12th Grade > Biology
ECOSYSTEM MCQs
Total Questions : 48
| Page 4 of 5 pages
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Decomposers like detritivores and soil microbes depend on the dead and decaying matter as the source of nourishment or energy as they draw their energy by decomposing the complex organic matter in the dead remains of plant and animal species into simple compounds and inorganic molecules which is specifically reused by the plants in the ecosystem.
:
A
Decomposers like detritivores and soil microbes depend on the dead and decaying matter as the source of nourishment or energy as they draw their energy by decomposing the complex organic matter in the dead remains of plant and animal species into simple compounds and inorganic molecules which is specifically reused by the plants in the ecosystem.
Answer: Option D. -> A is correct, R is incorrect
:
D
Ecological pyramids were developed by Charles Elton and are, therefore, also called Eltonian pyramids. An ecological pyramid is the representation of energy flow in an ecosystem. It can be upright, inverted or spindle shaped depending on the type ofpyramid. There are three types-energy, biomass and numberat each trophic level,that isparasitic, aquatic or terrestrial ecosystems.
:
D
Ecological pyramids were developed by Charles Elton and are, therefore, also called Eltonian pyramids. An ecological pyramid is the representation of energy flow in an ecosystem. It can be upright, inverted or spindle shaped depending on the type ofpyramid. There are three types-energy, biomass and numberat each trophic level,that isparasitic, aquatic or terrestrial ecosystems.
Answer: Option A. -> Cobra
:
A
"A" can be represented by a cobra. Frogs are main food for snakes and snakes are eaten by eagles. A parrot, however, feeds on fruits, seeds, vegetables and small insects.Lions are carnivores or meat eaters and rabbits are herbivores so frogs are not a part of their diet.
:
A
"A" can be represented by a cobra. Frogs are main food for snakes and snakes are eaten by eagles. A parrot, however, feeds on fruits, seeds, vegetables and small insects.Lions are carnivores or meat eaters and rabbits are herbivores so frogs are not a part of their diet.
Answer: Option D. -> Net primary productivity
:
D
Net Primary Productivityis the amount of organic matter stored by plants per unit area, per unit time after meeting the cost of respiration and other metabolic requirements. It differs from Gross Primary Productivityas GPP is the total amount of organic matter synthesized by plants (photosynthesis) per unit area in unit time. Biomass is the total amount of living material in an ecosystem at a given time.
:
D
Net Primary Productivityis the amount of organic matter stored by plants per unit area, per unit time after meeting the cost of respiration and other metabolic requirements. It differs from Gross Primary Productivityas GPP is the total amount of organic matter synthesized by plants (photosynthesis) per unit area in unit time. Biomass is the total amount of living material in an ecosystem at a given time.
Answer: Option B. -> Number of trophic levels is usually less in terrestrial ecosystem than aquatic ecosystem
:
B
Terrestrial ecosystem includes grassland, deserts, decidous forest,etc. Terrestrial ecosystems usually have lesser number of trophic levels than aquatic ecosystems. This difference between terrestrial and marine ecosystems (ocean ecosystem) is due to differences in the fundamental characteristics of land and marine primary organisms. Most terrestrial ecosystems have no more than five trophic levels, and marine ecosystems generally have seven.
:
B
Terrestrial ecosystem includes grassland, deserts, decidous forest,etc. Terrestrial ecosystems usually have lesser number of trophic levels than aquatic ecosystems. This difference between terrestrial and marine ecosystems (ocean ecosystem) is due to differences in the fundamental characteristics of land and marine primary organisms. Most terrestrial ecosystems have no more than five trophic levels, and marine ecosystems generally have seven.
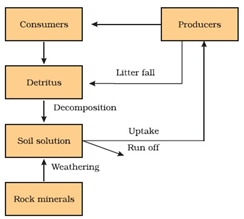
Answer: Option A. -> Phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem
:
A
The cycle represnted above is the phosphorus cycle. The phosphorus cycle is a sedimentary cycle, it has no gaseous component. The cycle starts from weathering of rocks and the phosphate salt mixes with soil which is then utilized by the producers and stored as organic phosphate. The organic phosphates formed by the producers are transferred to the consumers. And these phosphates return back to the soil from the biotc components when they are broken down by the decomposers. And the cycle begins again.
:
A
The cycle represnted above is the phosphorus cycle. The phosphorus cycle is a sedimentary cycle, it has no gaseous component. The cycle starts from weathering of rocks and the phosphate salt mixes with soil which is then utilized by the producers and stored as organic phosphate. The organic phosphates formed by the producers are transferred to the consumers. And these phosphates return back to the soil from the biotc components when they are broken down by the decomposers. And the cycle begins again.
Answer: Option D. -> Level PC is insects and level SC is small insectivorous birds
:
D
With respect to the given image, the first option represents an aquatic ecosystem where primary producers are the phytoplankton and tertiary consumers are the whales, this is incorrect because a single phytoplankton cannot sustain this ecosystem. The second option represents forest ecosystem where the primary producer is a tree, which is possible, however the secondary consumers cannot be sheep as sheep are primary consumers. In the third option, primary consumers being rats are unlikely as they are ominivores and do not feed exclusively on plants; further cats are top carnivores, there cannot be a tertiary consumer in this ecosystem. Therefore the fourth option is the correct answer, as it represents insects as the primary consumers, which forms the trophic level with highest number of organisms. They are mostly dependent on one primary producer, like a tree, and secondary consumers are insectivorous birds, which are comparatively lesser in number than the insects which form the previous trophic level.
:
D
With respect to the given image, the first option represents an aquatic ecosystem where primary producers are the phytoplankton and tertiary consumers are the whales, this is incorrect because a single phytoplankton cannot sustain this ecosystem. The second option represents forest ecosystem where the primary producer is a tree, which is possible, however the secondary consumers cannot be sheep as sheep are primary consumers. In the third option, primary consumers being rats are unlikely as they are ominivores and do not feed exclusively on plants; further cats are top carnivores, there cannot be a tertiary consumer in this ecosystem. Therefore the fourth option is the correct answer, as it represents insects as the primary consumers, which forms the trophic level with highest number of organisms. They are mostly dependent on one primary producer, like a tree, and secondary consumers are insectivorous birds, which are comparatively lesser in number than the insects which form the previous trophic level.
Answer: Option B. -> The successive colonization of a site by certain species accompanied by the extinction of others.
:
B
This tendency of an ecosystem to change from simple to complex or just change over time is termed as succession. Succession typically leads to the change in structure and species composition over time. The changed environmental conditions favour the growth of many more species while certain species can also go extinct due to the same changes.
:
B
This tendency of an ecosystem to change from simple to complex or just change over time is termed as succession. Succession typically leads to the change in structure and species composition over time. The changed environmental conditions favour the growth of many more species while certain species can also go extinct due to the same changes.
Answer: Option A. -> sere
:
A
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. During succession some species colonise an area and their populations become more numerous, whereas populations of other species decline and even disappear. The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area are called seres.
:
A
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. During succession some species colonise an area and their populations become more numerous, whereas populations of other species decline and even disappear. The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area are called seres.
Answer: Option D. -> Both A and R are false
:
D
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. Ecological succession are of two differenttypes- primary and secondary succession. Primarysuccessionoccurs in essentially lifeless areas in which the soil is incapable of sustaining life as a result of such factors as lava flows, newly formed sand dunes, or rocks left from a retreating glacier.Secondary succession begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed such as in abandoned farm lands, burned or cut forests, lands that have been flooded. Succession takes place, both in bare areas and on previously inhabited disturbed or damaged habitat, and is known as primary and secondary succession respectively.
:
D
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. Ecological succession are of two differenttypes- primary and secondary succession. Primarysuccessionoccurs in essentially lifeless areas in which the soil is incapable of sustaining life as a result of such factors as lava flows, newly formed sand dunes, or rocks left from a retreating glacier.Secondary succession begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed such as in abandoned farm lands, burned or cut forests, lands that have been flooded. Succession takes place, both in bare areas and on previously inhabited disturbed or damaged habitat, and is known as primary and secondary succession respectively.