11th And 12th > Chemistry
P-BLOCK GROUP 15 - PNICTOGENS MCQs
Total Questions : 15
| Page 1 of 2 pages
Answer: Option A. ->
NH3
:
A
We can look at the pKa table and see that NH3 is more stable than H2N−NH2.
:
A
We can look at the pKa table and see that NH3 is more stable than H2N−NH2.
Answer: Option D. ->
Metal Nitrite
:
D
Nitrates on heating with lead decompose to give the corresponding nitrites and Lead (II) Oxide
NaNO3+Pb→NaNO2+PbO
:
D
Nitrates on heating with lead decompose to give the corresponding nitrites and Lead (II) Oxide
NaNO3+Pb→NaNO2+PbO
Answer: Option B. ->
False
:
B
Sulphuric acid reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulphate
H2SO4+2NH3→(NH4)2SO4
Therefore, CaO is used to dry ammonia gas
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2
:
B
Sulphuric acid reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulphate
H2SO4+2NH3→(NH4)2SO4
Therefore, CaO is used to dry ammonia gas
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2
Answer: Option A. ->
True
:
A
HNO2 (Nitrous acid) is monobasic acid because it can donate only a single proton.
Basicity is the number of protons that an acid can give. From the structure,
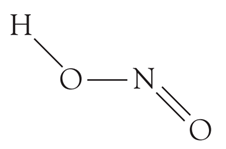
We can see that there is only one H atom and so only one proton can be abstracted from a HNO2 molecule. What can you say about the basicity of nitric acid?
:
A
HNO2 (Nitrous acid) is monobasic acid because it can donate only a single proton.
Basicity is the number of protons that an acid can give. From the structure,

We can see that there is only one H atom and so only one proton can be abstracted from a HNO2 molecule. What can you say about the basicity of nitric acid?
Answer: Option A. ->
True
:
Let us take a look at the structure of H3PO4: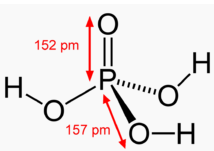
As we can see from the above structure, the Oxygen atom shown to have double bond character acts as a site to accept Hydrogen bonds while the other Hydrogen atoms attached via a single bond to Oxygen atoms can participate in Hydrogen bond. So in all, for every molecule there are 3 donor sites and one acceptor site.
:
Let us take a look at the structure of H3PO4:

As we can see from the above structure, the Oxygen atom shown to have double bond character acts as a site to accept Hydrogen bonds while the other Hydrogen atoms attached via a single bond to Oxygen atoms can participate in Hydrogen bond. So in all, for every molecule there are 3 donor sites and one acceptor site.
Answer: Option D. ->
Heating NH4NO2 carefully
:
D
Heating NH4NO3 carefully produces N2O but heating NH4NO2 liberates N2 gas.
:
D
Heating NH4NO3 carefully produces N2O but heating NH4NO2 liberates N2 gas.
Answer: Option D. ->
Nitrogen does not have any other allotropes under any circumstances
:
A, B, and C
Nitrogen atom is small in size and has the tendency to form pπ−pπ multiple bonds. In fact, the Nitrogen – Nitrogen triple bond in N2 molecule has very high thermodynamic stability with a dissociation energy of 942kJ.mol−1. This and other molecular orbital considerations account for the lack of allotropes of Nitrogen under normal conditions. However, it would be wrong to say that Nitrogen doesn’t have allotropes at all.
Gaseous nitrogen condenses into the β-hcp form at −210.01∘C. On freezing further, at temperatures below −237.6∘C Nitrogen assumes the cubic α form. At room temperature and atmospheric pressure, gaseous N2 does not have any other allotropes.
:
A, B, and C
Nitrogen atom is small in size and has the tendency to form pπ−pπ multiple bonds. In fact, the Nitrogen – Nitrogen triple bond in N2 molecule has very high thermodynamic stability with a dissociation energy of 942kJ.mol−1. This and other molecular orbital considerations account for the lack of allotropes of Nitrogen under normal conditions. However, it would be wrong to say that Nitrogen doesn’t have allotropes at all.
Gaseous nitrogen condenses into the β-hcp form at −210.01∘C. On freezing further, at temperatures below −237.6∘C Nitrogen assumes the cubic α form. At room temperature and atmospheric pressure, gaseous N2 does not have any other allotropes.
Answer: Option C. ->
N<P<As<Sb<Bi
:
C
This increase in atomic radii from N to Bi is due to the corresponding increase in the highest principal quantum number for each succeeding element. Thus option C is the correct one.
:
C
This increase in atomic radii from N to Bi is due to the corresponding increase in the highest principal quantum number for each succeeding element. Thus option C is the correct one.
Answer: Option A. ->
True
:
A
Cyanamide is an important organic chemical, which is used in agriculture and in the production of various pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It can be thought of as a nitrile group attached to an amine group.
Calcium Cyanamide is CaNCN, an inorganic compound that is extensively used as a fertilizer. It is synthesized by the famous Frank-Caro process (also known as the cyanamide process) where Calcium Carbide is heated with N2 gas in a reactor at 1273 K. The reaction is exothermic:
CaC2 + N2 → CaNCN + C
( Calcium (Nitrogen) ( Calcium (Carbon)
Carbide) Cyanamide)
CaCN2 + 4H2O → Ca(OH)2 + CO2 + 2NH3
(Calcium hydroxide) (Ammonia)
:
A
Cyanamide is an important organic chemical, which is used in agriculture and in the production of various pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It can be thought of as a nitrile group attached to an amine group.
Calcium Cyanamide is CaNCN, an inorganic compound that is extensively used as a fertilizer. It is synthesized by the famous Frank-Caro process (also known as the cyanamide process) where Calcium Carbide is heated with N2 gas in a reactor at 1273 K. The reaction is exothermic:
CaC2 + N2 → CaNCN + C
( Calcium (Nitrogen) ( Calcium (Carbon)
Carbide) Cyanamide)
CaCN2 + 4H2O → Ca(OH)2 + CO2 + 2NH3
(Calcium hydroxide) (Ammonia)
Answer: Option D. ->
All of these
:
D
Lead Heavy metal nitrates like copper (II) Nitrate or Lead (II) Nitrate decompose on heating to give the corresponding metal (II) oxide, nitrogen dioxide gas and dioxygen gas.
Pb(NO3)2→PbO+O2+NO2
:
D
Lead Heavy metal nitrates like copper (II) Nitrate or Lead (II) Nitrate decompose on heating to give the corresponding metal (II) oxide, nitrogen dioxide gas and dioxygen gas.
Pb(NO3)2→PbO+O2+NO2
















