10th Grade > Physics
LIGHT - REFLECTION REFRACTION MCQs
:
D
Given:
Speed of object, uo=5 ms−1
Speed of mirror, um=10 ms−1
Mirror and object are approaching each other.
To find:
Speed of image
Procedure:
Let initial position of object be at xoi=0
Let initial position of mirror be at xmi=u
Object distance equals the image distance. Hence, initial position of image is xii=2u
Distance is the product of speed and time.
After time t,
Position of object will be:
xof=xoi+uot=5t
Position of mirror will be:
xmf=xmi−uft=u−10t
Let the final position of image be xif
Using object distance equals image distance after time t.
xif−xmf=xmf−xof
xif=2u−25t
Distance moved by image in time t is:
si=xif−xii
si=−25t
Speed is the ratio of distance and time. Speed of the image is:
vi=sit=−25
Negative sign appears because image is moving leftwards.
Hence, speed of image is 25 ms−1
:
C
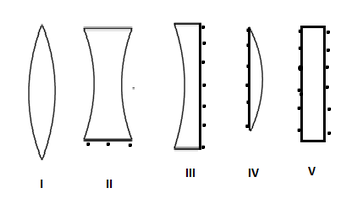
Lens should have at least one curved surface, so that it can converge or diverge the incoming light rays. The first optical system is called convex lens and the second one is concave lens. The third lens is called a plano-concave lens and the fourth one is called a plano-convex lens. The fifth optical system has two plane surfaces, and hence it can't be considered as lens.
:
D
Given:
Initial object distance, u=−60 m
Speed of object, vo=20 ms−1
Focal length, f=20 m
Time interval, t=2 s
Applying mirror formula to find the initial position of the image v:
1v+1u=1f
1v+1−60=120
v=15 m
Distance travelled by the object is the product of speed and time.
so=vot
so=20×2=40 m
Therefore, now the object distance:
uf=u+so=−60+40=−20 m
Applying mirror formula to find the final position of the image vf:
1vf+1uf=1f
1vf+1−20=120
vf=10 m
Average speed is the ratio of total distance travelled to the total time taken.
Average speed of the image:
vi=v−vft
vi=15−102=2.5 ms−1
:
D
Given:
Image distance v=−10 cm
Object distance u=−30 cm
(Using the sign conventions)
Let focal length of the lens be f.
Using the lens formula,
1f=1v−1u
1f=(1−10)−(1−30)
f=−15 cm
Here, negative sign for focal length shows that the lens is concave.
:
B
Given:
Radius of curvature, R=−40 m
Object distance, u=−60 m
Let the sign convention be such that the object distance is negative i.e. positive direction is taken along the direction of the incident ray.
From mirror formula,
1v+1u=1f
where:
v: Position of image
f: Focal length
But focal length is half of the radius.
⟹f=R2=−20 m
⟹1v+1−60=1−20
v=−30 m
Negative sign represents that object and image are on the same side of mirror.
:
B
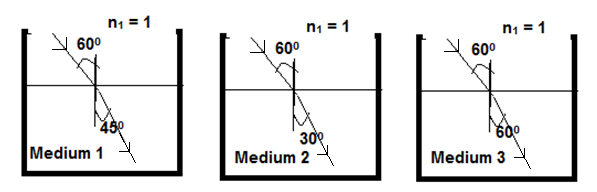
Angle of incidence i is same for all three media. Angle of refraction for the different media are:
rm1=45∘
rm2=30∘
rm3=60∘
Deviation will be highest for medium with highest optical density. Clearly, the deviation is highest (30∘) for Medium 2. Hence, Medium 2 has highest optical density.
:
A
According to Snell's law, for a light ray travelling from one medium to another, the ratio of sines of angle of incidence to the angle of refraction is a constant. This constant is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium one.
Here,
nair sinθair = nwatersinθwater or ⇒SinθairSinθwater=nwaternair correctly represents Snell's law.
:
C
The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length (in metres). When there is a combination of two lenses in contact, the effective power of the combination is the sum of the individual powers.
Total Power, P=P1 + P2
1f=1f1+1f2
f=f1f2f1+f2