12th Grade > Biology
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MCQs
Total Questions : 68
| Page 1 of 7 pages
Answer: Option D. -> Titin
:
D
Titinis a large abundantproteinof striated muscle.Titin'sprimaryfunctionsare to stabilize the thick filament, center it between the thin filaments, prevent overstretching of thesarcomere, and to recoil thesarcomerelike a spring after it is stretched.
Muscles contract through theactionof two proteins calledactinandmyosin along with regulatory proteins tropomyosin and troponin, control your voluntary movements.
:
D
Titinis a large abundantproteinof striated muscle.Titin'sprimaryfunctionsare to stabilize the thick filament, center it between the thin filaments, prevent overstretching of thesarcomere, and to recoil thesarcomerelike a spring after it is stretched.
Muscles contract through theactionof two proteins calledactinandmyosin along with regulatory proteins tropomyosin and troponin, control your voluntary movements.
Answer: Option A. -> Malleus, incus, stapes
:
A
The three tiniest bones in the body form the coupling between the vibration of the eardrum and the forces exerted on the oval window of the inner ear. Formally named the malleus, incus, and stapes, they are commonly referred to in English as the hammer, anvil, and stirrup.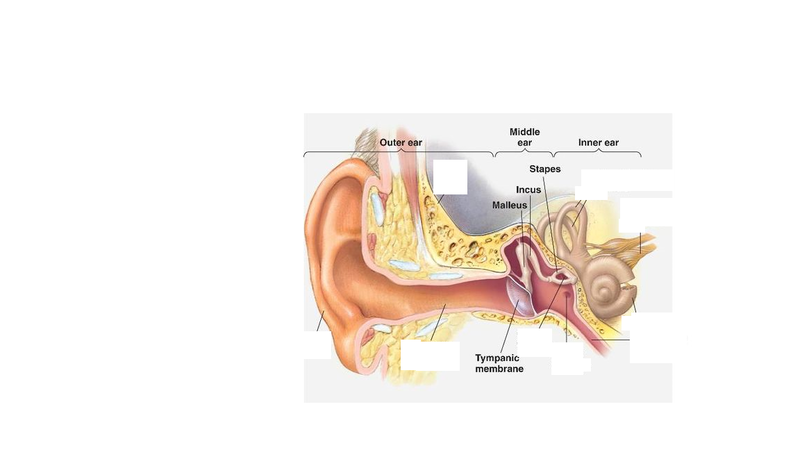
:
A
The three tiniest bones in the body form the coupling between the vibration of the eardrum and the forces exerted on the oval window of the inner ear. Formally named the malleus, incus, and stapes, they are commonly referred to in English as the hammer, anvil, and stirrup.

Answer: Option A. -> 1. Spinous process, 2. Vertebral arch, 3. Foramen, 4.Lamina, 5.Transverse process
:
A
Body – The body is the weight-bearing part of the vertebrae.
Vertebral arch -The arch is on the posterior aspect of the body and protects the spinal cord
Vertebral foramen -The opening through the arch is called the vertebral foramen
Processes-There are three different types of processes which serve as attachment points for ligaments and muscles and sites for moveable joints
:
A
Body – The body is the weight-bearing part of the vertebrae.
Vertebral arch -The arch is on the posterior aspect of the body and protects the spinal cord
Vertebral foramen -The opening through the arch is called the vertebral foramen
Processes-There are three different types of processes which serve as attachment points for ligaments and muscles and sites for moveable joints

Answer: Option A. -> Skeletal muscles
:
A
The peripheral nervous system(PNS) is under your voluntarycontrol- thenervesthat carry instructions from your brain to your limbs, for example. As well as controlling your muscles and joints, it sends all the information from your senses back to your brain.The autonomic nervous system(ANS) is a division of the peripheralnervous systemthat influences the function of internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines.
:
A
The peripheral nervous system(PNS) is under your voluntarycontrol- thenervesthat carry instructions from your brain to your limbs, for example. As well as controlling your muscles and joints, it sends all the information from your senses back to your brain.The autonomic nervous system(ANS) is a division of the peripheralnervous systemthat influences the function of internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines.
Answer: Option A. -> Myocytes
:
A
A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop frommyoblaststo form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties.
Leukocytes are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells.
A lymphocyte is a type of Leucocyte.
:
A
A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop frommyoblaststo form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties.
Leukocytes are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells.
A lymphocyte is a type of Leucocyte.
Answer: Option C. -> Ossification
:
C
The baby skeleton has more bones and cartilages. During development many of these cartilages become bones by the process called ossification and some bones fuse to form a bigger bone reducing the number of bones to 206.
:
C
The baby skeleton has more bones and cartilages. During development many of these cartilages become bones by the process called ossification and some bones fuse to form a bigger bone reducing the number of bones to 206.
Answer: Option D. -> Troponin
:
D
Thin filament of the sarcomere is made up of actin, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle contraction can happen when myosin head of thick filament binds to the myosin binding site of thin filament. But, this site is covered by troponin-tropomyosin complex. Upon stimulation of muscle by an neural impulse, calcium is released from sarcoplasmic reticulum which binds to troponin and brings about a change in the confirmation of tropomyosin. This exposes the myosin binding site of thin filament and causes binding and contraction.
:
D
Thin filament of the sarcomere is made up of actin, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle contraction can happen when myosin head of thick filament binds to the myosin binding site of thin filament. But, this site is covered by troponin-tropomyosin complex. Upon stimulation of muscle by an neural impulse, calcium is released from sarcoplasmic reticulum which binds to troponin and brings about a change in the confirmation of tropomyosin. This exposes the myosin binding site of thin filament and causes binding and contraction.
Answer: Option D. -> Craniostylic
:
D
The entire upper jaw is incorporated into the braincase in mammals and hence the jaw suspension is craniostylic.
Having the mandible suspended by the hyomandibular, or upper part of the hyoid arch, as in fishes is hyostylic suspension. Ex. Bony fishes.
When jaws are attached to the cranium by anterior and posterior ligaments, it is called autodiastylic. Ex: gnathostomes
Amphistylic jaw suspension is a type of jaw suspension seen in certain sharks, in which the upper jaw is braced against the cranium and is also supported by the hyomandibular ligaments.
:
D
The entire upper jaw is incorporated into the braincase in mammals and hence the jaw suspension is craniostylic.
Having the mandible suspended by the hyomandibular, or upper part of the hyoid arch, as in fishes is hyostylic suspension. Ex. Bony fishes.
When jaws are attached to the cranium by anterior and posterior ligaments, it is called autodiastylic. Ex: gnathostomes
Amphistylic jaw suspension is a type of jaw suspension seen in certain sharks, in which the upper jaw is braced against the cranium and is also supported by the hyomandibular ligaments.
Answer: Option A. -> Myosin
:
A
The myosin head contains binding sitesATP binding site and actin binding site. Actin molecule has 2 other proteins tropomyosinandtroponinare two other proteins found in small quantities in muscle. They help regulate muscle contraction.
:
A
The myosin head contains binding sitesATP binding site and actin binding site. Actin molecule has 2 other proteins tropomyosinandtroponinare two other proteins found in small quantities in muscle. They help regulate muscle contraction.
Question 10. Match the following:
Column - IColumn - IIi. Ethmoid a. are situated at the sides and base of the skullii. Sphenoidb. contains the large opening of the foramen magnumiii. Frontalc. situated on the sides and the roof of the skulliv. Parietald. forms the forehead.v. Temporale. is found in the nasal septumvi.Occipitalf. houses the optic canal
Column - IColumn - IIi. Ethmoid a. are situated at the sides and base of the skullii. Sphenoidb. contains the large opening of the foramen magnumiii. Frontalc. situated on the sides and the roof of the skulliv. Parietald. forms the forehead.v. Temporale. is found in the nasal septumvi.Occipitalf. houses the optic canal
Answer: Option A. -> (i) ⇒ a, (ii) ⇒ b, (iii) ⇒ d, (iv) ⇒ e, (v) ⇒ e, (vi) ⇒ f
:
A

Theethmoid boneis found in the nasal septum
Thesphenoid bone houses the optic canal
The frontal bone forms the forehead.
The parietal bone are situated on the sides and the roof of the skull
Thetemporal bonesare situated at the sides and base of the skull
The occipital bone contains the large opening of theforamen magnum
:
A

Theethmoid boneis found in the nasal septum
Thesphenoid bone houses the optic canal
The frontal bone forms the forehead.
The parietal bone are situated on the sides and the roof of the skull
Thetemporal bonesare situated at the sides and base of the skull
The occipital bone contains the large opening of theforamen magnum