
Total Questions : 49
| Page 2 of 5 pages
Answer: Option D. -> Homo habilis
:
D
Homo habilis, the first species of the genus Homo had a cranial capacity of about 600cc. However, it was much larger than that ofAustralopithecus. The cranial capacity of Homo erectus had increased to about 1100 cc and reached a maximum of 1500cc in Homo neanderthalensis. Homo sapiens have a cranial capacity of 1300cc, which is smaller than that ofHomo neanderthalensis.
:
D
Homo habilis, the first species of the genus Homo had a cranial capacity of about 600cc. However, it was much larger than that ofAustralopithecus. The cranial capacity of Homo erectus had increased to about 1100 cc and reached a maximum of 1500cc in Homo neanderthalensis. Homo sapiens have a cranial capacity of 1300cc, which is smaller than that ofHomo neanderthalensis.
Answer: Option C. -> The oceans of primitive earth
:
C
Earth was formed approximately 4.5 billion years ago. As it cooled down, a primitive atmosphere was created by the outgassing of early volcanoes. The early atmosphere contained no oxygen and could not support most of the life forms. In addition to the molten lava flowing into the ocean, some of the chemicals viz., hydrogen, helium, carbon dioxide, nitrogen etc. were supposedly washed down by the rains into the ocean where these chemicals gradually converted to simple organic molecules that eventually joined together into complex organic molecules like DNA and RNA. These chemical reactions made the ocean a reservoir of chemicals. Hence, it was known as the “organic soup”. Progressively, self-replication of simple nucleic acid molecules led to the origin of various simple life forms on Earth.
:
C
Earth was formed approximately 4.5 billion years ago. As it cooled down, a primitive atmosphere was created by the outgassing of early volcanoes. The early atmosphere contained no oxygen and could not support most of the life forms. In addition to the molten lava flowing into the ocean, some of the chemicals viz., hydrogen, helium, carbon dioxide, nitrogen etc. were supposedly washed down by the rains into the ocean where these chemicals gradually converted to simple organic molecules that eventually joined together into complex organic molecules like DNA and RNA. These chemical reactions made the ocean a reservoir of chemicals. Hence, it was known as the “organic soup”. Progressively, self-replication of simple nucleic acid molecules led to the origin of various simple life forms on Earth.
Answer: Option C. -> Cretaceous
:
C
Cretaceous period witnessed the extinction of dinosaurs and primitive birds, with the emergence of the first modern birds. Among plants,angiosperms or flowering plants emerged and diversified during this period.
:
C
Cretaceous period witnessed the extinction of dinosaurs and primitive birds, with the emergence of the first modern birds. Among plants,angiosperms or flowering plants emerged and diversified during this period.
Answer: Option D. -> Glutamic acid
:
D
In 1953, Stanley Miller and his advisor Harold Urey created experimental conditions similar to the proposed conditions on early earth, by Oparin and Haldane, - high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing methane, ammonia, hydrogenetc.They used a closed flask containing methane, ammonia, hydrogen(ratio 2:1:2) and passed steam over it by boiling water and connecting it with a glass tube. They needed an energy source to provide the conditions necessary for molecules to overcome their stability and fuse to form different structures. Miller and Urey took two tungsten electrodes and created a discharge between them, which raised the temperatures to almost 80∘C. In this high-energy chamber, they could synthesise several significant substances includingamino acids such asglycine, alanine and aspartic acid. Glutamic acid was not found in their observation.
:
D
In 1953, Stanley Miller and his advisor Harold Urey created experimental conditions similar to the proposed conditions on early earth, by Oparin and Haldane, - high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing methane, ammonia, hydrogenetc.They used a closed flask containing methane, ammonia, hydrogen(ratio 2:1:2) and passed steam over it by boiling water and connecting it with a glass tube. They needed an energy source to provide the conditions necessary for molecules to overcome their stability and fuse to form different structures. Miller and Urey took two tungsten electrodes and created a discharge between them, which raised the temperatures to almost 80∘C. In this high-energy chamber, they could synthesise several significant substances includingamino acids such asglycine, alanine and aspartic acid. Glutamic acid was not found in their observation.
Answer: Option A. -> predict the alleles in the gene pool of the next generation.
:
A
The Hardy - Weinberg equation helps predict the allelic composition in the gene pool of the next generation, without having to physically examine the genetic makeup of each individual. According to this equation, if ‘p’ represents the frequency of occurrence of a dominant allele in a population, and ‘q’ represents that of the respective recessive allele, then p2+2pq+q2=1.
:
A
The Hardy - Weinberg equation helps predict the allelic composition in the gene pool of the next generation, without having to physically examine the genetic makeup of each individual. According to this equation, if ‘p’ represents the frequency of occurrence of a dominant allele in a population, and ‘q’ represents that of the respective recessive allele, then p2+2pq+q2=1.
Answer: Option C. -> South America in the centre, Galapagos islands to its left and Africa to its right
:
C
The Galapagos group of islands is located off the left coast of South America. Africa on the other hand is situated to the right of South America. Even if the migration of tortoises happened originally from Africa to South America in the distant past as shown by plate tectonics, there are vast differences in the current setting. The tortoises which migrated from Africa and settled in South America, evolved adapting to local conditions and changed, and since Galapagos broke off from South America, on the other side, the tortoises which migrated from South America to Galapagos islands bear much more resemblance to the South American ones than their distant past cousins of Africa.
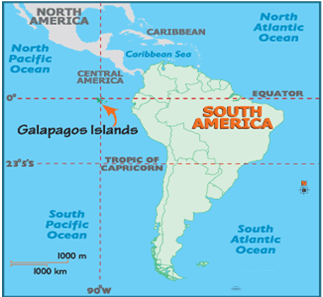
:
C
The Galapagos group of islands is located off the left coast of South America. Africa on the other hand is situated to the right of South America. Even if the migration of tortoises happened originally from Africa to South America in the distant past as shown by plate tectonics, there are vast differences in the current setting. The tortoises which migrated from Africa and settled in South America, evolved adapting to local conditions and changed, and since Galapagos broke off from South America, on the other side, the tortoises which migrated from South America to Galapagos islands bear much more resemblance to the South American ones than their distant past cousins of Africa.

:
Dryopithecus fossils were discovered in France in the 1850s. Since mostDryopithecus fossils were discovered in European countries like Spain, France and Hungary, they are called “European fossil apes”.
Answer: Option A. -> Paleocene → Eocene → Oligocene → Miocene → Pliocene
:
A
The tertiary period of the Cenozoic era is further subdivided into five epochs, in the order- Paleocene (67 - 55.5 mya), Eocene (55.5 - 33.7 mya), Oligocene (33.7 - 23.8 mya), Miocene (23.8 - 5.3 mya) and Pliocene (5.3 - 1.8 mya) epoch.
:
A
The tertiary period of the Cenozoic era is further subdivided into five epochs, in the order- Paleocene (67 - 55.5 mya), Eocene (55.5 - 33.7 mya), Oligocene (33.7 - 23.8 mya), Miocene (23.8 - 5.3 mya) and Pliocene (5.3 - 1.8 mya) epoch.
Answer: Option B. -> Convergent evolution of Australian marsupials and placental mammals
:
B
The Tasmanian wolf, now extinct, was native to Australia, Tasmania and New Guinea. The Australian marsupials resemble placental mammals living today on other continents. The similarity between some individual members of the two sets of mammals argues strongly that they are the result of convergent evolution, similar forms having evolved in different isolated areas because of similar selective pressues in similar environments. Because selection in these instances has tended to favour changes that made the two groups more alike, their phenotypes have converged.
:
B
The Tasmanian wolf, now extinct, was native to Australia, Tasmania and New Guinea. The Australian marsupials resemble placental mammals living today on other continents. The similarity between some individual members of the two sets of mammals argues strongly that they are the result of convergent evolution, similar forms having evolved in different isolated areas because of similar selective pressues in similar environments. Because selection in these instances has tended to favour changes that made the two groups more alike, their phenotypes have converged.
Answer: Option B. -> The homozygous recessive genotype in a given population
:
B
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is expressed as: p2+2pq+q2=1, where p is the frequency of the dominant allele (for instance, A) and q is the frequency of the recessive allele (for instance, a) in the population. In the equation, p2represents the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA in this case), q2represents the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa), and 2pq represents the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa).
:
B
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is expressed as: p2+2pq+q2=1, where p is the frequency of the dominant allele (for instance, A) and q is the frequency of the recessive allele (for instance, a) in the population. In the equation, p2represents the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA in this case), q2represents the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa), and 2pq represents the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa).