11th And 12th > Biology
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION MCQs
:
B
While lack of oxygen is the end cause for death in haemophilia, the reason for lack of oxygen is the continuous loss of blood due to failure of blood clotting. In this disease, a single protein that is a part of the cascade of proteins involved in the clotting of blood is affected. Due to this, in an affected individual a simple cut will result in non-stop bleeding.
:
B
In females, having a defective allele on the X-chromosome do not express the disorder, when the allele is recessive and the normal allele masks the activity of this allele. Males however having a single X chromosome, invariably expresses the disease, if they possess the defective allele. Since males get their X chromosome from the mother, the disease pedigree is from the carrier mother to her son.
Which among the following statements is/are correct with respect to the law of dominance?
A. Each character is controlled by pair of discrete units called factors.
B. In a dissimilar pair of factors one is dominant and the other is recessive.
C. It explains the expression of one trait in F1 and both traits in F2 generation.
D. Explains the proportion of phenotypes, 3:1 obtained in F2 generation.
:
D
Law of dominance explains that out of the two factors determining a character, one is dominant- this is the one that gets expressed in heterozygous condition. Thus the dominant character appears in F1 generation when the progenies are heterozygous. The law of dominance also explains the reappearance of the recessive factor in the F2 generation, when the recessive factors re-unite in a homozygous condition. Thus, it also explains the proportion of 3:1 obtained in the F2 generation.
:
A
Sutton and Boveri noted that the behavior of chromosomes was parallel to the behavior of genes, and used chromosome movement during cell division to explain Mendel’s laws. Sutton and Boveri argued that the pairing and separation of a pair of chromosomes would lead to the segregation of a pair of factors they carried. Sutton united the knowledge of chromosomal segregation with Mendelian principles and called it the chromosomal theory of inheritance.
:
B
Morgan conducted experiments on Drosophila related to X-linked inheritance. He suggested that the frequency of crossing over between two genes depends on distance between them. Physical crossing over during meiosis I is a normal event. The effect of this event is to rearrange heterozygous homologous chromsomes into new combinations. The term used for crossing over is recombination. Recombination can occur between any two genes on a chromosome, the amount of crossing over is a function of how close the genes are to each other on the chromosome. If two genes are far apart, for example at opposite ends of the chromosome, crossover and non-crossover events will occur in equal frequency. Genes that are closer together undergo fewer crossing over events and non-crossover gametes will exceed the number of crossover gametes. Therefore, determination of percentage of crossing over gives an idea about the position of genes on chromosomes.
:
A
In anaphase-I, the two alleles of the gene get separated as homologous pair of chromosomes separate at this stage. Parallel behaviour of genes and chromosomes was first observed by Sutton and Boveri and they used chromosome movement to explain Mendel's laws.
:
B
The sex of the child depends on the type of sperm that fertilises the egg. Each egg contains one X chromosome and a sperm may have either an X or a Y chromosome. It is a matter of chance as to which type of sperm fertilises the ovum. If the egg (having X chromosome) is fertilised by a X-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XX i.e., female. If the egg (having X chromosome) is fertilised by a Y-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XY i.e., male.
:
A
The white-eyed female (ww) produces gametes with only (w) allele. The male fly is red-eyed and produces gametes half of which carry (R) allele while the other half carry the Y chromosome. The progeny would comprise of 50% females and 50% males. All these females would be red-eyed (Rw; red being dominant), while the males would be white-eyed. The image below will explain the inheritance pattern.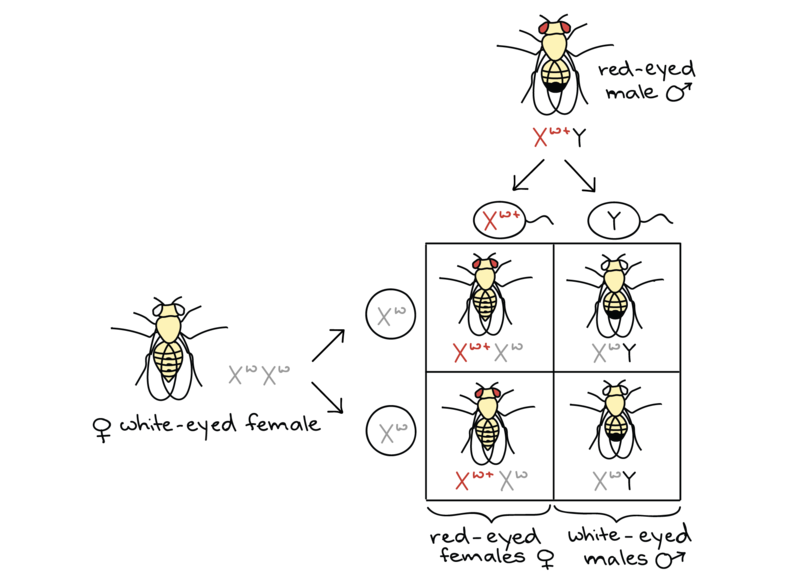
:
B
The cross between a suspected heterozygote with the recessive parent is called test cross. This cross basically helps to confirm if the organism in question is homozygous or heterozygous for the dominant allele.
An intercross is an organism that is the offspring of genetically dissimilar parents or stock; especially offspring produced by breeding plants or animals of different varieties, breeds, or species.
Top cross is a cross between a superior or purebred male and inferior female stock to improve the average quality of the progeny.
:
A
Biston betularia typica, (a light coloured peppered moth) and Biston betularaia carbonaria (a dark coloured moth) are two varieties of moth found in England. These two moths belonged to the same species but had a phenotypic variation, one being light in colour and the other being dark. The phenotypic variations affected the population size of both the moths during the time of industrial revolution in England.
















