12th Grade > Physics
OPTICS MCQs
Wave Optics, Ray Optics Refraction, Ray Optics Fundamentals, Ray Optics Curved Surface Refraction, Ray Optics Curved Mirrors
Total Questions : 111
| Page 3 of 12 pages
Answer: Option D. -> Trick question! The focus is defined for a convex mirror as the point where the reflected rays appear to meet.
:
D
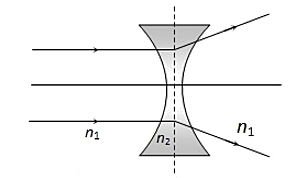
The design of a convex mirror is in such a way that parallel rays of light after reflection from the convex mirror, diverge. These rays do not converge at a point as in the case of a concave mirror. But if we extrapolate the reflected rays, we can say they appear to meet at a point on the non-reflecting side of the mirror. We actually define this point as focus of a convex mirror.
:
D
The design of a convex mirror is in such a way that parallel rays of light after reflection from the convex mirror, diverge. These rays do not converge at a point as in the case of a concave mirror. But if we extrapolate the reflected rays, we can say they appear to meet at a point on the non-reflecting side of the mirror. We actually define this point as focus of a convex mirror.

Answer: Option B. -> can be considered approximately parallel.
:
B
Nope, sunrays are not exactly parallel. And no, we don't just randomly assume it to make problems and life easy! Rather, it is a good approximation to consider sunrays to be parallel when they reach us, as the sun is really really far (149.6 million km!) from the Earth, hence the angle between the rays are very very small. Go watch the video again to realize this.
:
B
Nope, sunrays are not exactly parallel. And no, we don't just randomly assume it to make problems and life easy! Rather, it is a good approximation to consider sunrays to be parallel when they reach us, as the sun is really really far (149.6 million km!) from the Earth, hence the angle between the rays are very very small. Go watch the video again to realize this.
Answer: Option A. -> At −f, virtual and double its size.
:
A
Given u=−f2
1f=1v−1u
⇒1f=1v+(1f2)⇒1v=1f−2f
⇒1v=−1f
So v=−f i.e., the image will be formed at focus of the lens on the same side as that of the object.
Now magnificationm=vu=−f−f2=+2
So the image formed will be virtual with magnification +2.
:
A
Given u=−f2
1f=1v−1u
⇒1f=1v+(1f2)⇒1v=1f−2f
⇒1v=−1f
So v=−f i.e., the image will be formed at focus of the lens on the same side as that of the object.
Now magnificationm=vu=−f−f2=+2
So the image formed will be virtual with magnification +2.
Answer: Option C. -> 0.55 cm
:
C
By using IO=ff−u
Here O+5cm,f=−R2=−10cm,u=−1m=−100cm
So, I+5=−10−10−(−100)⇒I=−0.55cm.
:
C
By using IO=ff−u
Here O+5cm,f=−R2=−10cm,u=−1m=−100cm
So, I+5=−10−10−(−100)⇒I=−0.55cm.
Answer: Option D. -> 7.5 cm
:
D
R=-30cm ⇒ f=-15cm
O=+2.5cm,u=-10cm
By mirror formula 1−15=1v+1(−10)⇒v=20cm.
Also IO=vu⇒I(+2.5)=30(−10)⇒I=+7.5cm.
:
D
R=-30cm ⇒ f=-15cm
O=+2.5cm,u=-10cm
By mirror formula 1−15=1v+1(−10)⇒v=20cm.
Also IO=vu⇒I(+2.5)=30(−10)⇒I=+7.5cm.
Answer: Option A. -> 65
:
A
n1λ1=n2λ2
60×5890=n25460
n2=65
:
A
n1λ1=n2λ2
60×5890=n25460
n2=65