12th Grade > Physics
ROTATION THE LAWS MCQs
Total Questions : 28
| Page 2 of 3 pages
Answer: Option D. -> 250 J
:
D
Rotational kinetic energy 12Iω2=12(12MR2)ω2=12(12×10×(0.5)2)(20)2=250J
:
D
Rotational kinetic energy 12Iω2=12(12MR2)ω2=12(12×10×(0.5)2)(20)2=250J
Answer: Option A. -> vL
:
A
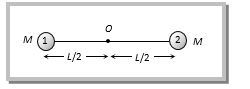
Initial angular momentum of the system about point O
= Linear momentum × Perpendicular distance of linear momentum from the axis of rotation =Mv(L2)...(i)
Final angular momentum of the system about point O=I1ω+I2ω=(I1+I2)ω
=[M(L2)2+M(L2)2]ω .....(ii)
Applying the law of conservation of angular momentum
⇒Mv(L2)=2M(L2)2ω ⇒ω=vL
:
A
Initial angular momentum of the system about point O
= Linear momentum × Perpendicular distance of linear momentum from the axis of rotation =Mv(L2)...(i)
Final angular momentum of the system about point O=I1ω+I2ω=(I1+I2)ω
=[M(L2)2+M(L2)2]ω .....(ii)
Applying the law of conservation of angular momentum
⇒Mv(L2)=2M(L2)2ω ⇒ω=vL

Answer: Option B. -> (1+μ2k)ω20R8πμk(1+μk)g
:
B
As the centre of mass of the cylinder does not accelerate, hence ∑F=0
∑Fx=0,N2−μkN1=0 ...(1)
∑Fx=0,N1−μkN2−mg=0 ...(2)
Solving these equations: N1=mg1+μ2k,N2=μkmg1+μ2k
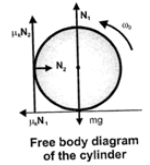
The torque on the cylinder about the axis of rotation
The moment of inertia about axis of rotation 1cm=12mR2
The torque equation T=1α
Using equation ω2=ω20+2αθ, Calculate the angular displacement θ,
Revolution accomplished,
:
B
As the centre of mass of the cylinder does not accelerate, hence ∑F=0
∑Fx=0,N2−μkN1=0 ...(1)
∑Fx=0,N1−μkN2−mg=0 ...(2)
Solving these equations: N1=mg1+μ2k,N2=μkmg1+μ2k

The torque on the cylinder about the axis of rotation
The moment of inertia about axis of rotation 1cm=12mR2
The torque equation T=1α
Using equation ω2=ω20+2αθ, Calculate the angular displacement θ,
Revolution accomplished,
Answer: Option B. -> 800%
:
B
As E=L22I⇒E2E1=(L2L1)2=(3L1L1)2 [AsL2=L1+200%.L1=3L1]
⇒E2=9E1=E1+800%ofE1
:
B
As E=L22I⇒E2E1=(L2L1)2=(3L1L1)2 [AsL2=L1+200%.L1=3L1]
⇒E2=9E1=E1+800%ofE1
Answer: Option B. -> mv302√2g(−^k)
:
B
Let us take the origin at P, X-axis along the horizontal and Y-axis along the vertically upward direction as shown in figure. For horizontal motion during the time 0 to t.

vx = v0cos45∘ = v0√2
and x = vxt = v0√2.v0g = v20√2g.
For vertical motion,
vy = v0sin45∘−gt = v0√2−v0 = (1−√2)√2v0
and y = (v0sin45∘)t−12gt2
= v20√2g - v202g = v202g(√2−1)
The angular momentum of the particle at time t about the origin is
L = →rx→p = m→rx→v
= m(→ix+→jy)x(→ivx+→jvy)
= m(→kxvy−→kyvx)
= m→k[(v20√2g)v0√2(1−√2)−v202g(√2−1)v0√2]
= −→kmv302√2g.
Thus, the angular momentum of the particle is mv302√2g in the negative Z - direction, i.e., perpendicular to the plane of motion, going into the plane.
:
B
Let us take the origin at P, X-axis along the horizontal and Y-axis along the vertically upward direction as shown in figure. For horizontal motion during the time 0 to t.

vx = v0cos45∘ = v0√2
and x = vxt = v0√2.v0g = v20√2g.
For vertical motion,
vy = v0sin45∘−gt = v0√2−v0 = (1−√2)√2v0
and y = (v0sin45∘)t−12gt2
= v20√2g - v202g = v202g(√2−1)
The angular momentum of the particle at time t about the origin is
L = →rx→p = m→rx→v
= m(→ix+→jy)x(→ivx+→jvy)
= m(→kxvy−→kyvx)
= m→k[(v20√2g)v0√2(1−√2)−v202g(√2−1)v0√2]
= −→kmv302√2g.
Thus, the angular momentum of the particle is mv302√2g in the negative Z - direction, i.e., perpendicular to the plane of motion, going into the plane.
Answer: Option B. -> Angular acceleration of the body has to be zero
:
B
Angular acceleration of the body may not necessarily be zero about any axis about which net external torque is non-zero.
:
B
Angular acceleration of the body may not necessarily be zero about any axis about which net external torque is non-zero.
Answer: Option B. -> 513
:
B
I=58mr2
R.K.ET.E=11+R2K2=11+85=513
:
B
I=58mr2
R.K.ET.E=11+R2K2=11+85=513
Answer: Option C. -> 30 J
:
C
ω1=20 rad\sec, ω2=0, t = 4 sec. So angular retardation α=ω1−ω2t=204=5radsec2
Now angular speed after 2 sec ω2=ω1−αt=20−5×2=10radsec
Work done by torque in 2 sec = loss in kinetic energy =12I(ω21−ω22)=12(0.20)((20)2−(10)2)
=12×0.2×300=30J.
:
C
ω1=20 rad\sec, ω2=0, t = 4 sec. So angular retardation α=ω1−ω2t=204=5radsec2
Now angular speed after 2 sec ω2=ω1−αt=20−5×2=10radsec
Work done by torque in 2 sec = loss in kinetic energy =12I(ω21−ω22)=12(0.20)((20)2−(10)2)
=12×0.2×300=30J.
Answer: Option C. -> 2304 J
:
C
Kinetic energy,K.E. =12Iω2=12(0.32)(120)2=2304J.
:
C
Kinetic energy,K.E. =12Iω2=12(0.32)(120)2=2304J.
Answer: Option D. -> 1 m/s
:
D
Rotational kinetic energy of the body =12Iω2 and translatory kinetic energy =12mv2
According to problem =12Iω2=12mv2⇒12×3×(2)2=12×12×v2⇒v=1m/s.
:
D
Rotational kinetic energy of the body =12Iω2 and translatory kinetic energy =12mv2
According to problem =12Iω2=12mv2⇒12×3×(2)2=12×12×v2⇒v=1m/s.

















