11th And 12th > Chemistry
S BLOCK ELEMENTS MCQs
The correct statements among the following are:
I. Due to greater polarizing power of Li+, Li2CO3 is most stable
II. LiHCO3 does not exist as solid
III. NaNO3 on strong heating gives NaNO2 whereas LiNO3 will give Li2O
IV. Sodium & Potassium ions are involved in the transport of sugars and amino acids into the cells
V. LiF is less soluble due to smaller hydration energy of Li+ ion
:
C
Li2CO3 is unstable and Li+ has high hydration energy.
:
B
The stability of alkali metal hydrides decreases with increase in the size of the metal cation. In other words, as we go down the group - the stability of the hydrides decreases.
:
D
Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na(Hg), is an alloy of mercury and sodium.
Na(Hg) is less reactive than Na. It will decrease the rate of reaction.
Sodium is highly reactive with water and decreasing the temperature does not decrease the rate of the reaction if we consider Le Chatelier's principle.
Sodium reacts with alcohol and acetic acid also. They will not affect the rate of reaction of sodium with water.
:
B
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light. The second statement describes the solvated cations (positively charged species) whereas the colour is due to the solvated electrons. Do note however that both the statements are accurate.
:
A
NaH+H2O→NaOH+H2(g)
As you can see - we get NaOH which is very strongly basic.
:
A
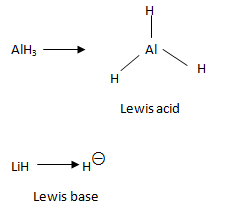
As shown in the figure, the central metal atom in AlH3 has only six valence electrons. Hence, it could accept a pair of electrons (Lewis acid) to complete its octet. On the other hand, H− is a Lewis base because it has two valence electrons thus having a completely filled shell. Further, since the ion readily shares or donates electrons - it acts as a Lewis base.
:
B
If we just look at only the ionic radii - then clearly Li+ should be the smallest and common sense might compel us to think that the small ion should exhibit the best conductivity. However, among alkali metal cations - Li+ has the highest charge density and is thus hydrated to the largest extent. Thus Li+ has the highest hydrated ion radius and least conductivity in water.
:
A
Violet belongs to the high-energy (low wavelength) section in the visible part of the Electromagnetic spectrum.

:
A
As we go down a group - density increases generally. However, there is a notable exception in potassium, which is less dense than sodium. Simply put, in the case of potassium the increase in shell size outweighs the pull of the core on the outer shell electron and so potassium is less dense than sodium.
:
A
X is NO2 & Y is O2 . Both the species have unpaired electrons in their electronic configurations (For O2 you will have to use MOT).
Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, both NO2 and O2 are paramagnetic.



















