12th Grade > Biology
HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE MCQs
Total Questions : 38
| Page 1 of 4 pages
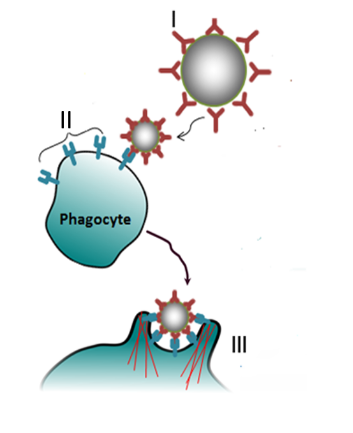
Answer: Option A. -> I - Opsonisation, II - Fc receptors, III - Phagocytosis
:
A
IgG molecules bind to the antigens on the pathogen. This makes the pathogen available forattack by phagocytic cells of our immune system. Fc receptors are present on phagocytic cells which bind the Fc region of the antibody. Thus the antibody enables phagocytic cells to recognise pathogens and mediates their phagocytosis. This process of marking the pathogen followed by phagocytosis, is termed as opsonisation.
:
A
IgG molecules bind to the antigens on the pathogen. This makes the pathogen available forattack by phagocytic cells of our immune system. Fc receptors are present on phagocytic cells which bind the Fc region of the antibody. Thus the antibody enables phagocytic cells to recognise pathogens and mediates their phagocytosis. This process of marking the pathogen followed by phagocytosis, is termed as opsonisation.
Answer: Option C. -> To provide specific and intensified response for the second invasion of the virus
:
C
When an infectious pathogen enters a person's body, the body launches a defense against the virus, during whichthe immune system is actually fighting the virus.All the necessary information about the virus is also saved. This specific action in the body is called primary response. Thus, the next time the virus attacks the immune system, it is pre-equipped to deal with the attackand hence, inactivates the virus even before an infection is established. This is called secondary response.
:
C
When an infectious pathogen enters a person's body, the body launches a defense against the virus, during whichthe immune system is actually fighting the virus.All the necessary information about the virus is also saved. This specific action in the body is called primary response. Thus, the next time the virus attacks the immune system, it is pre-equipped to deal with the attackand hence, inactivates the virus even before an infection is established. This is called secondary response.
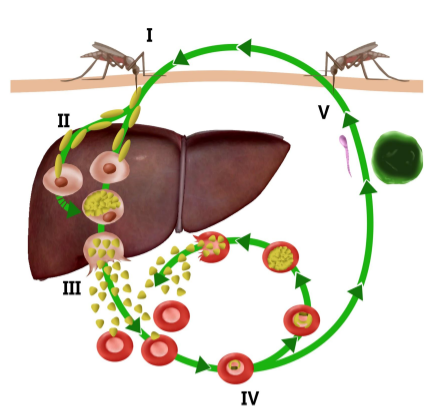
Answer: Option A. -> 1 - Female Anopheles, 2 - Sporozoites, 3 - Merozoites, 4 - Trophozoites, 5 - Gametocytes
:
A
Malaria is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. The infectious forms injected by the mosquito are the sporozoites. Next the sporozoites grow and multiply, and form haploid merozoites. This is the stage invading the erythrocytes. In the erythrocytes, trophozoites are formed.The trophozoite develops into a schizont which is a mother cell.The schizonts rupture, releasing newly formed merozoites that then re-invade other red blood cells.Some of these merozoite-infected blood cells leave the cycle of asexual replication, and instead, the merozoites in these cells develop into sexual forms of the parasite, called male and female gametocytes.
:
A
Malaria is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. The infectious forms injected by the mosquito are the sporozoites. Next the sporozoites grow and multiply, and form haploid merozoites. This is the stage invading the erythrocytes. In the erythrocytes, trophozoites are formed.The trophozoite develops into a schizont which is a mother cell.The schizonts rupture, releasing newly formed merozoites that then re-invade other red blood cells.Some of these merozoite-infected blood cells leave the cycle of asexual replication, and instead, the merozoites in these cells develop into sexual forms of the parasite, called male and female gametocytes.
Answer: Option A. -> ssRNA
:
A
Human immunodeficiency virus or HIV is a member of a group of viruses called retroviruses, which have an envelope enclosing the RNA genome. The HIV has a single stranded RNA genome.
:
A
Human immunodeficiency virus or HIV is a member of a group of viruses called retroviruses, which have an envelope enclosing the RNA genome. The HIV has a single stranded RNA genome.
Answer: Option B. -> Rickettsia prowazekii
:
B
Typhus was the strange disease which brought the grand French army at its knees. This disease was caused by a bacterium called Rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia is an obligate intracellular parasitic bacterium that cannot survive for long outside living cells. It is transmitted to humans via external parasites such as human lice. Rickettsia grows in the gut of the lice and is excreted in their faeces. They can remain viable and virulent in the dried faeces for many days. The bacterium gains entry into the human body through the wound caused by the lice bite.
:
B
Typhus was the strange disease which brought the grand French army at its knees. This disease was caused by a bacterium called Rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia is an obligate intracellular parasitic bacterium that cannot survive for long outside living cells. It is transmitted to humans via external parasites such as human lice. Rickettsia grows in the gut of the lice and is excreted in their faeces. They can remain viable and virulent in the dried faeces for many days. The bacterium gains entry into the human body through the wound caused by the lice bite.
Answer: Option B. -> Morphine - pain killer
:
B
Morphine is a very effective sedative and pain killer (analgesic) and is very useful in patients who have undergone surgery. Amphetamine is a central nervous system stimulant that affects chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control. Benzodiazepines are used as tranquilisers to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety and insomnia. LSD is a psychedelic drug producing a range of psychologic effects.
:
B
Morphine is a very effective sedative and pain killer (analgesic) and is very useful in patients who have undergone surgery. Amphetamine is a central nervous system stimulant that affects chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control. Benzodiazepines are used as tranquilisers to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety and insomnia. LSD is a psychedelic drug producing a range of psychologic effects.
Question 7. Match the following images with the respective given steps P,Q,R,S:
P. Macrophage receptors recognise the invading virus.
Q. The virus is drawn into the macrophage.
R. The virus get packaged into a sac pinched off from the cell membrane of the macrophage.
S. The sac fuses with lysozyme which safely dismantles the bacterium without digesting the macrophage itself.
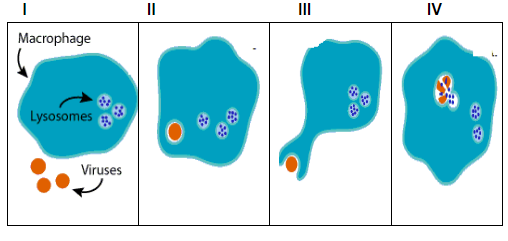
P. Macrophage receptors recognise the invading virus.
Q. The virus is drawn into the macrophage.
R. The virus get packaged into a sac pinched off from the cell membrane of the macrophage.
S. The sac fuses with lysozyme which safely dismantles the bacterium without digesting the macrophage itself.

Answer: Option C. -> I - P, II - R, III - Q, IV - S
:
C
To a macrophage, anything foreign is there to be eaten. When bacteria or viruses enter the body and find their way into the tissue, they leave a chemical trail that is detected by receptors on a patrolling macrophage's cell membrane. If receptors on these extensions recognise specific markers on the bacterial or viral surface, they bind to them. Once captured, the virus or bacteriumis drawn into the macrophage and packaged in a sac pinched off from the cell membrane. As it moves through the cytoplasm, the sac fuses with lysozyme. These safely dismantle the bacterium without digesting the macrophage itself.
:
C
To a macrophage, anything foreign is there to be eaten. When bacteria or viruses enter the body and find their way into the tissue, they leave a chemical trail that is detected by receptors on a patrolling macrophage's cell membrane. If receptors on these extensions recognise specific markers on the bacterial or viral surface, they bind to them. Once captured, the virus or bacteriumis drawn into the macrophage and packaged in a sac pinched off from the cell membrane. As it moves through the cytoplasm, the sac fuses with lysozyme. These safely dismantle the bacterium without digesting the macrophage itself.
Answer: Option B. -> Heroin
:
B
Heroin, commonly called smack, is chemically diacetyl morphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine.
:
B
Heroin, commonly called smack, is chemically diacetyl morphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
For the completion of their life cycle, some parasites require more than just the host. For example, tapeworm completes its life cycle in humans and cows/pigs. In humans which is the definitive host, it multiplies and causes the symptoms. In cows and pigs (the reservoir host), it just resides and does not show any ill effects.
:
A
For the completion of their life cycle, some parasites require more than just the host. For example, tapeworm completes its life cycle in humans and cows/pigs. In humans which is the definitive host, it multiplies and causes the symptoms. In cows and pigs (the reservoir host), it just resides and does not show any ill effects.
Answer: Option A. -> A - Valves, B - Capsule, C - Efferent vessel, D - Immune cells, E - Cortex, F - Afferent vessel
:
A
Lymph nodes are very important parts of the immune system, harbouring many immune cells that clear pathogens which drain in along with the lymph. The outermost covering of the lymph node is a tough layer called the capsule. The capsule has extensions which divide the cortex into many compartments. There are many afferent vessels that bring lymph into the lymph nodes. Valves present in the afferent vessels prevent lymph from flowing back. As the lymph reaches the lymph nodes carrying pathogens and cell debri, they are cleared by macrophages and other immune cells present in the lymph node. The lymph, free of all pathogens, is returned to circulation via the efferent lymph vessel.
:
A
Lymph nodes are very important parts of the immune system, harbouring many immune cells that clear pathogens which drain in along with the lymph. The outermost covering of the lymph node is a tough layer called the capsule. The capsule has extensions which divide the cortex into many compartments. There are many afferent vessels that bring lymph into the lymph nodes. Valves present in the afferent vessels prevent lymph from flowing back. As the lymph reaches the lymph nodes carrying pathogens and cell debri, they are cleared by macrophages and other immune cells present in the lymph node. The lymph, free of all pathogens, is returned to circulation via the efferent lymph vessel.