12th Grade > Biology
BIOMOLECULES MCQs
Total Questions : 58
| Page 5 of 6 pages
Answer: Option C. -> Isomerases
:
C
Epimerasesare isomerase enzymes that catalyze the inversion of stereochemistry in biological molecules.
Hydrolasesare hydrolytic enzymes, biochemical catalysts that use water to cleave chemical bonds, usually dividing a large molecule into two smaller molecules.
Ligases are enzymes that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond, usually with accompanying hydrolysis of a small energy molecule like ATP.
Oxidoreductasesare enzymes that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP or NAD+ as cofactors.
:
C
Epimerasesare isomerase enzymes that catalyze the inversion of stereochemistry in biological molecules.
Hydrolasesare hydrolytic enzymes, biochemical catalysts that use water to cleave chemical bonds, usually dividing a large molecule into two smaller molecules.
Ligases are enzymes that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond, usually with accompanying hydrolysis of a small energy molecule like ATP.
Oxidoreductasesare enzymes that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP or NAD+ as cofactors.
Answer: Option B. -> Glycoprotein
:
B
A protein conjugated with a carbohydrate is a glycoprotein.
Lecithoproteins are proteins conjugated to lecithin. Lipoproteins are proteins conjugated to lipids and metalloproteins are proteins conjugated to metals.
:
B
A protein conjugated with a carbohydrate is a glycoprotein.
Lecithoproteins are proteins conjugated to lecithin. Lipoproteins are proteins conjugated to lipids and metalloproteins are proteins conjugated to metals.
Answer: Option A. -> Condensation (dehydration) reaction
:
A
An amino group reacts with the carboxyl group, forming a bond and leading to the elimination of a water molecule. This type of reaction, which involves two molecules binding to each other with eliminatiion of water is called a condensation reaction. This type of reaction is common between two amino acids, leading to the formation of a peptide bond. The general term for such reactions is condensation and the reaction can be termed peptide bond formation only when it involves two amino acids.
Hydrolysis is the reverse reaction of condensation, this involves the breakdown of a large molecule into two smaller molecules by the addition of water.
And oxidation is reaction involving addition of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
:
A
An amino group reacts with the carboxyl group, forming a bond and leading to the elimination of a water molecule. This type of reaction, which involves two molecules binding to each other with eliminatiion of water is called a condensation reaction. This type of reaction is common between two amino acids, leading to the formation of a peptide bond. The general term for such reactions is condensation and the reaction can be termed peptide bond formation only when it involves two amino acids.
Hydrolysis is the reverse reaction of condensation, this involves the breakdown of a large molecule into two smaller molecules by the addition of water.
And oxidation is reaction involving addition of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
Answer: Option D. -> Actin
:
D
Actin is a contractile protein found in muscles. Albumin is a carrier protein found in blood plasma. Globulins are proteins that form the antibodies. And fibrinogen is a clotting factor found in blood. Therefore all the other proteins except actin are plasma proteins.
:
D
Actin is a contractile protein found in muscles. Albumin is a carrier protein found in blood plasma. Globulins are proteins that form the antibodies. And fibrinogen is a clotting factor found in blood. Therefore all the other proteins except actin are plasma proteins.
Answer: Option D. -> Palmitic acid
:
D
Oleic acid -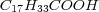 , linoleic acid -
, linoleic acid - ,linolenic acid -
,linolenic acid - ,palmitic acid -
,palmitic acid - .
.
Saturatedmonocarboxylic acids forma homologous series which has a general formula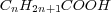 or
or . Although all the fatty acids mentioned here are present in nature, onlypalmitic acid follows this formula, all others are unsaturated fatty acids.
. Although all the fatty acids mentioned here are present in nature, onlypalmitic acid follows this formula, all others are unsaturated fatty acids.
:
D
Oleic acid -
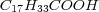 , linoleic acid -
, linoleic acid - ,linolenic acid -
,linolenic acid - ,palmitic acid -
,palmitic acid - .
.Saturatedmonocarboxylic acids forma homologous series which has a general formula
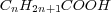 or
or . Although all the fatty acids mentioned here are present in nature, onlypalmitic acid follows this formula, all others are unsaturated fatty acids.
. Although all the fatty acids mentioned here are present in nature, onlypalmitic acid follows this formula, all others are unsaturated fatty acids. Answer: Option B. -> Enzymes
:
B
In an organism, biochemical reactions or metabolic activities related to physiology are enhanced by biocatalysts called enzymes. Enzymes are proteins whichare very specific both in their activity and targets.
:
B
In an organism, biochemical reactions or metabolic activities related to physiology are enhanced by biocatalysts called enzymes. Enzymes are proteins whichare very specific both in their activity and targets.
Answer: Option D. -> All forms of life
:
D
Nucleic acids either in the form of DNA or RNA occur in all forms of life as the genetic material.
:
D
Nucleic acids either in the form of DNA or RNA occur in all forms of life as the genetic material.