12th Grade > Biology
NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION MCQs
Total Questions : 57
| Page 5 of 6 pages
Answer: Option A. -> Nodes of Ranvier
:
A
Nodes of Ranvier, also known as myelin sheath gaps, are periodic gaps in the insulating myelin sheaths of myelinated axons where the axonal membrane is exposed to the extracellular space.
:
A
Nodes of Ranvier, also known as myelin sheath gaps, are periodic gaps in the insulating myelin sheaths of myelinated axons where the axonal membrane is exposed to the extracellular space.
Answer: Option B. -> Stroke
:
B
A stroke means that the blood supply to a part of the brain is suddenly cut off. The brain cells need a constant supply of oxygen from the blood. Soon after the blood supply is cut off, the cells in the affected area of brain become damaged or die. A stroke is sometimes called a brain attack.
:
B
A stroke means that the blood supply to a part of the brain is suddenly cut off. The brain cells need a constant supply of oxygen from the blood. Soon after the blood supply is cut off, the cells in the affected area of brain become damaged or die. A stroke is sometimes called a brain attack.
Answer: Option C. -> Faster
:
C
Conduction of impulses in myelinated neurons is faster than unmyelinated neurons. This is because myelin forcesthe action potential to jump from one node of Ranvier to the next. Na+ channels accumulate in the nodes of Ranvier In large myelinated axons, the conduction can be as much as 100 m/sec, or 220 miles per hour.The propagation speed is slower in small, unmyelinated fibers.
:
C
Conduction of impulses in myelinated neurons is faster than unmyelinated neurons. This is because myelin forcesthe action potential to jump from one node of Ranvier to the next. Na+ channels accumulate in the nodes of Ranvier In large myelinated axons, the conduction can be as much as 100 m/sec, or 220 miles per hour.The propagation speed is slower in small, unmyelinated fibers.
Answer: Option B. -> cranial and spinal nerves
:
B
Peripheral nervous system is divided into somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic nervous system consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves.There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in the brain connecting head and upper body, while 31 pairs of spinal nerves connecting the rest of the body. While some cranial nerves contain only sensory neurons, most cranial nerves and all spinal nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons (mixed type).
:
B
Peripheral nervous system is divided into somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic nervous system consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves.There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in the brain connecting head and upper body, while 31 pairs of spinal nerves connecting the rest of the body. While some cranial nerves contain only sensory neurons, most cranial nerves and all spinal nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons (mixed type).
Answer: Option A. -> Neuron
:
A
Neuron or nerve cells are the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. These have a special structure but vary greatly in size and shape. Each neuron has a cell body which encloses cytoplasm and has a nucleus. A number of processes arise from the cell body. They usually have a single axon and variable number of dendrites.
:
A
Neuron or nerve cells are the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. These have a special structure but vary greatly in size and shape. Each neuron has a cell body which encloses cytoplasm and has a nucleus. A number of processes arise from the cell body. They usually have a single axon and variable number of dendrites.
Answer: Option A. -> Sodium potassium ATPase pump
:
A
The Sodium potassium pump and the K+ leakage channels are responsible for establishing and maintaining the resting membrane potential. The K+ leakage channels allow the primary positive ion in the cell to diffuse out along its chemical gradient, and the sodium potassium pump transporting 2 positive ions inside for every 3 positive ions thrown outside also help establish the electric potential of a resting neuron. Neurons do not have Na+ leakage channels and the ligand gated sodium channels play a role in depolarisation of the neuron and voltage gated calcium channels in synaptic transmission.
:
A
The Sodium potassium pump and the K+ leakage channels are responsible for establishing and maintaining the resting membrane potential. The K+ leakage channels allow the primary positive ion in the cell to diffuse out along its chemical gradient, and the sodium potassium pump transporting 2 positive ions inside for every 3 positive ions thrown outside also help establish the electric potential of a resting neuron. Neurons do not have Na+ leakage channels and the ligand gated sodium channels play a role in depolarisation of the neuron and voltage gated calcium channels in synaptic transmission.
Answer: Option C. -> Na+ ions from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
:
C
Once an action potential has started, it moves (propagated) along an axon automatically. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane, the membrane at the site becomes freely permeable to Na+. This leads to a rapid influx of Na+ from the extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid, followed by the reversal of the polarity at that site, i.e., the outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged. The polarity of the membrane at the site is thus reversed and hence depolarised. The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane at a particular siteis called the action potential, which is in fact termed as a nerve impulse.
:
C
Once an action potential has started, it moves (propagated) along an axon automatically. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane, the membrane at the site becomes freely permeable to Na+. This leads to a rapid influx of Na+ from the extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid, followed by the reversal of the polarity at that site, i.e., the outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged. The polarity of the membrane at the site is thus reversed and hence depolarised. The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane at a particular siteis called the action potential, which is in fact termed as a nerve impulse.
Answer: Option B. -> Hypothalamus
:
B
Inhumansas in other mammals,thermoregulationis an important aspect of homeostasis. The hypothalamus lies at the base of the thalamus and contains a number of centres which regulate body temperature, thirst and appetite.
:
B
Inhumansas in other mammals,thermoregulationis an important aspect of homeostasis. The hypothalamus lies at the base of the thalamus and contains a number of centres which regulate body temperature, thirst and appetite.
Answer: Option B. -> Cochlear canal
:
B
The organ of Corti is located in the cochleaof the inner ear, between the vestibularductand the tympanicduct. It is composed of mechanosensory cells, also known as hair cells. Itproduces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations.
:
B
The organ of Corti is located in the cochleaof the inner ear, between the vestibularductand the tympanicduct. It is composed of mechanosensory cells, also known as hair cells. Itproduces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations.
Answer: Option A. -> Depolarisation
:
A
The pre synaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, these neurotransmitters then bind to the ligand gated channels, thus activating them. The ligand gated channels open up and allow the influx of sodium, which depolarizes the cell. This depolarization activates nearby voltage gated ion channels, which open up and let in even more sodium. Voltage gated sodium channels open up one region at a time, the previous region providing enough depolarization to activate the next regions voltage gated channels. This effectively allows the action potential to propagate through the cell.
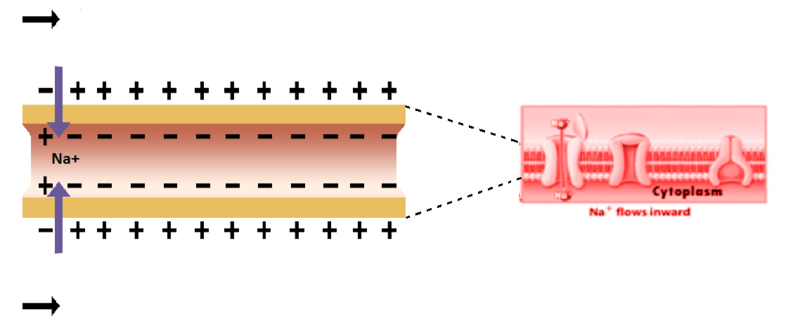
:
A
The pre synaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, these neurotransmitters then bind to the ligand gated channels, thus activating them. The ligand gated channels open up and allow the influx of sodium, which depolarizes the cell. This depolarization activates nearby voltage gated ion channels, which open up and let in even more sodium. Voltage gated sodium channels open up one region at a time, the previous region providing enough depolarization to activate the next regions voltage gated channels. This effectively allows the action potential to propagate through the cell.

















