9th Grade > Mathematics
AREAS OF TRIANGLES AND PARALLELOGRAMS MCQs
:
A
The above statement is true. This is because the perpendicular distance between two parallel lines is constant thus making the altitude for both parallelograms same. As they already have same or equal bases, their areas will also be same.
:
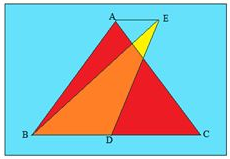
B
If we draw EC, we can see that △ABC and △BEC will have equal area. Because triangles on same base and between same parallels are equal in area.
In △ABC and △BDE the altitude is same but the length of the base is different.
Base length (△ABC) = 2 × Base length (△BDE) (∵ D is the mid point)
So, Area (△ABC) = 2 × Area (△BDE)
Area (△BDE) = 42 cm2
:
The part of the plane enclosed by a simple closed figure is called a planar region. The magnitude or measure of this planar region is called its area.
:
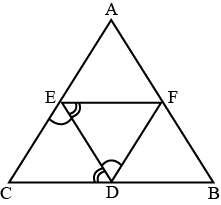
B
EF is parallel to BC (Midpoint theorem)
In ΔCED and ΔEDF,
∠FED =∠EDC (Alternate angles)
EF = EF (common side)
∠CED =∠EDF (Alternate angles)
Hence, ΔCED and ΔEDF are congruent by ASA condition.
Area of ΔCED = Area of ΔEDF.
Therefore, EFDC is a parallelogram
(Diagonals divide a parallelogram into two congruent triangles)
Similarly, FD is parallel to AC and ED is parallel to AB. So, it can be proved that AEFD and EFDB are also parallelograms.
Thus, Area of ΔCED = Area of ΔEDF = Area of ΔAEF = Area of ΔFDB
∴ Area of (DEF)=14Area of (ΔABC)
:
A
Two triangles having the same base (or equal bases) and equal areas lie between the same parallels.
When two triangles have the same base and equal areas, it means they have equal altitudes or heights. So the third vertex will lie on the line parallel to their base. Thus, on joining them, the line produced will be parallel to the base.
:
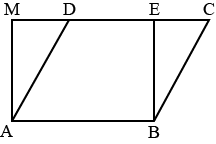
C and D
The area of a parallelogram is the product of base and height. Hence if we consider AD as the base then its corresponding height is BM and the area will be AD×BM
ii) If we consider DC as the base then the corresponding height will be BN or DL . and the area will be given by DC x BN or DC×DL
:
B
In right angled ΔAMD
AD2 = AM2 + MD2 (by Pythagoras theorem)
⇒AD>AM
Similarly, In right angled ΔBEC
BC2 = BE2 + EC2
⇒BC>BE
AB = DC = ME (opposite sides of rectangle and parallelogram)
Perimeter of rectangle = AM + ME + EB + AB.
Perimeter of parallelogram = AB + BC + DC + AD.
Hence Perimeter of ADCB > Perimeter of AMEB.
:
D
Diagonals of a trapezium do not divide the trapezium into two equal parts, but in parallelogram, it is divided into two congruent triangles of equal areas.
:
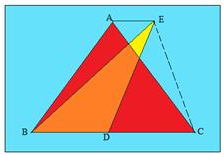
If a triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between the same parallels, then the area of the triangle is equal to half the area of the parallelogram.
Thus, area of triangle AEB is 12×54=27 cm2.