7th Grade > Mathematics
PRACTICAL GEOMETRY MCQs
:
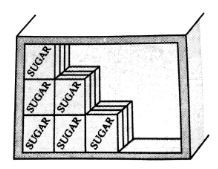
Each corner has three mutually perpendicular lines and a cuboid has 8 corners. Hence, the total number of right angles in a cubical room is 8×3=24.
:
Each part: 1 Mark
For SAS, the criterion is as follows:
a) Lengths of any two sides.
b) The measure of the angle between these sides.
For ASA, the criterion are as follows
a) Measures of any two angles.
b) Lengths of the side between these angles.
:
Constructions: 2 Marks
Steps: 1 Mark
Step 1: Draw a line segment ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯BC=48 cm
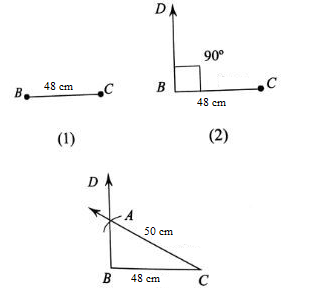
Step 2: Draw ∠CBD=90∘ at B using protractor or compass.
Step 3: With C as centre and radius equal to 50 cm, draw an arc to cut the ray ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯BD at A and join ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯AC
ABC is the required triangle.
:
Construction: 1 Mark
Steps: 2 Marks
Draw a line segment PQ of length 5 cm.
At P, draw a ray PX by making an angle of 60∘ with PQ (according to the given condition, R lies on ray PX).
At Q, draw a ray QY by making an angle of 45∘ with PQ (according to the given condition, R also lies on ray QY).
The intersection point of ray PX and QY is the point where R lies.
:
Steps: 1 Mark
Final answer: 1 Mark
Adding up the sides, taking two at a time, we get
5 cm + 19 cm = 24 cm > 20 cm
5 cm + 20 cm = 25 cm > 19 cm
19 cm + 20 cm = 39 cm > 5 cm
So we see that the sum of the pair of sides when added is greater than the third side.
Therefore, we can construct the triangle with these measurements.
(a) For constructing a triangle, we must know two sides and included angle. Which triangle can be uniquely constructed by knowing two sides and any other angle?
(b) Which of the following congruency conditions is preferred to draw a triangle exactly congruent to a right-angled triangle? [2 MARKS]
:
Each part: 1 Mark
(a) We only need to know R (Right angle), H (Hypotenuse) and S (Side) to construct a right-angled triangle. The right angle is not included between the hypotenuse and the other side.
(b) If the hypotenuse and any one leg of one right-angled triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of another right-angled triangle, the two triangles are congruent.
It means that if we have two right-angled triangles with the same length of the hypotenuse and the same length for one of the other two legs, then both right triangles are identical.
:
Construction: 1 Mark
Steps: 3 Marks
Let assume that AB = 5, BC = 12 and AC = 13
1) Draw a line segment BC of length 12 cm.
2) From B, point A is at a distance of 5 cm. So, with B as the centre, draw an arc of radius 5 cm. (Now A will be somewhere on this arc.)
3) From C, point A is at a distance of 13 cm. So, with C as the centre, draw an arc of radius 13 cm. (A will be somewhere on this arc)
4) A has to be on both the arcs drawn. So, it is the point of intersection of arcs. Mark the point of intersection of arcs as A. Join AB and AC. ΔABC is now ready.