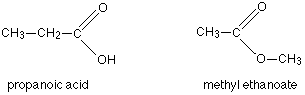11th And 12th > Chemistry
ISOMERISM MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option D. ->
RCH2NO2
:
D
Nitro compound exhibit tautomerism RCH2NO2
:
D
Nitro compound exhibit tautomerism RCH2NO2
Answer: Option A. ->
Metamerism
:
A
CH3COOC2H5 and C2H5COOCH3 , the alkyl groups on either side are different. Hence, they are metamers.
The difference is that in the first one a methyl group is attached to the carbon whereas in the second an ethyl group is attached to the carbon.
:
A
CH3COOC2H5 and C2H5COOCH3 , the alkyl groups on either side are different. Hence, they are metamers.
The difference is that in the first one a methyl group is attached to the carbon whereas in the second an ethyl group is attached to the carbon.
Answer: Option C. ->
2-Butanol
:
C
Aldehydes and ketones can be functional isomers. But alcohols are not isomeric with aldehydes.
You can just write down the structures of each and count the number of carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens to be certain.
:
C
Aldehydes and ketones can be functional isomers. But alcohols are not isomeric with aldehydes.
You can just write down the structures of each and count the number of carbons, hydrogens, and oxygens to be certain.
Answer: Option D. ->
Butanone
:
D
Ketone cannot be an isomer of ether. No matter how you arrange diethyl ether, you cannot get a ketone compound.
First one is simple right? Just remove one carbon on one side and add to the other side.
C2H5−O−C2H5 → C3H7−O−CH3
It can also become an alcohol. We need to add one hydrogen to the oxygen and shift it to the end.
C2H5−O−C2H5 → CH3−CH2−CH2−OH
For third one, follow similar procedure as above. Just use a 3 carbon chain.
:
D
Ketone cannot be an isomer of ether. No matter how you arrange diethyl ether, you cannot get a ketone compound.
First one is simple right? Just remove one carbon on one side and add to the other side.
C2H5−O−C2H5 → C3H7−O−CH3
It can also become an alcohol. We need to add one hydrogen to the oxygen and shift it to the end.
C2H5−O−C2H5 → CH3−CH2−CH2−OH
For third one, follow similar procedure as above. Just use a 3 carbon chain.
Answer: Option B. ->
Functional isomerism
:
B
Alcohols and ethers are functional isomers.
:
B
Alcohols and ethers are functional isomers.
Answer: Option D. ->
dimethyl ether
:
D
Isomers have same molecular formula but differ in their structures or in spatial arrangement.
CompoundStructural Molecular formulaEthanol C2H5OH C2H6OMethanolCH3OHCH4ODiethyl etherC2H5OC2H5C4H10ODimethyl etherCH3OCH3C2H6O
:
D
Isomers have same molecular formula but differ in their structures or in spatial arrangement.
CompoundStructural Molecular formulaEthanol C2H5OH C2H6OMethanolCH3OHCH4ODiethyl etherC2H5OC2H5C4H10ODimethyl etherCH3OCH3C2H6O
Answer: Option C. ->
Nonane
:
C
Structure of 2-methyl-3-ethylhexane is C|CH3H3−C2H5|CH−CH−CB2−CH2−CH3
It contains 9 carbon atoms.
So, a 9 carbon straight chain can be made which is nonane.
:
C
Structure of 2-methyl-3-ethylhexane is C|CH3H3−C2H5|CH−CH−CB2−CH2−CH3
It contains 9 carbon atoms.
So, a 9 carbon straight chain can be made which is nonane.
Answer: Option A. ->
2-butene
:
A
The compounds with each doubly bonded carbon attached to two different groups (like Cab=Cab, Cab=Ccd) exhibit geometrical isomerism i.e., cis and trans forms. The geometrical isomerism arises due to the restricted rotation of the double bond.
However, even though there is restricted rotation for a triple bond, alkynes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism, since the triply bonded carbons are attached to only one group each.
:
A
The compounds with each doubly bonded carbon attached to two different groups (like Cab=Cab, Cab=Ccd) exhibit geometrical isomerism i.e., cis and trans forms. The geometrical isomerism arises due to the restricted rotation of the double bond.
However, even though there is restricted rotation for a triple bond, alkynes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism, since the triply bonded carbons are attached to only one group each.