10th Grade > Mathematics
TRIANGLES MCQs
Total Questions : 58
| Page 2 of 6 pages
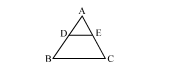
Answer: Option B. -> 9: 16
:
B
Let the triangles be △ABC and △DEF
Then AB=3 units and DE=4 units.
Each angle of both △ABC and △DEF is 60∘.
△ABE∼△ACF
(AAA similarity)
So,
ar(ABC)ar(DEF)=BC2EF2=3242=916
:
B
Let the triangles be △ABC and △DEF
Then AB=3 units and DE=4 units.
Each angle of both △ABC and △DEF is 60∘.
△ABE∼△ACF
(AAA similarity)
So,
ar(ABC)ar(DEF)=BC2EF2=3242=916
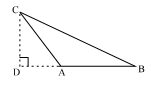
Answer: Option C. -> a2 = b2 + c2 + bc
:
C
In △CDB,
BC2=CD2+BD2[Pythagoras theorem]
BC2=CD2+(DA+AB)2
BC2=CD2+DA2+AB2+(2×DA×AB)...(i)
In △ADC,
CD2+DA2=AC2...(ii)[Pythagoras Theorem]
Here, ∠CAB=120∘ (given)
⇒∠CAD=60∘ (since∠CAD and∠CAB form a linear pair of angles)
Also, cos60∘=ADAC
AC=2AD...(iii)
Substituting the values from (ii)&(iii)in(i) we get,
BC2=AC2+AB2+(AC×AB)
a2=b2+c2+bc
Alternatively,
Since ∠A is an obtuse angle in △ABCso,
BC2=AB2+AC2+2AB.AD=AB2+AC2+2×AB×12×AC[∵AD=ACcos60∘=12AC]=AB2+AC2+AB×AC
⇒a2=b2+c2+bc
:
C
In △CDB,
BC2=CD2+BD2[Pythagoras theorem]
BC2=CD2+(DA+AB)2
BC2=CD2+DA2+AB2+(2×DA×AB)...(i)
In △ADC,
CD2+DA2=AC2...(ii)[Pythagoras Theorem]
Here, ∠CAB=120∘ (given)
⇒∠CAD=60∘ (since∠CAD and∠CAB form a linear pair of angles)
Also, cos60∘=ADAC
AC=2AD...(iii)
Substituting the values from (ii)&(iii)in(i) we get,
BC2=AC2+AB2+(AC×AB)
a2=b2+c2+bc
Alternatively,
Since ∠A is an obtuse angle in △ABCso,
BC2=AB2+AC2+2AB.AD=AB2+AC2+2×AB×12×AC[∵AD=ACcos60∘=12AC]=AB2+AC2+AB×AC
⇒a2=b2+c2+bc
:
By applying Pythagoras theorem:
AB2+BC2=AC2
62+2.52=AC2
We get, AC = 6.5m
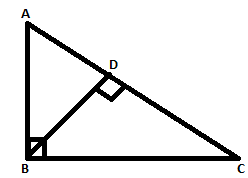
Answer: Option B. -> BC2
:
B
Consider △ADB and△ABC
∠BAD =∠BAC [common angle]
∠BDA=∠ABC [ 90∘]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion,△ADB and△ABC are similar.
So,ABAC=ADAB⇒AB2= AC.AD ---(I)
Similarly,△BDC and△ABC are similar.
So,BCAC =DCBC⇒BC2= AC.DC ---(II)
Dividing (I) and (II) and cancelling out AC, we get,(ABBC)2 = ADDC----(III)
Also, In△ADB,AB2 =AD2 + DB2 and in△BDC,CB2 = CD2 +DB2[Pythagoras theorem]
Subtracting these two equations above and cancelling offDB2 on both sides, we get
AB2 -BC2 = AD2 - CD2 ⇒AB2 +CD2 =AD2 +BC2 --------------(IV)
Dividing this equation with BC2 on both sides,AB2BC2 +CD2BC2 =AD2BC2 +BC2BC2 ⇒AB2BC2 +CD2BC2 =AD2BC2 + 1
⟹ AB2BC2 - 1 =AD2BC2-CD2BC2
⟹ ADDC - 1 =AD2−CD2BC2 [Using (III)]
⟹AD−DCDC =(AD−CD)(AD+CD)BC2
⟹1DC =ACBC2
⟹BC2 = AC.DC
Alternatively,
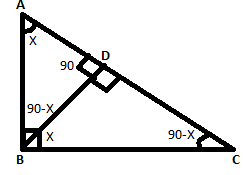
Consider △ABC and△BDC,
∠ABC=∠BDC=90∘
∠C=∠C [Common angle]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion,△ABC and△BDC are similar.
ACBC =BCDC
BC2 = AC×DC
:
B
Consider △ADB and△ABC
∠BAD =∠BAC [common angle]
∠BDA=∠ABC [ 90∘]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion,△ADB and△ABC are similar.
So,ABAC=ADAB⇒AB2= AC.AD ---(I)
Similarly,△BDC and△ABC are similar.
So,BCAC =DCBC⇒BC2= AC.DC ---(II)
Dividing (I) and (II) and cancelling out AC, we get,(ABBC)2 = ADDC----(III)
Also, In△ADB,AB2 =AD2 + DB2 and in△BDC,CB2 = CD2 +DB2[Pythagoras theorem]
Subtracting these two equations above and cancelling offDB2 on both sides, we get
AB2 -BC2 = AD2 - CD2 ⇒AB2 +CD2 =AD2 +BC2 --------------(IV)
Dividing this equation with BC2 on both sides,AB2BC2 +CD2BC2 =AD2BC2 +BC2BC2 ⇒AB2BC2 +CD2BC2 =AD2BC2 + 1
⟹ AB2BC2 - 1 =AD2BC2-CD2BC2
⟹ ADDC - 1 =AD2−CD2BC2 [Using (III)]
⟹AD−DCDC =(AD−CD)(AD+CD)BC2
⟹1DC =ACBC2
⟹BC2 = AC.DC
Alternatively,

Consider △ABC and△BDC,
∠ABC=∠BDC=90∘
∠C=∠C [Common angle]
Therefore by AA similarity criterion,△ABC and△BDC are similar.
ACBC =BCDC
BC2 = AC×DC
Answer: Option B. -> d√5
:
B
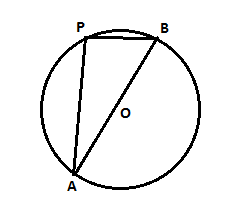
Let O be the centre of the circle. The angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.(here that point is P).
∠AOB=180∘
⇒∠APB=∠AOB2=90∘
∴△APB is a triangle, right angled at P.
⇒ By pythagoras theorem,
AB2=AP2+PB2=(2PB)2+PB2=5PB2
⇒AB=√5PB
⇒PB=AB√5=d√5
:
B
Let O be the centre of the circle. The angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.(here that point is P).
∠AOB=180∘
⇒∠APB=∠AOB2=90∘
∴△APB is a triangle, right angled at P.
⇒ By pythagoras theorem,
AB2=AP2+PB2=(2PB)2+PB2=5PB2
⇒AB=√5PB
⇒PB=AB√5=d√5