12th Grade > Biology
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS MCQs
Total Questions : 69
| Page 5 of 7 pages
Answer: Option B. -> A middle piece of sugarcane internode
:
B
Sugarcane is propagated vegetatively primarily through stem cuttings or sections of the stalks called "setts", that is a section of thestem with at least one bud. Each sett contains one or more buds. The buds, located in at the nodes, and give rise to embryonic shoots consisting of a miniature stalk with small leaves. Therefore the internode of a sugarcane contain no bud and cannot be used as a vegetative propagule, whereas the eyes of a potato tuber, the rhizome of ginger and the leaflets on the margin of Bryophyllum are all vegetative propagules.
:
B
Sugarcane is propagated vegetatively primarily through stem cuttings or sections of the stalks called "setts", that is a section of thestem with at least one bud. Each sett contains one or more buds. The buds, located in at the nodes, and give rise to embryonic shoots consisting of a miniature stalk with small leaves. Therefore the internode of a sugarcane contain no bud and cannot be used as a vegetative propagule, whereas the eyes of a potato tuber, the rhizome of ginger and the leaflets on the margin of Bryophyllum are all vegetative propagules.
Answer: Option D. -> Once in 50-100 yrs
:
D
Some plants are monocarpic i.e. they flower only once in their lifetime. Bamboo (Bambusa) produces flowers only after 50-100 years, produce large number of fruits once in their lifetime and die. Another such example is the Neelakuranji (Strobilanthus kunthiana) which flowers synchronously after every 12 years, set seeds and die.
:
D
Some plants are monocarpic i.e. they flower only once in their lifetime. Bamboo (Bambusa) produces flowers only after 50-100 years, produce large number of fruits once in their lifetime and die. Another such example is the Neelakuranji (Strobilanthus kunthiana) which flowers synchronously after every 12 years, set seeds and die.
Answer: Option B. -> Clones
:
B
Clones are identical to each other and their parents as they are produced from a single parent, with no modification of their genetic material. Therefore theyare exact genetic copies. Gametes however, tend to have only half the DNA of the parent and identical twins have DNA identical to each other, but not to the parent.
:
B
Clones are identical to each other and their parents as they are produced from a single parent, with no modification of their genetic material. Therefore theyare exact genetic copies. Gametes however, tend to have only half the DNA of the parent and identical twins have DNA identical to each other, but not to the parent.
Answer: Option C. -> 20
:
C
A meiocyte is a type of cell that differentiates into a gamete through the process of meiosis. Through meiosis, the diploid meiocyte divides into four genetically different haploid gametes. Therefore a meiocyte typically has a haploid set of chromosomes, that is half the number relative to the somatic cell.In maize, however the meiocyte is diploid and so is its somatic cell. Hence both the meiocyte and somatic cells have 20 chromosomes.
:
C
A meiocyte is a type of cell that differentiates into a gamete through the process of meiosis. Through meiosis, the diploid meiocyte divides into four genetically different haploid gametes. Therefore a meiocyte typically has a haploid set of chromosomes, that is half the number relative to the somatic cell.In maize, however the meiocyte is diploid and so is its somatic cell. Hence both the meiocyte and somatic cells have 20 chromosomes.
Answer: Option A. -> Reproduction
:
A
Reproduction is the process of formation of a new individual of a species from the pre-existing one. It is meant for perpetuation of a species because the older individuals of each species undergo senescence and die.
:
A
Reproduction is the process of formation of a new individual of a species from the pre-existing one. It is meant for perpetuation of a species because the older individuals of each species undergo senescence and die.
Answer: Option C. -> 3 → 5 → 1 → 2→ 4
:
C
During sexual reproduction after gamete formation or gametogenesis, haploid gametes move towards each other, that is a process calledgamete transferand they fuse together. This process is called syngamy or fertilisation and it leads to the formation of a diploid zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo in a sequence of events that is collectively termed as embryogenesis.
:
C
During sexual reproduction after gamete formation or gametogenesis, haploid gametes move towards each other, that is a process calledgamete transferand they fuse together. This process is called syngamy or fertilisation and it leads to the formation of a diploid zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo in a sequence of events that is collectively termed as embryogenesis.
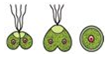
Answer: Option C. -> Sexual reproduction
:
C
In the given figure, two motile isogametes are fusing together to form a single celled zygote. Since fusion of male and female gamete is taking place it is sexual reproduction.
:
C
In the given figure, two motile isogametes are fusing together to form a single celled zygote. Since fusion of male and female gamete is taking place it is sexual reproduction.
Answer: Option B. -> This compensates for the loss of male gametes during transport
:
B
The number of male gametes produced is much more than the number of female gametes in most the organisms. The reason is that male gametes needs to move to reach the female gamete and in that process many gametes might be lost and so they have to be produced in large number.
:
B
The number of male gametes produced is much more than the number of female gametes in most the organisms. The reason is that male gametes needs to move to reach the female gamete and in that process many gametes might be lost and so they have to be produced in large number.
Answer: Option C. -> Embryogenesis
:
C
The first process in sexual reproduction is the production of gametes which is gametogenesis and after that the male gametes may be transferred to the site where the female gamete is present. Fertilization is the process of fusion of these 2 gametes. On fertilization the zygote is formed and this zygote undergoes embryogenesis. Therefore the development of zygote that collectively forms the post-fertilization events is termed embryogenesis.
:
C
The first process in sexual reproduction is the production of gametes which is gametogenesis and after that the male gametes may be transferred to the site where the female gamete is present. Fertilization is the process of fusion of these 2 gametes. On fertilization the zygote is formed and this zygote undergoes embryogenesis. Therefore the development of zygote that collectively forms the post-fertilization events is termed embryogenesis.
Answer: Option A. -> Juvenile phase
:
A
The life cycle of an organism can be divided into three different phases- the juvenile or vegetative phase, reproductive or mature phase and senescence or old age. The transition between these three phases are also guided by hormones. And the period of growth and maturity in organisms before they can reproduce sexually is known as juvenile.
:
A
The life cycle of an organism can be divided into three different phases- the juvenile or vegetative phase, reproductive or mature phase and senescence or old age. The transition between these three phases are also guided by hormones. And the period of growth and maturity in organisms before they can reproduce sexually is known as juvenile.