7th Grade > Biology
NUTRITION IN ANIMALS MCQs
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Requirements: 1 Mark
The absorption of nutrients into the body after digestion and its utilization by the body is called assimilation.
Two processes which happen before assimilation are digestion and absorption.
:
Structure: 1 Mark
Length of small intestine: 1 Mark
Length of large intestine: 1 Mark
The digestive system begins with the mouth and is followed by the pharynx, the oesophagus, the stomach, and the intestine, which is divided into two major sections: the small intestine and the large intestine.
The small intestine is a long and narrow tube about 6 to 7 metres (20 to 23 feet) long.
The large intestine is wider and shorter than small intestine. It is about 1.5 metre in length.
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Direction: 1 Mark
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that help in moving food to different processing areas in the digestive tract.
The process of peristalsis begins in the oesophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed and moves till the anus.
:
Each point: 1 Mark
1. A microscopic outgrowth on the surface of some tissues and organs, which serves to increase the surface area of the organ is called villi.
2. Numerous villi line the interior of the small intestine.Their shape may vary from finger-like (in the duodenum) to spade-like (in the ileum).
3. Intestinal villi are specialized for the absorption of soluble food material. Each villus contains blood vessels and a lymph vessel.
Complete the following table: [5 MARKS]
Digestive juices and enzymesSubstance digestedProduct FormedSalivaAmylaseGastric juiceProtease (pepsin) and hydrochloric acidPancreatic juiceProteases(trypsin)LipasesAmylaseIntestinal enzymesPeptidasesSucraseLactaseMaltaseBile from the liverBile salts
:
Rows of the table: 1 Mark each
Digestive juices and enzymesSubstance digestedProduct FormedSalivaStarchMaltoseAmylaseGastric juiceProteinsPeptonesProtease (pepsin) and hydrochloric acidPancreatic juiceProteases(trypsin)ProteinsPeptides and amino acidsLipasesFats emulsified by bileFatty acids and glycerolAmylaseStarchMaltoseIntestinal enzymesPeptidasesPeptidesAmino acidsSucraseSucrose (sugar)Glucose and fructoseLactaseLactose (milk sugar)Glucose and galactoseMaltaseMaltoseGlucoseBile from the liverBile saltsFat globulesSmaller Fat Globules
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Function: 1 Mark
Digestion: 1 Mark
Gastric glands are microscopic glandular cells present in the inner lining of the stomach.
The function of the gastric glands is to secrete a gastric juice comprising HCl, pepsin and prorennin.
This gastric juice helps in the digestion of proteins.
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Movement: 1 Mark
Digestion: 3 Marks
Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. Amoeba has a cell membrane, a round, dense nucleus and many small bubble-like vacuoles in its cytoplasm.
Movement:
Amoeba constantly changes its shape and position. It pushes out one or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet for movement and capturing food.
Digestion:
1. Amoeba feeds on some microscopic organisms. When it senses food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it. The food gets trapped in a food vacuole.
2. Digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole. They act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. Gradually the digested food is absorbed. The absorbed substances are used for growth, maintenance, and multiplication.
3. The undigested residue of the food is expelled outside by the vacuole. The basic process of digestion of food and release of energy is the same in all the organisms.
:
Enzymes: 1 Mark each
Any 3
1)Salivary Amylase - saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase, which acts on the starch in food and breaks it down to maltose.
2) Pancreatic Amylase - the pancreas secretes pancreatic juices, which contain the enzyme pancreatic amylase. This enzyme acts on the remaining complex carbohydrates and breaks them into simple carbohydrates.
3) Maltase - It acts on maltose and breaks it down into two glucose units.
4) Sucrase - It digests sucrose or table sugar into its constituent units of glucose and fructose.
5)Lactase - It breaks lactose or milk sugar into glucose and galactose.
:
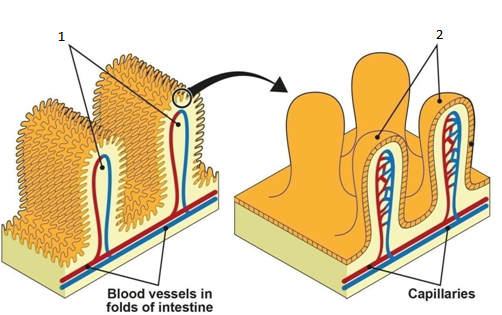
Labelling - 1 Mark each
Reason for folds: 1 Mark
1 - Villi
2 - Microvilli
Villi exist in the small intestine, and the main function of the small intestine is absorption. Absorption is directly dependent on surface area. So to increase the surface area, the internal surface of the intestinal wall is folded onto itself creating villi.
Again the surface of each villus is convoluted in a similar fashion and the resulting microscopic structures are called as microvilli (brush border).
:
Arrangement of teeth: 1 Mark each
1. The first set of teeth called as primary teeth, and are present in children. There are 20 in total and are gradually lost over time.
2. In humans, a total of 32 teeth eventually form in the adult. They are called permanent teeth. Each adult jaw contains a set of four incisors, which are used for biting. They are chisel-shaped and are present in the middle of the mouth.
3. These four are covered on both sides by single canines, sharp tearing teeth, which are much longer in carnivorous animals like lions and tigers.
4. Towards the rear of the jaw is a pair of premolars and then three larger molars on each side. The premolars and molars are flattened, ridged teeth with large surfaces adapted for grinding and powdering food.
5. During biting and chewing, a near-perfect placement of upper and lower sets of teeth is vital for efficiently processing ingested food. Misplacement may lead to pain, as well as poor processing of food.