12th Grade > Biology
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS MCQs
Total Questions : 62
| Page 6 of 7 pages
Answer: Option A. -> Cytoplasm
:
A
The cellular respiration starts with the glycolytic pathway. It is a common pathway for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration and it takes placein the cytoplasm.
:
A
The cellular respiration starts with the glycolytic pathway. It is a common pathway for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration and it takes placein the cytoplasm.
Answer: Option B. -> Alcohol and carbon dioxide
:
B
Incomplete breakdown of sugar in anaerobic respiration forms alcohol and carbon dioxide.
:
B
Incomplete breakdown of sugar in anaerobic respiration forms alcohol and carbon dioxide.
Answer: Option D. -> Substrate level phosphorylation
:
D
PEP+ADP→pyruvicacid+ATP
During the conversion of phophoenol pyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid, the phosphate group from PEP is transferred to ADP. Therefore it is substrate level phosphorylatron. In oxidative phophorylation, the electrons from high energy carirer travel along an ETC, and finally to an external electron acceptor, that is oxygen. The energy from this process is used to synthesize ATP. Hence known as the oxidative phosphorylation.
:
D
PEP+ADP→pyruvicacid+ATP
During the conversion of phophoenol pyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid, the phosphate group from PEP is transferred to ADP. Therefore it is substrate level phosphorylatron. In oxidative phophorylation, the electrons from high energy carirer travel along an ETC, and finally to an external electron acceptor, that is oxygen. The energy from this process is used to synthesize ATP. Hence known as the oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer: Option B. -> Pyruvic acid
:
B
Pyruvic acid is an intermediate compound common for aerobic and anaerobic respiration because it is the end product in glycolysis and initial product in anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis is a pathway that is common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
:
B
Pyruvic acid is an intermediate compound common for aerobic and anaerobic respiration because it is the end product in glycolysis and initial product in anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis is a pathway that is common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
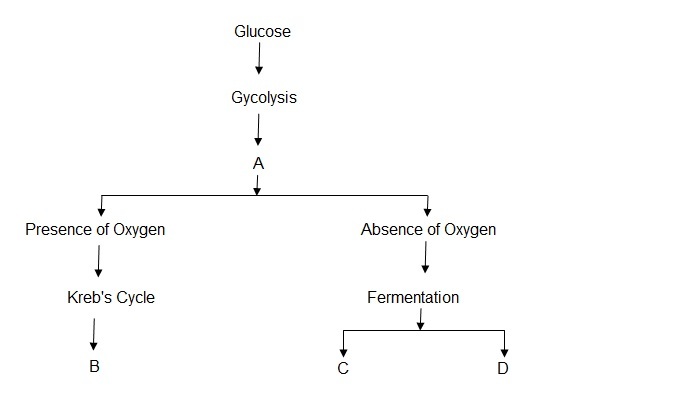
Answer: Option C. -> A – Pyruvic acid, B - Carbon dioxide and water, C - Ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide, D - Lactic acid
:
C
The product of glycolysis is A. pyruvic acid, the pyruvate formed enters the Kreb's cycle in aerobic respiration and the products of Kreb’s cycle are CO2 and water. Therefore B. is carbon dioxide and water. In the absence of oxygen the glycolytic product pyruvate enters the anaerobic pathway, it then undergoes fermentation to form either ethylalcohol or lactic acid. Formation of ethylalcohol is accompanied by formation of carbon dioxide. Therefore C. is ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide and D. is lactic acid.
:
C
The product of glycolysis is A. pyruvic acid, the pyruvate formed enters the Kreb's cycle in aerobic respiration and the products of Kreb’s cycle are CO2 and water. Therefore B. is carbon dioxide and water. In the absence of oxygen the glycolytic product pyruvate enters the anaerobic pathway, it then undergoes fermentation to form either ethylalcohol or lactic acid. Formation of ethylalcohol is accompanied by formation of carbon dioxide. Therefore C. is ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide and D. is lactic acid.
Answer: Option C. -> NADH dehydrogenase and cytochrome – c oxidase complex
:
C
Complex 1 of electron transport chain (ETS) is NADH dehydrogenase, which oxidises NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix during citric acid cycle. Complex IV of ETS refers to cytochrome oxidase complex containing cytochrome-aanda3and two copper centres.
:
C
Complex 1 of electron transport chain (ETS) is NADH dehydrogenase, which oxidises NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix during citric acid cycle. Complex IV of ETS refers to cytochrome oxidase complex containing cytochrome-aanda3and two copper centres.
Answer: Option D. -> IV, I, III, II
:
D
Enolase works on 2-phosphoglyceric acid (3C compound) to form phosphoenolpyruvate in the glycolysis pathway, aconitase on citric acid (6C compound), fumarase on fumaric acid (4C compound) and alcohol dehydrogenase on acetaldehyde (2C-compound). Thus, increasing order of these enzymes based on carbon number of their substrates is - IV, I, III, II.
:
D
Enolase works on 2-phosphoglyceric acid (3C compound) to form phosphoenolpyruvate in the glycolysis pathway, aconitase on citric acid (6C compound), fumarase on fumaric acid (4C compound) and alcohol dehydrogenase on acetaldehyde (2C-compound). Thus, increasing order of these enzymes based on carbon number of their substrates is - IV, I, III, II.
Answer: Option D. -> ATP synthase
:
D
The complex V of ETS of mitochondrial membrane is ATP synthase, which has a head piece, stalk and a base piece. Out of these, the head piece is identified as coupling factor 1 (F1), stalk portion is necessary for binding F1to inner mitochondrial membrane and base piece is isolated as F0and present within the inner mitochondrial membrane.
:
D
The complex V of ETS of mitochondrial membrane is ATP synthase, which has a head piece, stalk and a base piece. Out of these, the head piece is identified as coupling factor 1 (F1), stalk portion is necessary for binding F1to inner mitochondrial membrane and base piece is isolated as F0and present within the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Answer: Option B. -> Succinic acid -> Fumaric acid
:
B
In Kreb’s cycle, when succininc acid undergoes oxidation or dehydrogenation to form fumaric acid, two hydrogens are transferred to FAD. FAD is reduced to FADH2 and enzyme involved in this step is succinic acid dehydrogenase.
:
B
In Kreb’s cycle, when succininc acid undergoes oxidation or dehydrogenation to form fumaric acid, two hydrogens are transferred to FAD. FAD is reduced to FADH2 and enzyme involved in this step is succinic acid dehydrogenase.
Answer: Option B. -> CO2
:
B
CO2 is released during respiration and forms the product of respiration. Whereas in photosynthesis, the carbon dioxide molecule is fixed to form glucose. ThereforeCO2forms the substrate in photosynthesis.
:
B
CO2 is released during respiration and forms the product of respiration. Whereas in photosynthesis, the carbon dioxide molecule is fixed to form glucose. ThereforeCO2forms the substrate in photosynthesis.