11th And 12th > Physics
CIRCULAR KINEMATICS MCQs
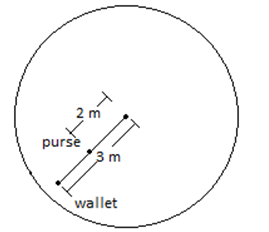
A purse at radius 2.00 m and a wallet at radius 3.00 m travel in uniform circular motion on the floor of a merry-go-round as the ride turns. They are on the same radial line. At one instant, the acceleration of the purse is (2.00 m/ s2)^i + (4.00 m/ s2)^j . At that instant and in unit-vector notation, what is the acceleration of the wallet? IIT JEE- 2001
:
C
dθdt is constant.
In other words in uniform circular motion the angular velocity remains constant body doesn't have any tangential acceleration but normal acceleartion.
aN=v2R or ω2R
For purse aN=√(2)2+(4)2=√20;R=2
⇒√20=ω22
⇒ω2=√5
For wallet aN=ω2R
Hence ωis same
But~R=3
⇒aN=√5×3
aN=3√5
So the above answer matches with the magnitude of third option in the given answers.
A balloon starts rising from the surface of the Earth. The ascension rate is constant and equal to vo. Due to the wind the balloon gathers the horizontal velocity component vx=ay, where a is a constant and y is the height of ascent. Find the total, tangential, and normal accelerations of the balloon.
:
C
The path of the balloon will look something like this
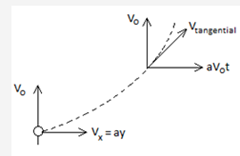
After t sec ballon would have gone a height of v0tthen at that very instance the balloon's vx will be
vx=av0t⇒ax=av0
Vy=v0
ay=0
ar=total acceleration=av0.......(1)
vtangentical is actually the resultant velocity
⇒vt=√v20+(av0t)2
⇒vt=v0√1+a2t2
at=dvtdt=v0a2t√1+a2t2⇒a2y√1+(ayv0)2
Now we know a2t+a2N=a2r
⇒v20a4t2(1+a2t2)+a2N=a2v20
aN=√v20a4t2−v20a4t2(1+a2t2)
aN=av0√1+a2t2−a2t2(1+a2t2)
aN=av0√1+a2t2
⇒av0√1+(ayv0)2
A hollow vertical cylinder of radius R and height h has smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim at a point P. It is given a horizontal speed vo tangential to rim. It leaves the lower rim at point Q, vertically below P. The number of revolutions made by the particle will
:
D
since the body has no initial velocity in the vertical direction.
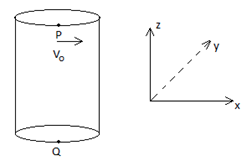
az=-g, vertical displacement z=-h.
∴z=at+12at2
⇒−h=0+12(−g)t2
⇒T=√2hg time taken to reach the bottom
let,t be the time taken to complete one revolution.
Then t=2πRv0
∴ number of revolution=Tt=√2hg2πRv0=v02πR√2hg
:
D
S=t3+5
Speed,v=dsdt=3t2 and rate of change of speed =dvdt=6t
∴ tangential acceleration at t=2S,at = 6 × 2=12m/s2
At t=2s,v=3(2)2=12m/s2
∴ centripetal acceleration,
=v2R=14420m/s2
∴ net acceleration=√a2t+a2i≈14m/s2
:
B and D
The linear speed at t = 3 s is
v = 2t = 6 m/s
The radial acceleration at t = 3 s is
ar=v2r=180 m/s2
The tangential acceleration is
at=dvdt=2 m/s2
:
B
aresultant=√a2radial+a2tangential=√v4r2+a2
:
D
The net acceleration is always directed between radially inward and tangential direction.
:
A, B, C, and D
(i) The direction of tangential acceleration is in the line of velocity and the normal acceleration is in the direction perpendicular to velocity direction. The tangential and normal directions at O & P are shown in figure.
The net acceleration of the particle during motion is acceleration due to gravity i.e., 'g' is acting vertically downward.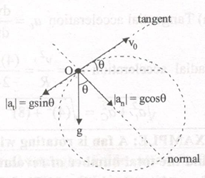
At O:(at t=0)
Tangential acceleration at=-gsinθ
Normal acceleration an= gcosθ
At P (at highest point)
Tangential acceleration
at=0 an=g
(ii) Let radius of curvature at O be R0. The normal acceleration at O is g cos θ.
an=v2R⇒R0=v20an=v20gcosθ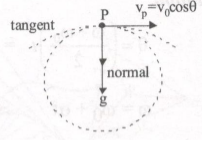
Radius of curvature at P
Normal acceleration at P is 'g'
Rp=v2an=(v0cosθ)2g=v20cos2θg