12th Grade > Biology
HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE MCQs
Total Questions : 38
| Page 3 of 4 pages
Answer: Option B. -> Fungi
:
B
Ringworm is a very common skin infection. It is caused by three kinds of fungi - Microsporum, Trichophytonand Epidermophyton. Although the name of the disease, "ringworm" can be misleading, this disease is caused by fungi and not by helminths.
:
B
Ringworm is a very common skin infection. It is caused by three kinds of fungi - Microsporum, Trichophytonand Epidermophyton. Although the name of the disease, "ringworm" can be misleading, this disease is caused by fungi and not by helminths.
Answer: Option A. -> Lymph nodes
:
A
Wuchereria bancrofti is a species of parasitic roundworm, which causes a severe disease known as ‘Elephantiasis’ or ‘Lymphatic filariasis’. The swollen lymph nodes of the patient contain the parasitic worms. The female parasite gives rise to the larvae called microfilariae in the lymph nodes.
:
A
Wuchereria bancrofti is a species of parasitic roundworm, which causes a severe disease known as ‘Elephantiasis’ or ‘Lymphatic filariasis’. The swollen lymph nodes of the patient contain the parasitic worms. The female parasite gives rise to the larvae called microfilariae in the lymph nodes.
Answer: Option D. -> Undergoing rapid division.
:
D
Cancer cells are easily damaged by radiation as they are undergoing rapid division. Moreover, since cancer cells are less organized than healthy cells, it is harder for them to repair the damage done by radiation. So cancer cells are more easily destroyed by radiation, while healthy, normal cells are better able to repair themselves and survive the treatment.
:
D
Cancer cells are easily damaged by radiation as they are undergoing rapid division. Moreover, since cancer cells are less organized than healthy cells, it is harder for them to repair the damage done by radiation. So cancer cells are more easily destroyed by radiation, while healthy, normal cells are better able to repair themselves and survive the treatment.
Answer: Option B. -> Metastasis
:
B
In the case of a malignant tumor, the cells divide more rapidly as they are inclined to grow faster and are more invasive. This tumor grows rapidly due to the nourishmentand blood supply it gets. At times, a few cells breakoff from the tumorigenic mass and findtheirway into the bloodstream. This is known as metastasis.
:
B
In the case of a malignant tumor, the cells divide more rapidly as they are inclined to grow faster and are more invasive. This tumor grows rapidly due to the nourishmentand blood supply it gets. At times, a few cells breakoff from the tumorigenic mass and findtheirway into the bloodstream. This is known as metastasis.
Answer: Option A. -> MHC molecules of the donor and recipient do not match
:
A
MHC is a cluster of proteins displayed on the surface of each and every cell of our body. MHC is unique for a person. Our cells are continuously breaking down old proteins into smaller peptides. These small peptides are held by MHC and displayed on the surface of the cell. If all the peptides displayed are from within the body, the immune system can recognise this cell as self. Any cell displaying a protein fragment that is not from within the body, but of a foreign pathogen, is recognised as non-self.When a human transplant is performed, MHC molecules from a donor are recognised by the recipient's immune system triggering an alloimmune response. Matching of donor and recipient for MHC antigens has been shown to have a significant positive effect on graft acceptance.
:
A
MHC is a cluster of proteins displayed on the surface of each and every cell of our body. MHC is unique for a person. Our cells are continuously breaking down old proteins into smaller peptides. These small peptides are held by MHC and displayed on the surface of the cell. If all the peptides displayed are from within the body, the immune system can recognise this cell as self. Any cell displaying a protein fragment that is not from within the body, but of a foreign pathogen, is recognised as non-self.When a human transplant is performed, MHC molecules from a donor are recognised by the recipient's immune system triggering an alloimmune response. Matching of donor and recipient for MHC antigens has been shown to have a significant positive effect on graft acceptance.
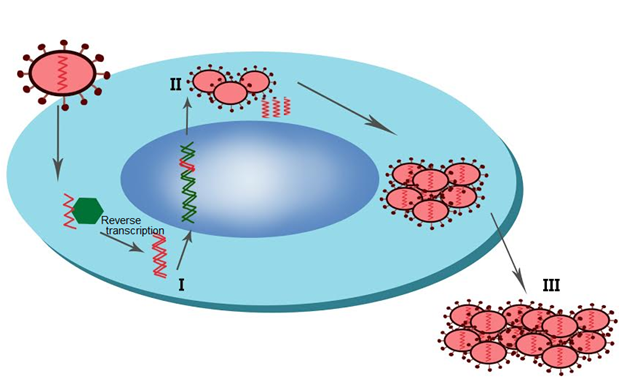
Answer: Option D. -> I - Viral DNA, II - Viral particles and Viral RNA, III - Copies of virus with RNA
:
D
Replication of HIV:
1. When the HIV virus enters the human body it attacks macrophages, begins replication, and simultaneously enters T helper cells where it eventually disintegrates the T helper cells after replication.
2. The surface of T helper cells has numerous glycoprotein receptors to which the flexible HIV surface proteins attach.
3. After binding on to the T helper cell's surface, the viral envelope diffuses on its surface and only HIV RNA enters the cell, and undergoes reverse transcription using the host cell's machinery to form HIV DNA.
4. HIV DNA incorporates into the T helper cells' DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viral particles (HIV RNA and viral particles - viral envelope, capsid, enzymes).
5. Copies of viral particles assemble and are then released out of the infected T helper cells.
6. Viruses mature and become capable of infecting other TH cells. This infected TH cell finally disintegrates. After some years, the infected TH cells start dying more quickly than they can be replaced and thus, immunity is severely compromised.
:
D
Replication of HIV:
1. When the HIV virus enters the human body it attacks macrophages, begins replication, and simultaneously enters T helper cells where it eventually disintegrates the T helper cells after replication.
2. The surface of T helper cells has numerous glycoprotein receptors to which the flexible HIV surface proteins attach.
3. After binding on to the T helper cell's surface, the viral envelope diffuses on its surface and only HIV RNA enters the cell, and undergoes reverse transcription using the host cell's machinery to form HIV DNA.
4. HIV DNA incorporates into the T helper cells' DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viral particles (HIV RNA and viral particles - viral envelope, capsid, enzymes).
5. Copies of viral particles assemble and are then released out of the infected T helper cells.
6. Viruses mature and become capable of infecting other TH cells. This infected TH cell finally disintegrates. After some years, the infected TH cells start dying more quickly than they can be replaced and thus, immunity is severely compromised.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
AIDS (AcquiredImmuno Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by HIV. This virus selectively infects and kills the T-lymphocytes.The first step post infection is the reverse transcription of RNA into DNA so that this r-DNA can get inserted into the human genome. This is brought about by a viral enzyme, known as HIV-RT, in which RT stands for reverse transcriptase. There is a class of drugs called Antiretroviral drugs (ARV) which are essentially inhibitors of this enzyme.
:
A
AIDS (AcquiredImmuno Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by HIV. This virus selectively infects and kills the T-lymphocytes.The first step post infection is the reverse transcription of RNA into DNA so that this r-DNA can get inserted into the human genome. This is brought about by a viral enzyme, known as HIV-RT, in which RT stands for reverse transcriptase. There is a class of drugs called Antiretroviral drugs (ARV) which are essentially inhibitors of this enzyme.
Answer: Option C. -> Antihistamines
:
C
The class of drugs used to treat allergic reactions is called antihistamines. Mast cells release substances called histamines which cause inflammation. This results in common allergy symptoms such as itching, sneezing, runny nose and watery eyes. Antihistamines help prevent or relieve allergy symptoms by preventing histamines from attaching to the cells and causing symptoms.
:
C
The class of drugs used to treat allergic reactions is called antihistamines. Mast cells release substances called histamines which cause inflammation. This results in common allergy symptoms such as itching, sneezing, runny nose and watery eyes. Antihistamines help prevent or relieve allergy symptoms by preventing histamines from attaching to the cells and causing symptoms.
Answer: Option C. -> A dangerous allergic reaction
:
C
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction which can also become deadly on exposure to an allergen. It could be insect sting, food, medicine, insect bites, etc.
The symptoms can include
:
C
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction which can also become deadly on exposure to an allergen. It could be insect sting, food, medicine, insect bites, etc.
The symptoms can include
- A swollen throat
- Trouble swallowing and breathing
- A sudden drop in blood pressure
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousnes
- Facial swelling
Answer: Option A. -> I - Vesicle with neurotransmitters, II - Synaptic cleft, III - Postsynaptic receptor
:
A
The brain consists of millions of neurons. Neurons communicate with each other at junctions called synapses. The neuron prior to the synapse is termed presynaptic neuron and the one subsequent to it is called the postsynaptic neuron. The end of the presynaptic neuron bears a swelling known as a synaptic knob. The synaptic knob has vesicles which contain chemicals called neurotransmitters. When an impulse arrives at the synaptic knob, the vesicles release neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. Here, the released neurotransmiiters bindto the receptors located at the postsynaptic neuron and transmita signal.
:
A
The brain consists of millions of neurons. Neurons communicate with each other at junctions called synapses. The neuron prior to the synapse is termed presynaptic neuron and the one subsequent to it is called the postsynaptic neuron. The end of the presynaptic neuron bears a swelling known as a synaptic knob. The synaptic knob has vesicles which contain chemicals called neurotransmitters. When an impulse arrives at the synaptic knob, the vesicles release neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. Here, the released neurotransmiiters bindto the receptors located at the postsynaptic neuron and transmita signal.