12th Grade > Biology
BIOMOLECULES MCQs
Total Questions : 58
| Page 2 of 6 pages
Answer: Option B. -> Induced fit
:
B
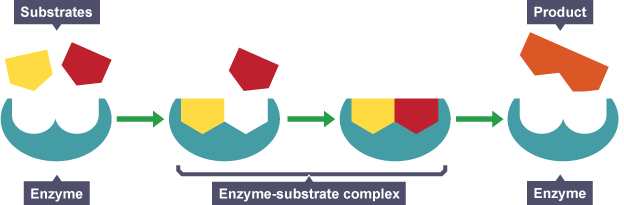
In the image given here the substrates do not fit into the enzyme active site like a lock and key, instead the substrates induces a change in the enzyme active site on binding the enzyme, thereby enabling the interaction between the substrates and formation of products. Therefore the representation shown here is the induced fit model of enzyme action.
In the lock and key model the substrate structure has to be the right fit for the enzyme active site, like that of a key and its lock. Similar to how akeyhas to be the correct one for alock, no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind the enzyme.
:
B
In the image given here the substrates do not fit into the enzyme active site like a lock and key, instead the substrates induces a change in the enzyme active site on binding the enzyme, thereby enabling the interaction between the substrates and formation of products. Therefore the representation shown here is the induced fit model of enzyme action.
In the lock and key model the substrate structure has to be the right fit for the enzyme active site, like that of a key and its lock. Similar to how akeyhas to be the correct one for alock, no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind the enzyme.
Answer: Option A. -> Fibroin
:
A
Given here is the list of substances where the proteins mentioned here are found.
Fibroin - Silk
Albumin- Egg, Blood plasma
Keratin- Hair, Skin
Globulin- Blood plasma
:
A
Given here is the list of substances where the proteins mentioned here are found.
Fibroin - Silk
Albumin- Egg, Blood plasma
Keratin- Hair, Skin
Globulin- Blood plasma
Answer: Option C. -> Synthesis by condensation
:
C
A ligaseis an enzyme that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond.
Oxidation and reduction are carried out by oxidoreductases and group transfer reactions are carried out by transferases.
:
C
A ligaseis an enzyme that can catalyze the joining of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond.
Oxidation and reduction are carried out by oxidoreductases and group transfer reactions are carried out by transferases.
Question 14. Which of the following statement(s) is false, regarding Proteins ?
I. A protein is a heteropolymer but not a homopolymer.
II. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the animal world.
III. RUBISCO is the most abundant protein in the biosphere.
IV The first amino acid in a polypeptide chain is C- terminal amino acid and the last is N- terminal amino acid.
I. A protein is a heteropolymer but not a homopolymer.
II. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the animal world.
III. RUBISCO is the most abundant protein in the biosphere.
IV The first amino acid in a polypeptide chain is C- terminal amino acid and the last is N- terminal amino acid.
Answer: Option D. -> IV
:
D
Statement IV is incorrect because,proteinsare naturallysynthesizedstarting from theN-terminusand ending at theC-terminus. Therefore conventionally,the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain is N- terminal amino acid and the last is the C- terminal amino acid.
:
D
Statement IV is incorrect because,proteinsare naturallysynthesizedstarting from theN-terminusand ending at theC-terminus. Therefore conventionally,the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain is N- terminal amino acid and the last is the C- terminal amino acid.
Answer: Option A. -> Keratin
:
A
Keratin is a structural protein found in hair and nails etc.
Hemoglobin is a protein in blood, that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. It is a functional protein.
Amino acid is the monomer unit of a protein and gelatin is a form of irreversibly hydrolyzed collagen.
:
A
Keratin is a structural protein found in hair and nails etc.
Hemoglobin is a protein in blood, that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. It is a functional protein.
Amino acid is the monomer unit of a protein and gelatin is a form of irreversibly hydrolyzed collagen.
:
Substances, which obstruct enzyme activity are called inhibitors.
Answer: Option A. -> Scurvy
:
A
The deficiency of vitamin-Ccauses “scurvy”, characterized byweakness, tiredness, gum disease etc.
Ricketsis defective mineralization or calcification of bones in immature mammals due to deficiency of vitamin D.
Pyrrohea orPeriodontitis,is an advanced stage of gum disease in which the gums and bones that provide support to the teeth become inflamed.
PerniciousAnaemiaoccurs when your body can’t absorb enough vitamin B-12, which is needed to make healthy red blood cells.
:
A
The deficiency of vitamin-Ccauses “scurvy”, characterized byweakness, tiredness, gum disease etc.
Ricketsis defective mineralization or calcification of bones in immature mammals due to deficiency of vitamin D.
Pyrrohea orPeriodontitis,is an advanced stage of gum disease in which the gums and bones that provide support to the teeth become inflamed.
PerniciousAnaemiaoccurs when your body can’t absorb enough vitamin B-12, which is needed to make healthy red blood cells.
Answer: Option C. -> When the velocity of the reaction is half the maximum velocity
:
C
In an enzymatic reaction, the rate of the reaction increases as we increase the substrate concentration, till a point where the reaction reaches the maximum velocity Vmax. Once this upper limit has been attained, further increase in substrate concentration will not increase the rate of the reaction, as all the substrate binding sites on the enzyme will be saturated. The substrate concentration at half the maximum velocity is defined as the Michaelis constant, Km.

:
C
In an enzymatic reaction, the rate of the reaction increases as we increase the substrate concentration, till a point where the reaction reaches the maximum velocity Vmax. Once this upper limit has been attained, further increase in substrate concentration will not increase the rate of the reaction, as all the substrate binding sites on the enzyme will be saturated. The substrate concentration at half the maximum velocity is defined as the Michaelis constant, Km.

Answer: Option B. -> (i) Homopolymer (ii) Heteropolymer
:
B
Polysaccharides can be homopolymers (contain only one sugar residue) like Cellulose (glucose in beta 1-4 linkages) or heteropolymers (contain more than one sugar residue) like Hemicellulose which contain xylose, mannose, galactose, rhamnose, and arabinose; which are different monomers of sugar.
:
B
Polysaccharides can be homopolymers (contain only one sugar residue) like Cellulose (glucose in beta 1-4 linkages) or heteropolymers (contain more than one sugar residue) like Hemicellulose which contain xylose, mannose, galactose, rhamnose, and arabinose; which are different monomers of sugar.
Answer: Option A. -> Deoxyribonucleotide has an -- H instead of an --OH at C-2.
:
A
A deoxyribonucleotide and a ribonucleotide are both formed by a sugar moiety, attached to a nitrogenous base and one or more phosphate groups. If the sugar present in the nucleotide is ribose sugar, it is a ribonucleotide. Whereas if the sugar present is derived from ribose by deoxygenation of the the -OH on the C-2, it is called a deoxyribose sugar and this moiety combines with the nitrogenous base and phosphate groups to form the deoxyribonucleotide.

:
A
A deoxyribonucleotide and a ribonucleotide are both formed by a sugar moiety, attached to a nitrogenous base and one or more phosphate groups. If the sugar present in the nucleotide is ribose sugar, it is a ribonucleotide. Whereas if the sugar present is derived from ribose by deoxygenation of the the -OH on the C-2, it is called a deoxyribose sugar and this moiety combines with the nitrogenous base and phosphate groups to form the deoxyribonucleotide.