11th And 12th > Physics
ROTATION ROCK AND ROLL MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option A. ->
MωM+4m
:
A
Initial angular momentum of ring =Iω=MR2ω
If four object each of mass m, and kept gently to the opposite ends of two perpendicular
diameters of the ring then final angular momentum =(MR2+4mR2)ω′
By the conservation of angular momentum
Initial angular momentum = Final angular momentum
MR2ω=(MR2+4mR2)ω′⇒ω′=(MM+4m)ω.
:
A
Initial angular momentum of ring =Iω=MR2ω
If four object each of mass m, and kept gently to the opposite ends of two perpendicular
diameters of the ring then final angular momentum =(MR2+4mR2)ω′
By the conservation of angular momentum
Initial angular momentum = Final angular momentum
MR2ω=(MR2+4mR2)ω′⇒ω′=(MM+4m)ω.
Question 2.
A circular platform is free to rotate in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis passing through its center. A tortoise is sitting at the edge of the platform. Now, the platform is given an angular velocity ω0. When the tortoise moves along a chord of the platform with a constant velocity (with respect to the platform), the angular velocity of the platform ω(t) will vary with time t as
Answer: Option B. ->

:
B
The angular momentum (L) of the system is conserved i.e. L = Iω = constant
When the tortoise walks along a chord, it first moves closer to the centre and then away from the centre. Hence, M.I. first decreases and then increases. As a result, ω will first increase and then decrease. Also the change in ω will be non-linear function of time.

:
B
The angular momentum (L) of the system is conserved i.e. L = Iω = constant
When the tortoise walks along a chord, it first moves closer to the centre and then away from the centre. Hence, M.I. first decreases and then increases. As a result, ω will first increase and then decrease. Also the change in ω will be non-linear function of time.
Answer: Option B. ->
(I1ω1+I2ω2)22(I1+I2)
:
B
By the law of conservation of angular momentum I1ω1+I2ω2=(I1+I2)ω
Angular velocity of system ω=I1ω1+I2ω2I1+I2
Rotational kinetic energy =12(I1+I2)ω2=12(I1+I2)(I1ω1+I2ω2I1+I2)2=(I1ω1+I2ω2)22(I1+I2).
:
B
By the law of conservation of angular momentum I1ω1+I2ω2=(I1+I2)ω
Angular velocity of system ω=I1ω1+I2ω2I1+I2
Rotational kinetic energy =12(I1+I2)ω2=12(I1+I2)(I1ω1+I2ω2I1+I2)2=(I1ω1+I2ω2)22(I1+I2).
Answer: Option D. ->
All will make same number of rotations
:
D
As W=τθ=Energy⇒θ=Energyτ=2nπ
So, if energy and torque are same then all the bodies will make same number of rotation.
:
D
As W=τθ=Energy⇒θ=Energyτ=2nπ
So, if energy and torque are same then all the bodies will make same number of rotation.
Answer: Option B. ->
√43gh
:
B
Velocity at the bottom (v)=√2gh1+K2R2=√2gh1+12=√43gh.
:
B
Velocity at the bottom (v)=√2gh1+K2R2=√2gh1+12=√43gh.
Answer: Option A. ->
57gsinθ
:
A
Acceleration (a) =gsinθ1+K2R2=gsinθ1+25=57gsinθ.
:
A
Acceleration (a) =gsinθ1+K2R2=gsinθ1+25=57gsinθ.
Answer: Option C. ->
g4
:
C
a=gsinθ1+k2R2=gsin30∘1+1=g4 [As k2R2=1 and θ=30∘]
:
C
a=gsinθ1+k2R2=gsin30∘1+1=g4 [As k2R2=1 and θ=30∘]
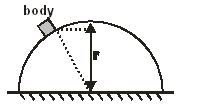
Answer: Option A. ->
2r3
:
A
Let normal reaction makes an angle θ from vertical, then v2=2gr(1−cosθ) and mv2r=mgcosθ ⇒ height from ground h=2r3
:
A
Let normal reaction makes an angle θ from vertical, then v2=2gr(1−cosθ) and mv2r=mgcosθ ⇒ height from ground h=2r3
Question 9.
A small meteorite of mass 'm' travelling towards the centre of earth strikes the earth at the equator. The earth is a uniform sphere of mass 'M' and radius 'R'. The length of the day was 'T' before the meteorite struck. After the meteorite strikes the earth, the length of day increases (in sec) by
Answer: Option A. ->
5mT2M
:
A
I1ω1=I2ω2
25MR2×(2πT1)=(25MR2+mR2)2πT2
T2T1=1+5m2M
T2−T1T1=5m2M
T2−T1=5mT2M [i.e;T1=T]
:
A
I1ω1=I2ω2
25MR2×(2πT1)=(25MR2+mR2)2πT2
T2T1=1+5m2M
T2−T1T1=5m2M
T2−T1=5mT2M [i.e;T1=T]
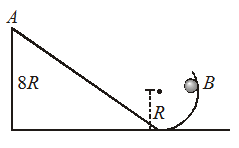
Answer: Option A. ->
[10gR]1/2
:
A
Applying the conservation of energy at points A and B, we have
mg(8R)=mv22+12Iω2+mgR
or mg(8R)=mv22+12(25mR2)(vR)2+mgR
=710mv2+mgR
mg(8R−R)=710mv2
[10gR]1/2
:
A
Applying the conservation of energy at points A and B, we have
mg(8R)=mv22+12Iω2+mgR
or mg(8R)=mv22+12(25mR2)(vR)2+mgR
=710mv2+mgR
mg(8R−R)=710mv2
[10gR]1/2