10th Grade > Mathematics
TRIANGLES MCQs
:
B
The ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to ratio of squares of corresponding sides.
4964=(Side of first 1st triangle)2(Corresponding side of 2nd triangle)2
78=Side of first 1st triangleCorresponding side of 2nd triangle
⇒ Ratio of corresponding sides =7:8
:
B, C, and D
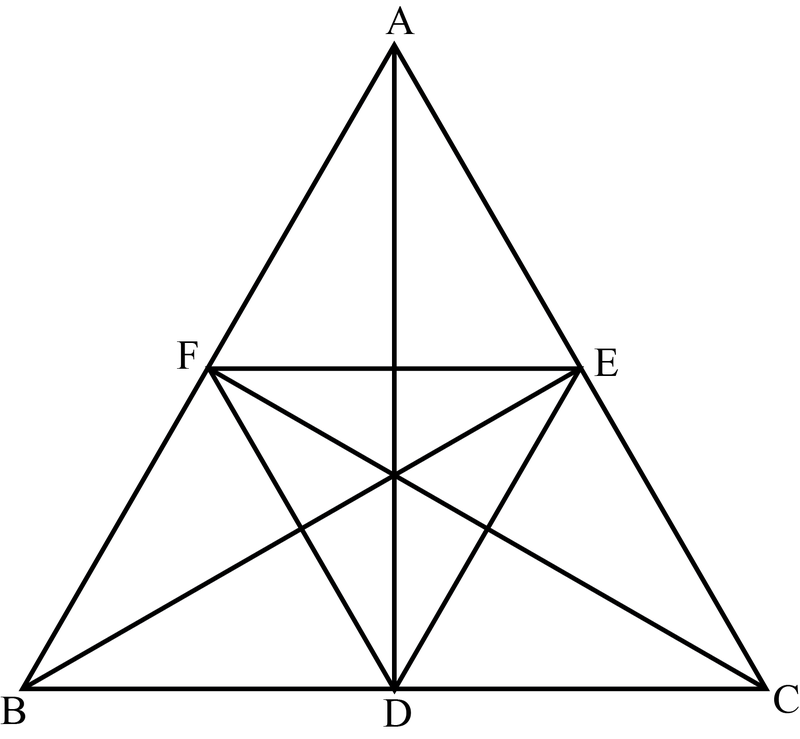
Consider △AEF
AE = AF (As △ABC is equilateral and E and F are midpoints of sides AC and AB respectively)
⇒∠AFE=∠AEF=∠A=60o
⇒△AEF is equilateral.
Similarly we can prove that △DEC and △BFD are equilateral.
Since △DEF share a common side with each of the other three triangles, △DEF is also equilateral.
⇒△DEF≅△AEF
⇒△DEF≅△DEC
⇒△DEF≅△BFD by using SSS postulate.
:
By applying Pythagoras theorem:
AB2+BC2=AC2
62+2.52=AC2
We get, AC = 6.5m
:
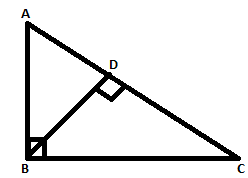
B
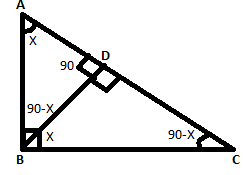
Consider △ADB and △ABC
∠BAD = ∠BAC [common angle]
∠BDA = ∠ABC [ 90∘]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion, △ADB and △ABC are similar.
So, ABAC=ADAB ⇒ AB2 = AC.AD ---(I)
Similarly, △BDC and △ABC are similar.
So, BCAC = DCBC ⇒ BC2 = AC.DC ---(II)
Dividing (I) and (II) and cancelling out AC, we get, (ABBC)2 = ADDC ----(III)
Also, In △ADB, AB2 = AD2 + DB2 and in △BDC, CB2 = CD2 + DB2 [Pythagoras theorem]
Subtracting these two equations above and cancelling off DB2 on both sides, we get
AB2 - BC2 = AD2 - CD2 ⇒ AB2 + CD2 = AD2 + BC2 --------------(IV)
Dividing this equation with BC2 on both sides, AB2BC2 + CD2BC2 = AD2BC2 + BC2BC2 ⇒ AB2BC2 + CD2BC2 = AD2BC2 + 1
⟹ AB2BC2 - 1 = AD2BC2 - CD2BC2
⟹ ADDC - 1 = AD2−CD2BC2 [Using (III)]
⟹AD−DCDC = (AD−CD)(AD+CD)BC2
⟹1DC = ACBC2
⟹ BC2 = AC.DC
Consider △ABC and △BDC,
∠ABC=∠BDC=90∘
∠C=∠C [Common angle]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion, △ABC and △BDC are similar.
ACBC = BCDC
BC2 = AC×DC
Refer to the following figure. Three squares are constructed on each side of the triangle as shown, with the length of each square equal to the side on which it is constructed. If the largest side is 13, sum of the areas of the three squares is __. The angle opposite to the blue colour square is the right angle.
:
Let the other two sides of the triangle be a and b. Since the largest side is the hypotenuse, we have, by Pythagoras theorem,
Hypotenuse2 = a2 + b2
132 = a2 + b2 = 169 ------------------- (I)
Now,
Sum of the areas of the three squares = (side of yellow square)2 + (side of brownish square)2 +
(side of blue square)2
Sum of the areas of the three squares =a2 + b2 + 132 = 132 + 132 (from (I))
Sum of the areas of the three squares = 169 + 169 = 338.
:
B
Let O be the centre of the circle. The angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle. (here that point is P).
∠AOB=180∘
⇒∠APB=∠AOB2=90∘
∴ △APB is a triangle, right angled at P.
⇒ By pythagoras theorem,
AB2=AP2+PB2=(2PB)2+PB2 =5 PB2
⇒AB=√5 PB
⇒PB=AB√5=d√5
:
C
The ratio of the area of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding heights
So,
(Height of smaller △)2(Height of bigger △)2=1248=14
Let the height of bigger triangle be x
∴(2.1)2x2=14⇔x=√4×(2.1)2
=(2×2.1)=4.2 cm
:
A
All congruent figures are similar but the similar figures need not be congruent as in case of similar figures only shape is considered whereas, in the case of congruent figures, both shape and sizes are considered. Hence, the statement is correct.