7th Grade > Biology
REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS MCQs
Total Questions : 118
| Page 2 of 12 pages
:
Each point: 1 Mark
1. After fertilization, the ovary grows into a fruit.
2.The seeds develop from the ovules.
3.The other parts of the flower fall off.
:
Explanation: 1 Mark
Examples: 2 Marks
Bulbs are stems which are very small and disc-like and function as food storage organs during dormancy.From the stem arise scaly and fleshy leaves which bear buds in their axils. Examples- onions and garlic.
:
Each point: 1 Mark
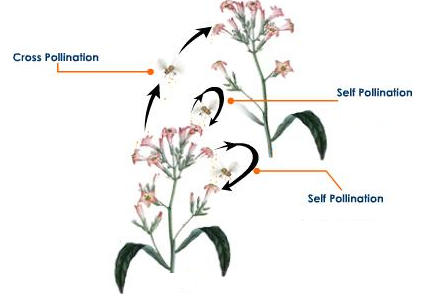
1. The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
2. The two types of pollination are self-pollination and cross-pollination.
3. If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower or when the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plantit is called self-pollination. When pollenlands on the stigma of a different flower on another plant but of the same species, it is called cross-pollination.
:
Naming all parts: 1 Mark
Explanation: 1 Mark each
Following are the different parts of a flower:
a)Sepal- The green leafy partof a flower that protects the flower during the bud stage.
b)Petal- The bright, colourful partof a flower that attract insects for pollination.
c)Stamen- The male reproductive partof a flower. Stamen has two parts - anther and filament. Anther produces the pollen grains.
d)Pistil- The female reproductive partof a flower. It has three parts - stigma, style and ovary. Ovary contains the ovule which produces the egg cells.
:
Explanation: 1 Mark
Examples: 2 Marks
The transfer of seeds away from the parent plant is called seed dispersal.
Seeds can be dispersed by bursting of the fruit/pod. Due to high pressure while bursting, the seeds are scattered far from the parent plant.
Eg: castor and balsam.
:
Naming: 1 Mark
Explanation: 2 Marks
Stamen is the male part of the flower while pistil is the female part of a flower.
Stamen consists of two parts - anther and filament. Anther produces pollen grains which contain the male gamete. Filament connects the anther to the flower.
A pistil consists of three parts - stigma, stile and ovary. Stigma receives the pollen grains while pollination. style connects the stigma to the ovary. Ovary contains ovule which houses the female gamete.
:
Dispersal: 1 Mark
Example: 1 Mark
When the seeds of plants growing near water bodies, land up in water, they get transferred from one place to another along with the water currents. This is seed dispersal by water.
Seeds that are dispersed by water develop floating ability by forming spongy, fibrous coat.
Eg: Coconut
:
Explanation: 2 Mark
Diagram: 1 Mark
Amoeba is a single-celled organism. It begins the process of reproduction by the division of its nucleus into two nuclei. This is followed by division of its body into two, each part receiving a nucleus. Finally, two amoebae are produced from one parent amoeba. This type of asexual reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is called binary fission.
:
Characteristics: 1 Mark
Example: 1 Mark
Seeds dispersed by wind have following characteristics
1. Small in size.
2. Light in weight.
3. Presence of wings. Eg., maple and drumstick.
4. Presence of hairy growths. Eg. grass and sunflower.
:
Each point: 1 Mark
1. After pollination,pollen grains from the stamen starts germinating on the stigma to give rise to pollen tubes.
2. The pollen tube growsthrough style to reach the ovulein the ovary.
3. As it reaches the ovule, the tip of the tube opens and releases the male gametes to fertilize the egg cell.
4. The fusion of the male and the female gamete results in the formation of zygote. The zygote develops into an embryo.
5. Fertilized ovary becomes a fruit and ovules develop into seeds.
















