12th Grade > Biology
BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MCQs
Total Questions : 59
| Page 6 of 6 pages
Answer: Option A. -> Resting bradycardia
:
A
When athletes are trained intensively, or for that matter if any person exerts himself in tiring work, the oxygen and consequently the blood supply demand from the body increases. Therefore, the heart compensates by pumping more blood per min or beat to make up for the demand. Therefore, when that person is at rest, because his heart is able to pump more blood per beat, what blood would have been pumped by 70 beats, now gets pumped by only 60 beats. This is referred to as resting bradycardia. Healthy young adults and athletes often have heart rates of less than 60 beats a minute.
:
A
When athletes are trained intensively, or for that matter if any person exerts himself in tiring work, the oxygen and consequently the blood supply demand from the body increases. Therefore, the heart compensates by pumping more blood per min or beat to make up for the demand. Therefore, when that person is at rest, because his heart is able to pump more blood per beat, what blood would have been pumped by 70 beats, now gets pumped by only 60 beats. This is referred to as resting bradycardia. Healthy young adults and athletes often have heart rates of less than 60 beats a minute.
Answer: Option B. -> Spleen
:
B
Old RBCs are destroyed along with the pathogens by phagocytosis that is carried out by macrophages. Macrophages can be found in large numbers in the lymphatic system, especially the spleen. Thus, the spleen acts as a graveyard of RBCs.
:
B
Old RBCs are destroyed along with the pathogens by phagocytosis that is carried out by macrophages. Macrophages can be found in large numbers in the lymphatic system, especially the spleen. Thus, the spleen acts as a graveyard of RBCs.
Answer: Option B. -> medulla and pons
:
B
Therespiratory control centers(RCs) are located in the medulla oblongata and pons, which are parts of the brainstem. The RCs receive controlling signals of neural, chemical and hormonal nature andcontrolthe rate and depth ofrespiratorymovements of the diaphragm and otherrespiratorymuscles.
:
B
Therespiratory control centers(RCs) are located in the medulla oblongata and pons, which are parts of the brainstem. The RCs receive controlling signals of neural, chemical and hormonal nature andcontrolthe rate and depth ofrespiratorymovements of the diaphragm and otherrespiratorymuscles.
Answer: Option A. -> leaves the heart
:
A
Systole is the contraction of the left and right ventricles, resulting in blood flow to the body and lungs, respectively. Diastole includes the contraction of the atria and the filling of the ventricles. Thus, in the systolic phase of cardiac cycle, blood leaves the heart.
:
A
Systole is the contraction of the left and right ventricles, resulting in blood flow to the body and lungs, respectively. Diastole includes the contraction of the atria and the filling of the ventricles. Thus, in the systolic phase of cardiac cycle, blood leaves the heart.
Answer: Option D. -> Skeletal muscle contraction, peristalsis of muscles around lymphatic vessels and the action of one-way valves.
:
D
Unlike the circulatory system, that has the heart to pump blood through the system, the lymphatic system does not have a pump. The Lymph is moved through the lymphatic vessels by contractions of the lymphatic vessels and the movement of the surrounding digestive system and skeletal muscles. Also the one-way action of valves within the lymphatic capillaries, help in its motion or circulation.
:
D
Unlike the circulatory system, that has the heart to pump blood through the system, the lymphatic system does not have a pump. The Lymph is moved through the lymphatic vessels by contractions of the lymphatic vessels and the movement of the surrounding digestive system and skeletal muscles. Also the one-way action of valves within the lymphatic capillaries, help in its motion or circulation.
Answer: Option A. -> atrial depolarization → ventricular depolarization → atrial and ventricular repolarization
:
A
The conduction mechanism can be broken down into three major stages. The stages in order are atrial depolarization, ventricular depolarization which is followed by combined atrial and ventricular repolarization. Depolarization refers to the decrease in negative charge in the conduction cells of the heart and this drives contraction of the heart chambers.Repolarisation on the other hand increases negative charge in the conduction cells of the heart bringing about relaxation of heart chambers.
:
A
The conduction mechanism can be broken down into three major stages. The stages in order are atrial depolarization, ventricular depolarization which is followed by combined atrial and ventricular repolarization. Depolarization refers to the decrease in negative charge in the conduction cells of the heart and this drives contraction of the heart chambers.Repolarisation on the other hand increases negative charge in the conduction cells of the heart bringing about relaxation of heart chambers.
Answer: Option A. -> 1- Right atrium 2- Right ventricle 3- Pulmonary artery 4- Lungs 5- Left atrium 6-Left ventricle
:
A
All blood enters the right side of the heart through two veins: The superior vena cava (SVC) and the inferior vena cava(IVC). The SVC collects blood from the upper half of the body. The IVC collects blood from the lower half of the body. Blood leaves the SVC and the IVC and enters the right atrium (RA). When the RA contracts, the blood goes through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle (RV). When the RV contracts, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve, into the pulmonary artery (PA) and into the lungs where it picks up oxygen. Blood now returns to the heart from the lungs by way of the pulmonary veins and goes into the left atrium (LA). When the LA contracts, blood travels through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle (LV). The LV is a very important chamber that pumps blood through the aortic valve and into the aorta. The aorta is the main artery of the body. It receives all the blood that the heart has pumped out and distributes it to the rest of the body.
:
A
All blood enters the right side of the heart through two veins: The superior vena cava (SVC) and the inferior vena cava(IVC). The SVC collects blood from the upper half of the body. The IVC collects blood from the lower half of the body. Blood leaves the SVC and the IVC and enters the right atrium (RA). When the RA contracts, the blood goes through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle (RV). When the RV contracts, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve, into the pulmonary artery (PA) and into the lungs where it picks up oxygen. Blood now returns to the heart from the lungs by way of the pulmonary veins and goes into the left atrium (LA). When the LA contracts, blood travels through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle (LV). The LV is a very important chamber that pumps blood through the aortic valve and into the aorta. The aorta is the main artery of the body. It receives all the blood that the heart has pumped out and distributes it to the rest of the body.
Answer: Option A. -> To supply blood to the musculature of heart.
:
A
The function of the coronary circulation is to supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles as well as removal of deoxygenated blood from them.
:
A
The function of the coronary circulation is to supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles as well as removal of deoxygenated blood from them.
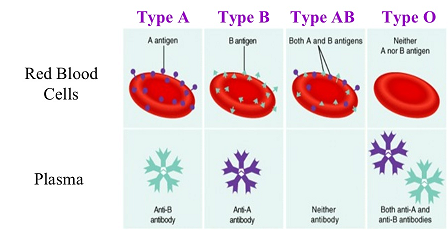
Answer: Option D. -> Type A or type B blood antigens.
:
D
Plasma transports nutrients like glucose, fatty acids, phospholipids, cholesterol, fats and amino acids. It also transports waste products such as ammonia, urea, uric acid and by-products of protein breakdown.
Plasma does not have antigens of type A or type B blood, it has antibodies against the respective blood types, but not the antigens.
:
D
Plasma transports nutrients like glucose, fatty acids, phospholipids, cholesterol, fats and amino acids. It also transports waste products such as ammonia, urea, uric acid and by-products of protein breakdown.
Plasma does not have antigens of type A or type B blood, it has antibodies against the respective blood types, but not the antigens.