7th Grade > Biology
NUTRITION IN PLANTS MCQs
:
Adaptations: 1 Mark each
Name of plants like cacti: 1 Mark
Any two:
1. Cacti have their leaves reduced to spines to prevent water loss.
2. By storing carbon dioxide during the night and closing their stomata in the morning, they also prevent water loss.
3. The fleshy succulent stems store water and food.
4. They have very efficient roots that go very deep into the soil to get enough water.
Plants like cacti are called xerophytes.
:
Differences: 1 Mark each
S.No.AutotrophsHeterotrophs1They produce their own food through photosynthesis.They depend on autotrophs for nutrition.2They are usually green plants that contain chloroplasts.They are non-green plants that do not contain chloroplasts.3They depend on solar energy.They do not directly depend on solar energy.Examples:All green plantsAll animals
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Opening mechanism: 1 Mark
Function: 1 Mark
Stomata are minute apertures found typically on the outer leaf skin layer, also known as the epidermis. Stomatal opening is guarded by two bean-shaped cells called
guard cells. When guard cells are turgid i.e. filled with water, the stomatal pore opens and when guard cells lose water and become flaccid, the stomatal pore closes.
Their main function is to allow diffusion of gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapour, and oxygen.
:
Definition: 1 Mark
Necessity: 1 Mark
Modes of nutrition: 1 Mark
The process by which organisms take in food and utilize it is called as nutrition.
We need nutrients because they give us energy, and energy is needed for any organism to work, grow and reproduce.
The two modes of nutrition are:
1. Autotrophic
2. Heterotrophic
:
1. Green plants prepare their own food by a process called photosynthesis.
2. Glucose is prepared by using raw materials like carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. As a byproduct oxygen is also produced.
3. The oxygen produced is released into the air which is consumed by other living beings for their survival.
Equation: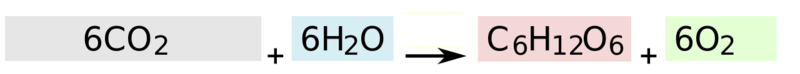
:
Explanation: 2 Marks
Examples + reason: 1.5 Mark each
Parasitic mode of nutrition is where an organism (parasite) lives on the body surface or inside the body of another type of organism (host). The parasite obtains nutrition directly from the body of the host and in turn harm the host. This type of nutrition comes under heterotrophic nutrition.
Examples
Cuscuta: It is a parasitic plant which develops special roots called haustoria. They are non-green and they derive nourishment by using their haustoria to gain access to the food and water conducting tissues of the host plant.
Mistletoe is also a parasitic plant which derives nourishment by gaining access to the vascular tissue of the host plant. Similar to that in Cuscuta.
:
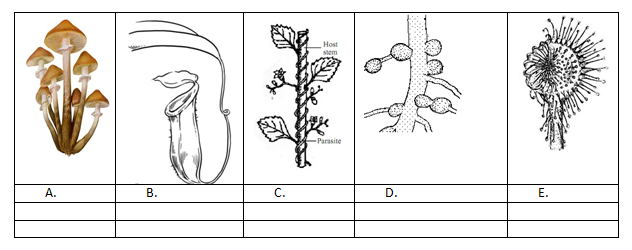
Each Name and category: 1 Mark
S.No
Name
Category
A.
Mushroom
Saprophytes
B.
Pitcher Plant
Insectivores
C.
Cuscuta
Parasites
D.
Rhizobium in root nodules
Symbionts
E.
Rosita
Insectivores