9th Grade > Physics
FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION MCQs
Total Questions : 39
| Page 2 of 4 pages
Answer: Option B. -> Unbalanced force
:
B
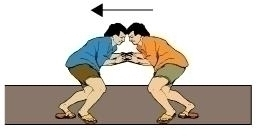
It is clear from the given information that Arun is pushing harder, i.e., their pushes are unequal. Hence, the net force between them will be unbalanced and the direction of force will be as shown in the given figure.
:
B
It is clear from the given information that Arun is pushing harder, i.e., their pushes are unequal. Hence, the net force between them will be unbalanced and the direction of force will be as shown in the given figure.
Answer: Option A. -> 1.25 s
:
A
Let mass of cannon bem1 = 400kg
Let mass of cannon ball be m2 =2kg
Let initial velocities of the cannon and cannon ball be u1 and u2 respectively.
Let final velocity of cannon and cannon ball be v1 and v2 respectively.
From thelaw of conservation of momentum,
total momentum before firing = total momentum after firing.
∴ m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
As the cannon and cannon ball is at rest initially, the initial velocity will be zero, i.e
0=m1v1+m2v2
Substituting the values:
0=400×(−2)+2×v
⇒v=400×22=400ms−1
Hence, the velocity of the cannonball will be 400ms−1
Since we know,
time=displacementvelocity
Thus, time taken to hit the target= 500400 = 1.25s
:
A
Let mass of cannon bem1 = 400kg
Let mass of cannon ball be m2 =2kg
Let initial velocities of the cannon and cannon ball be u1 and u2 respectively.
Let final velocity of cannon and cannon ball be v1 and v2 respectively.
From thelaw of conservation of momentum,
total momentum before firing = total momentum after firing.
∴ m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
As the cannon and cannon ball is at rest initially, the initial velocity will be zero, i.e
0=m1v1+m2v2
Substituting the values:
0=400×(−2)+2×v
⇒v=400×22=400ms−1
Hence, the velocity of the cannonball will be 400ms−1
Since we know,
time=displacementvelocity
Thus, time taken to hit the target= 500400 = 1.25s
Answer: Option A. -> Opposite to the bullet's direction.
:
A
The total momentum of the bullet-pistol system was initially zero as both of them were at rest with respect to ground. During the shooting of the bullet, net external force on the gun and bullet system is zero. Hence, according to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the system will be zero even after firing the shot. Since the momentum of the bullet will be in forward direction, in order to balance it, the momentum of the pistol should be in backward direction or the pistol should move backwards.
:
A
The total momentum of the bullet-pistol system was initially zero as both of them were at rest with respect to ground. During the shooting of the bullet, net external force on the gun and bullet system is zero. Hence, according to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the system will be zero even after firing the shot. Since the momentum of the bullet will be in forward direction, in order to balance it, the momentum of the pistol should be in backward direction or the pistol should move backwards.
Answer: Option C. -> 20 ms−1
:
C
Let mass of bullet be m1=20g
Let mass of the wooden block be m2=80g
Let initial velocity of the bullet beu1 = 100ms−1 and final velocity of the bullet be v1.
Let the initial velocity of wooden block be u2, since it wasat rest, the initial velocity is zero, i.eu2=0ms−1
Let final velocity of the wooden block be v2.
By applying law of conservation of momentum,
intialmomentum of the system = final momentum of the system
i.e,m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
After the bullet is fired, the bullet gets embedded on the block.
Therefore, it acts as a system
Hence , the final velocity of the bullet and wooden block after collision will be equal as it works as a system
i.e v1=v2=v where v is the velocity of the system after collision.
Substituting onthe equation, we get
(0.020×100)+(0.080×0)=v×(0.020+0.080)
⇒ 2=0.1×v
⇒ v=20ms−1
∴Velocity of system after collision = 20ms−1
:
C
Let mass of bullet be m1=20g
Let mass of the wooden block be m2=80g
Let initial velocity of the bullet beu1 = 100ms−1 and final velocity of the bullet be v1.
Let the initial velocity of wooden block be u2, since it wasat rest, the initial velocity is zero, i.eu2=0ms−1
Let final velocity of the wooden block be v2.
By applying law of conservation of momentum,
intialmomentum of the system = final momentum of the system
i.e,m1u1+m2u2=m1v1+m2v2
After the bullet is fired, the bullet gets embedded on the block.
Therefore, it acts as a system
Hence , the final velocity of the bullet and wooden block after collision will be equal as it works as a system
i.e v1=v2=v where v is the velocity of the system after collision.
Substituting onthe equation, we get
(0.020×100)+(0.080×0)=v×(0.020+0.080)
⇒ 2=0.1×v
⇒ v=20ms−1
∴Velocity of system after collision = 20ms−1
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
As we know, Force=mass×acceleration. Hence, force is directly proportional to mass. Here, cricket ball has more mass than the tennis ball. So, even if the velocity is the same, the mass of the cricketball and the associated momentum(which is the product of mass and velocity) is greaterthan that of the tennis ball and hence, it is easier to stop a tennis ball as compared to a cricket ball having the same velocity.
:
A
As we know, Force=mass×acceleration. Hence, force is directly proportional to mass. Here, cricket ball has more mass than the tennis ball. So, even if the velocity is the same, the mass of the cricketball and the associated momentum(which is the product of mass and velocity) is greaterthan that of the tennis ball and hence, it is easier to stop a tennis ball as compared to a cricket ball having the same velocity.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Initially, the total momentum was zero and after the man starts moving, the total momentum would still be zero as no external force is acting on the system of the man and the boat (law of conservation of momentum). So,the boat will move in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the man.
:
A
Initially, the total momentum was zero and after the man starts moving, the total momentum would still be zero as no external force is acting on the system of the man and the boat (law of conservation of momentum). So,the boat will move in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the man.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Newton's second law of motion gives us the quantitative analysis of force. It gives us the mathematical expression of force as it states thatthe rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied, and this change in momentum takes place in the direction of the applied force.
:
A
Newton's second law of motion gives us the quantitative analysis of force. It gives us the mathematical expression of force as it states thatthe rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied, and this change in momentum takes place in the direction of the applied force.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
According to newton's second law of motion-"the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to force applied and the change in momentum is in the direction of force applied." Newton's second law of motion gives mathematical expression of force.
Force ∝ dpdt
:
A
According to newton's second law of motion-"the rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to force applied and the change in momentum is in the direction of force applied." Newton's second law of motion gives mathematical expression of force.
Force ∝ dpdt
Answer: Option B. -> 0
:
B
Ideally, a frictionless horizontal table has no resistance to motion.
Therefore, the object will continue to slide at4ms−1 without any application of force.
∴ The force required to keep the object moving = 0
:
B
Ideally, a frictionless horizontal table has no resistance to motion.
Therefore, the object will continue to slide at4ms−1 without any application of force.
∴ The force required to keep the object moving = 0
Answer: Option A. ->
4,000 N
:
A
:
A
For calculating force, we need to calculate deceleration first. From the third equation of motion,
v2−u2=2aS where, v- final velocity, u- initial velocity, a- acceleration and S- distance travelled.
Given, u=20 ms−1, S=50 m, mass m=1000 kg and v=0.
Therefore, 0−202=2×a×50
⇒a=−4 ms−2
Let the force acting on the car be F.
From Newton's second law,
F=ma
⇒F=1000×(−4)=−4000 N
Hence, the net force is −4,000 N. The negative sign indicates that the force is acting opposite to the direction of initial velocity and causes deceleration. This net force is actually the frictional force acting between the ground and the tyre of the car.