11th And 12th > Physics
CURRENT ELECTRICITY MCQs
:
B
Let m cells be connected in series and n such groups are connected in parallel
If the emf of each cell is E and internal resistance r then the total emf of m in series is mE and the total internal resistance is mr. When n such groups are in parallel the effective internal resistance is mr/n. Then the current through an external resistance R is
l=mER+mrn=mnEnR+mr=mnE(√nR−√mr)2+2√mnRr
Now i will be maximum if the denominator is the minimum i.e. if nR=mr
Using R= 3 ohm and r=1 ohm we have 3n = m
But mn = 48
therefore m×m3=48
which gives m= 12
thus n=4
:
D
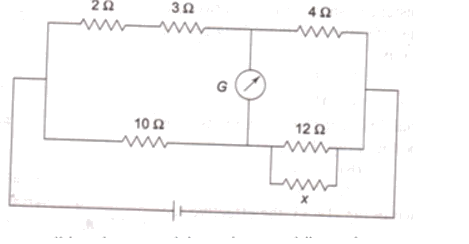
The given circuit is Wheatstone's bridge.The current through the galvanometer will be zero if the bridge is balanced
PQ+RS where P = 2+3 =5 ohm, Q = 10 ohm and R=4 ohm
The value of S is given by
510=4S
or S= 8 ohm
thus the effective resistance of the parallel combination of 12 ohm and x ohm must be 8 ohm
therefore
112+1x=18
which gives x = 24 ohm
:
A
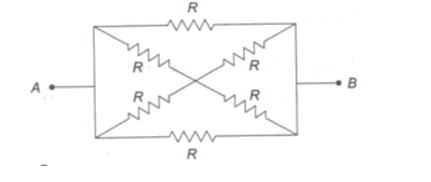
Resistance R,(R+R)= 2R, (R+R)=2R and R are in parallel
Hence effective resistance is given by
1Reff=1R+12R+12R+1R
which gives Reff=R3
:
D
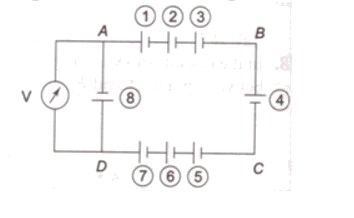
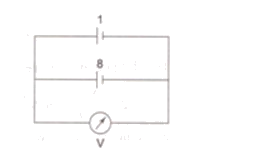
The emfs of cells connected in reverse polarity cancel each other. Hence cells marked 2, 3 and 4 together cancel the effect of cells marked 5, 6 and 7 and the circuit reduces to that shown in figure. Now cells 1 and 8 are in reverse polarity. Hence the voltmeter reading = 5 – 5 = 0 V
:
B
Q=V2R
But R=plπ r2
Therefore Q=(π V2p)r21
Q is doubled if both l and r are doubled
:
D
copper is a conductor whereas Germanium is a semi conductor
:
D
The drift speed depends on A the cross sectional area of the conductor but the current is independent of A
:
D
The equivalent resistance between points A and B to the right of AB is 4 ohm. Therefore total resistance =3+4+2= 9 ohm. Current I =99=1 A. This current is equally divided in the 8 ohm resistor between A and B and the remainder 8 ohm resistor. Hence current in AC =0.5 A. This current is equally divided between the 8 ohm resistor in CD and the circuit to the right of CD. Therefore current in the 4 ohm resistor = 0.25 A
:
C
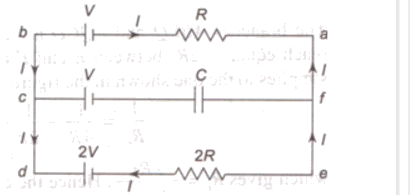
In the steady state no current flows in the branch containing the capacitor .Thus the current say l flows in the branches containing R and 2R. Applying Kirchoff's second rule to the loop abcdefa
2V-I(2R)-IR-V=0
l=V3R
Potential drop across capacitor =2V-V-l(2R)=V−v3R× 2R
=V−2v3=v3
:
A
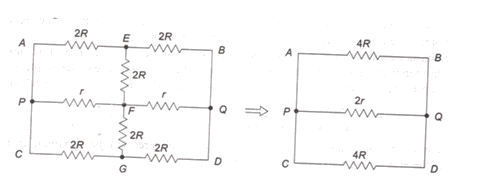
The branches ABPQ and PQCD are a balanced Wheatstone's bridge. Therefore resistances between E and E and between F and G do not contribute and the circuit simplies to the one show in figure. The effective resistance Re between P and Q is given by
1Re=14R+12r+14R
which gives Re=2Rr(R+r)