11th And 12th > Biology
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MCQs
:
D
Hip bone is called as the innominate bone. It is made up of 3 fused bones: Ilium, ischium and pubis. It is also referred to as ‘Pelvic bone’ or ‘Coxal bone’.
:
C
The best example of a saddle joint in the body is the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb that is formed between the trapezium bone and the first metacarpal.
Interphalangeal joints are the hinge joints located between the fingers and the toes.
An example of a pivot joint is the joint of the first and second vertebrae of the neck that allows the head to move back and forth.
Ball and socket are found in the hip, where the rounded head of the femur (ball) rests in the cup-like acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis.
:
A
Femur, or thighbone, is the largest bone in your body.
The stapes is the third bone of the three ossicles in the middle ear.
The humerus is a long bone in the arm or forelimb that runs from the shoulder to the elbow.
The patella also known as the kneecap or kneepan, is a thick, circular-triangular bone.
:
B
A hinge joint is a common class of synovial joint that includes the ankle, elbow, and knee joints. Hinge joints are formed between two or more bones where the bones can only move along one axis to flex or extend.
An example of a pivot joint in the human skeletal system is the rotation of the atlas around the axis.
The shoulder joint is formed where the humerus (upper arm bone) fits into the scapula (shoulder blade), like a ball and socket.
:
A and C
Muscle hypertrophy involves an increase in the size of skeletal muscle through a growth in the size of its component cells. Main reason for muscle hypertrophy is physical activity.
Muscle atrophy is when muscles waste away. The main reason for muscle wasting is a lack of physical activity. This can happen when a disease or injury makes it difficult or impossible for you to move an arm or leg.
:
A
Syndesmology is the study of ligamnets. Ligaments are made of tough connective tissues and connect bone to bone.
Myology is the medical specialty concerned with the study of the structure, function, and diseases and disorders of muscles.
:
A
Phosphagen is a high-energy phosphoric ester that serves as a reservoir of phosphate-bond energy, as phosphocreatine in vertebrates.
:
A
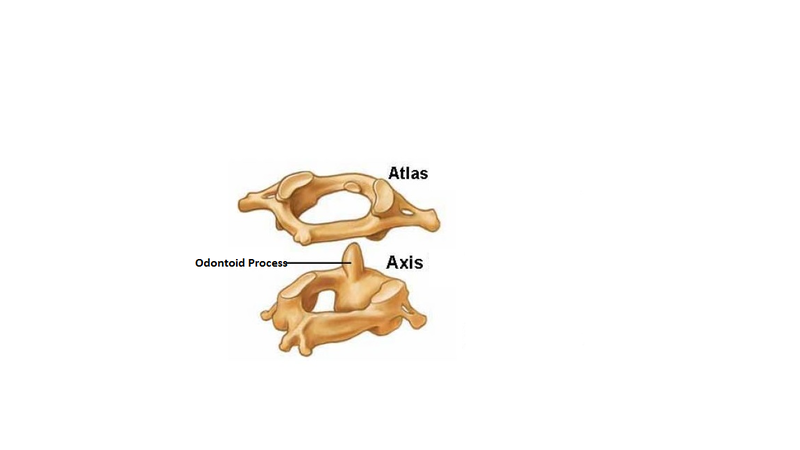
The Atlas and Axis Vertebrae (diagram below), the first and second cervical vertebrae, are the most distinctive in terms of size and morphology. The Atlas bone (C1) lies between the cranium (connecting with the condyles of the occipital bone) and the Axis vertebrae (C2). The atlas lacks a ‘vertebral body, a spinous process and has no articular disks either superior or inferior to it.The Axis bone also lacks a typical vertebral body. It’s most distinctive feature is the odontoid peg, as seen in the diagram below.
:
A
The myosin head contains binding sites ATP binding site and actin binding site. Actin molecule has 2 other proteins tropomyosin and troponin are two other proteins found in small quantities in muscle. They help regulate muscle contraction.
Match the following:
Column - IColumn - IIi. Ethmoid a. are situated at the sides and base of the skullii. Sphenoidb. contains the large opening of the foramen magnumiii. Frontalc. situated on the sides and the roof of the skulliv. Parietald. forms the forehead.v. Temporale. is found in the nasal septumvi.Occipitalf. houses the optic canal
:
A
The ethmoid bone is found in the nasal septum
The sphenoid bone houses the optic canal
The frontal bone forms the forehead.
The parietal bone are situated on the sides and the roof of the skull
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull
The occipital bone contains the large opening of the foramen magnum
















