9th Grade > Mathematics
AREAS OF TRIANGLES AND PARALLELOGRAMS MCQs
:
B
If two figures are congruent, they must have the same area but the reverse may not be true. Two figures having the same area need not be congruent.
For example: Consider the figure below:
In this figure, both parallelograms have the same area because they have same base and height. But they aren't congruent.
:
A
Consider the figure given below.
In this figure, ABCD is a parallelogram and ABE is a triangle. Both of them have the same base i.e., AB. The perpendicular EF is an altitude for both triangle and parallelogram.
Now area of ΔABE=12AB×EF
And area of parallelogram is AB×EF.
Hence, Area of parallelogram is twice that of triangle and the ratio will be 2:1
:
B
Theorem used:
Area of triangle is half the area of parallelogram, if both are on same base and between the same parallels.
From the given figure:
AB∥CD (∵ ABCD is a parallelogram)
AB = CD = 6 cm (given)
Altitude BQ = 4 cm (given)
△ABP and parallelogram ABCD are on same base and between the same parallels.
∴Area of ΔAPB=12×Area of ABCD
Area of ABCD=Base×Altitude
=6×4=24cm2
Area of ΔAPB=12×Area of ABCD
=12×24
Area of ΔAPB=12 cm2
:
C
Let BG be perpendicular to AC.
From the given figure:
AC ∥ BF (given)
AC = 5cm (given)
Length of the altitude BG, perpendicular to AC = 6 cm (given)
△ACB and △ACF lie on the same base AC and are between the same parallels AC and BF.
∴Area △ACB = Area △ACF
Area △ACB=12×base ×Height= 12×5×6=15 cm2
∴Area △ACF =15 cm2
:
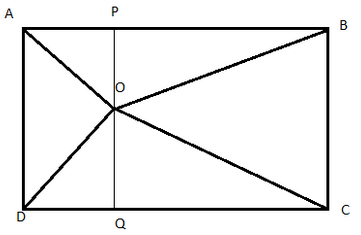
Draw a line through O parallel to ADas shown.Parallelogram APQD and triangle AOD are on same base AD and between same parallels.So, Area(AOD)=12Area (APQD)Area (APQD)=60cm2Parallelogram PBCQ and triangle BOC are on same base BC and between same parallels.So, Area (BOC)=12Area (PBCQ)Area (PBCQ)=120cm2Area (ABCD)=Area (APQD)+Area (PBCQ)=180cm2
:
C
Given: In △ABC, D,E and F are midpoints of BC, CA and AB.
Area (ΔABC) = 32 cm2
To find: Area of trapezium BFEC
Consider △ABC,
F and E are midpoints of AB and AC. (given)
∴ FE ∥ BC (Midpoint theorem)
∴ FE ∥ BD
Similarly ED ∥ AB and FD ∥ AC
∴ FEDB, FDEC and FDEA are all parallelograms.
Since a diagonal divides a parallelogram into two congruent triangles, hence
Area(ΔBFD)=Area(ΔEFD)=Area(ΔECD)=Area(ΔEFA)
=14Area(ΔABC)=8 cm2
Area(BFEC)
=Area(ΔBFD)+Area(ΔEFD)+Area(ΔECD)=24 cm2
:
C
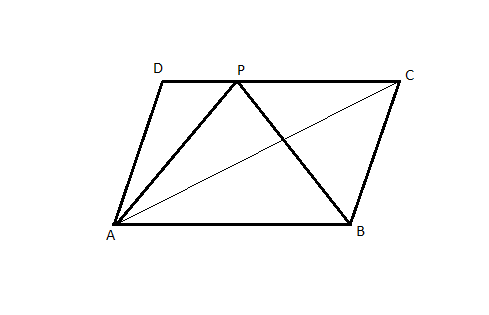 Given: ABCD is a parallelogram.
Given: ABCD is a parallelogram.
area(△DPA) = 35 cm2
area(△APC) = 15 cm2
To find: area(△APB)
Area(ΔACD)=Area(ΔDPA)+Area(ΔAPC)
=35cm2+15cm2
=50cm2
Now, ABCD is a parallelogram.
AC is the diagonal of parallelogram ABCD.
A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles.
⇒ Area(△ACD)=Area(△ACB) =50 cm2
△ACB and △APB are on same base AB and between same parallels AB and DC.
Hence,
Area(ΔAPB)=Area(ΔACB)
=50 cm2
:
D
Given : AD is median of Δ ABC
∴BD=DC
ar(ΔADP) : ar(ΔABD) = 2 : 3
To find: ar(ΔPDC) : ar(ΔABC)
Construction: Draw XY ∥ BC
Median divides the triangle into two equal areas and
Triangle ABD and ADC have equal base BD and CD and are within the same parallels XY and BC.
∴ area Δ ABD = area Δ ADC...(i)
area Δ ABD : area Δ ABC = 1 : 2 ...(ii)
area Δ ADP : area Δ ABD = 2 : 3 … (iii)
area Δ ADC = area Δ ADP + area Δ PDC
area Δ ABD = area Δ ADP + area Δ PDC
area Δ PDC
= area Δ ABD - area Δ ADP
= area Δ ABD - 23area Δ ABD
=13 area Δ ABD
∴area Δ PDC : area Δ ABD = 1 : 3...(iv)
areaΔPDCareaΔABC=13×12 ….. (from equations (i) and (iv)
area Δ PDC : area Δ ABC = 1 : 6
:
B
Given:
ABCD is a parallelogram.
Base BC = 4 cm
Height of a parallelogram = 5 cm
Area of parallelogram ABCD = Base x Height
=5 cm×4 cm
=20 cm2
A diagonal divides a parallelogram in two congruent triangles which have equal areas.
∴ Area ΔABD = Area ΔBDC
∴ Area ΔABD =12 Area of ABCD
= 10 cm2
Let R be the midpoint of the diagonal. Join P and Q to R.
P and Q are midpoints of AB and AD.
Therefore PQ is parallel to BD (Midpoint theorem)
Similarly, QR is parallel to AB and PR is parallel to AD
Therefore, APQR, DQPR and BPQR are all parallelograms
∴ Area ΔAQP = Area ΔRQP
= Area ΔBPR = Area ΔQPR ...(i)
Area ΔABD = Area ΔAQP + Area ΔRQP + Area ΔBPR + Area ΔQPR
Area ΔABD =4× Area ΔAQP = 14× Area ΔABD
∴ Area ΔAQP = 14×10
=2.5cm2