12th Grade > Physics
ROTATION THE LAWS MCQs
Total Questions : 28
| Page 1 of 3 pages
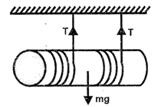
Question 1. A solid cylinder of mass m = 4 kg and radius R = 10 cm has two ropes wrapped around it, one near each end. The cylinder is held horizontally by fixing the two free ends of the cords to the hooks on the ceiling such that both the cords are exactly vertical. The cylinder is released to fall under gravity. Find the tension in the cords when they unwind and the linear acceleration of the cylinder.
Answer: Option A. -> 6.5ms2,6.5N
:
A
Let a = linear acceleration and α = angular acceleration of the cylinder.
for the linear motion of the cylinder : mg - 2T = ma
for the rotational motion : net torque = 1α
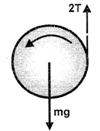
Also, the linear acceleration of cylinder is same as the tangential acceleration of any point on its surface. A = Rα
Combining the three equations, we get : mg=ma+m2a
⇒a=2g3=6.53ms2andT=mg−ma2=6.53N.
:
A
Let a = linear acceleration and α = angular acceleration of the cylinder.
for the linear motion of the cylinder : mg - 2T = ma
for the rotational motion : net torque = 1α
Also, the linear acceleration of cylinder is same as the tangential acceleration of any point on its surface. A = Rα
Combining the three equations, we get : mg=ma+m2a
⇒a=2g3=6.53ms2andT=mg−ma2=6.53N.
Answer: Option D. -> m√2gh3
:
D
L=mvxh
⇒L=m(vcos45∘)v2sin245∘2g
⇒L=mv34√2g
Further L=mvxh
⇒L=m(vcos45∘)ho
But h=v2sin245∘2g
⇒v=2√gh
⇒L=mv√22√ghh
⇒L=m√2gh3.
:
D
L=mvxh
⇒L=m(vcos45∘)v2sin245∘2g
⇒L=mv34√2g
Further L=mvxh
⇒L=m(vcos45∘)ho
But h=v2sin245∘2g
⇒v=2√gh
⇒L=mv√22√ghh
⇒L=m√2gh3.
Question 3. A solid cylinder of mass 2 kg and radius 0.2 m is rotating about its own axis without friction with angular velocity 3 rad/s. A particle of mass 0.5 kg moving with a velocity 5 m/s strikes the cylinder and sticks to it as shown in figure below. The angular momentum of the cylinder before collision will be
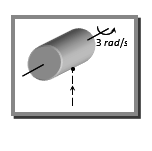

Answer: Option A. -> 0.12 J-s
:
A
Angular momentum of the cylinder before collision L=Iω=12MR2ω=12(2)(0.2)2×3=0.12J−s.
:
A
Angular momentum of the cylinder before collision L=Iω=12MR2ω=12(2)(0.2)2×3=0.12J−s.
Answer: Option A. -> X-axis
:
A
⃗L=⃗r×⃗p=∣∣
∣
∣∣ˆiˆjˆk12−134−2∣∣
∣
∣∣=0ˆi−ˆj−2ˆk=−ˆj−2ˆk and the X-axis is given by i+0ˆj+0ˆk
:
A
⃗L=⃗r×⃗p=∣∣
∣
∣∣ˆiˆjˆk12−134−2∣∣
∣
∣∣=0ˆi−ˆj−2ˆk=−ˆj−2ˆk and the X-axis is given by i+0ˆj+0ˆk
Answer: Option B. -> Increases linearly with time
:
B
Angular impulse = change in angular momentum
we have L = τ *t
or, L = F*(2R)*t
i.e.L increases linearly with time.
:
B
Angular impulse = change in angular momentum
we have L = τ *t
or, L = F*(2R)*t
i.e.L increases linearly with time.
Question 7. A uniform wheel of moment of inertia 'I' is pivoted on a horizontal axis through its centre so that its plane is vertical as shown in the figure. A small mass 'm' is stuck on the rim of the wheel as shown. The angular acceleration of the wheel when mass is at point A is αA and when mass is at point B is αB. Then,
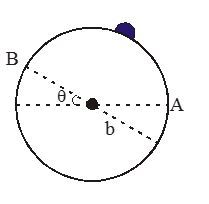

Answer: Option C. -> αBαA=cosθ
:
C
The torque due to the weight of m at A is τAand that when it is at B is τB
⇒τBτA=IαBIαA=bcosθb=cosθ.
:
C
The torque due to the weight of m at A is τAand that when it is at B is τB
⇒τBτA=IαBIαA=bcosθb=cosθ.
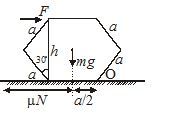
Answer: Option D. -> 2F5mrightwards and 16F5mleftwards
:
D
Let the acceleration of bar and cart be a and a' respectively; alsoαbe the angular acceleration of the bar.
Writing newton's equation of motion
For the bar: F - F' =ma ...(i)
For the cart: F' = ma' ...(ii)
Torque equation for rod about center of mass
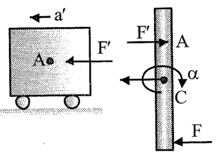
For rotation of the rod (F + F)L2=ML212α
F+F'=MLα6 ...(iii)
The acceleration of point A on the rod will be same as the acceleration of the cart,
-a' =αL2-aora' =a−L2α →aA=→aAC+→ac ...(iv)
On solving eqation (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get, α=7F5mandα=18F5mL
|a'| =|aA|=a−L2−α−2F5m; |aB|=a+L2α=16F5m
:
D
Let the acceleration of bar and cart be a and a' respectively; alsoαbe the angular acceleration of the bar.
Writing newton's equation of motion
For the bar: F - F' =ma ...(i)
For the cart: F' = ma' ...(ii)
Torque equation for rod about center of mass
For rotation of the rod (F + F)L2=ML212α
F+F'=MLα6 ...(iii)
The acceleration of point A on the rod will be same as the acceleration of the cart,
-a' =αL2-aora' =a−L2α →aA=→aAC+→ac ...(iv)
On solving eqation (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get, α=7F5mandα=18F5mL
|a'| =|aA|=a−L2−α−2F5m; |aB|=a+L2α=16F5m
Answer: Option A. -> ML212ω
:
A
The situation is depicted in the figure shown,
As we know, for this rigid body,
|→L| = Iω
= ML212ω {where I = moment of Inertia of rod about its axis of rotation}
:
A
The situation is depicted in the figure shown,
As we know, for this rigid body,
|→L| = Iω
= ML212ω {where I = moment of Inertia of rod about its axis of rotation}
Answer: Option C. -> 531 N-m
:
C
P=τω⇒τ=100×1032π180060=531N−m
:
C
P=τω⇒τ=100×1032π180060=531N−m