12th Grade > Biology
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION MCQs
Total Questions : 45
| Page 5 of 5 pages
Answer: Option B. -> Bleeder’s Disease
:
B
Bleeder’s disease is known as Haemophilia. This is caused by a defective gene present on the X chromosome. The disease is characterized by the patient’s inability to clot blood when a wound is inflicted. The affected person would tend to lose blood, and eventually dies unless proper medical care is given.
:
B
Bleeder’s disease is known as Haemophilia. This is caused by a defective gene present on the X chromosome. The disease is characterized by the patient’s inability to clot blood when a wound is inflicted. The affected person would tend to lose blood, and eventually dies unless proper medical care is given.
Answer: Option B. -> Incomplete dominance
:
B
In a monohybrid cross, if the F1 hybrid exhibits a new phenotype that seems intermediate between those of parents, and yet, does not completely resemble either of them, it is a case of incomplete dominance.
Codominance is when both the traits are expressed fully, also leading to a new phenotype, but the phenotypedoes not seem like an intermediateof the two traits.
:
B
In a monohybrid cross, if the F1 hybrid exhibits a new phenotype that seems intermediate between those of parents, and yet, does not completely resemble either of them, it is a case of incomplete dominance.
Codominance is when both the traits are expressed fully, also leading to a new phenotype, but the phenotypedoes not seem like an intermediateof the two traits.
Answer: Option B. -> 14, 12 and 14
:
B
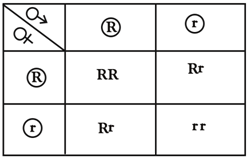
The F2 genotypic ratio of this monohybrid cross is 1:2:1. As the Punnett Square explains, out of the 4 combinations, the probability of homozygous dominant character is 14, that of heterozygous dominant character is 24=12 , and homozygous recessive character is 14 .
:
B

The F2 genotypic ratio of this monohybrid cross is 1:2:1. As the Punnett Square explains, out of the 4 combinations, the probability of homozygous dominant character is 14, that of heterozygous dominant character is 24=12 , and homozygous recessive character is 14 .
Answer: Option C. -> Grasshopper
:
C
Grasshopper is an example of XO type of sex determination in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes, whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.In human beings and in Drosophila the males have one X and one Y chromosome, whereas females have a pair of X chromosomes besides autosomes. In birds,the total number of chromosome is same in both males and females. But two different types of gametes in terms of the sex chromosomes, are produced by females, i.e., female heterogamety. The two different sex chromosomes of a female bird has been designated to be the Z and W chromosomes. In these organisms the females have one Z and one W chromosome, whereas males have a pair of Z-chromosomes besides the autosomes.
:
C
Grasshopper is an example of XO type of sex determination in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes, whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.In human beings and in Drosophila the males have one X and one Y chromosome, whereas females have a pair of X chromosomes besides autosomes. In birds,the total number of chromosome is same in both males and females. But two different types of gametes in terms of the sex chromosomes, are produced by females, i.e., female heterogamety. The two different sex chromosomes of a female bird has been designated to be the Z and W chromosomes. In these organisms the females have one Z and one W chromosome, whereas males have a pair of Z-chromosomes besides the autosomes.
Answer: Option D. -> A, B, C & D
:
D
Mendel selected the pea plant for his experiments because this plant has a short life cycle, and shows distinct contrasting characters. It possesses bisexual flowers that undergo self-fertilisation, while they could also be conveniently cross-fertilised. Also, he could obtain large number of progeny which made his experimental results more valid.
:
D
Mendel selected the pea plant for his experiments because this plant has a short life cycle, and shows distinct contrasting characters. It possesses bisexual flowers that undergo self-fertilisation, while they could also be conveniently cross-fertilised. Also, he could obtain large number of progeny which made his experimental results more valid.
















