General Knowledge > Polity
INDIAN CONSTITUTION AT WORK MCQs
Constitutional Framework, Making Of Indian Constitution And Its Development
Total Questions : 371
| Page 6 of 38 pages
Answer: Option B. -> 1, 3 and 4 only
:
B
Explanation:
Statement 1, 3 and 4 are correct:
Federal Features of the Indian Union:
Statement 2 is Incorrect:
Unitary Features of the Indian Union
Hence statement 2 is not correct
:
B
Explanation:
Statement 1, 3 and 4 are correct:
Federal Features of the Indian Union:
- Governments at two levels – centre and states
- Division of powers between the centre and states – there are three lists given in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution which gives the subjects each level has jurisdiction in:Union List,State List and Concurrent List
- Supremacy of the constitution
- Independent judiciary – the constitution provides for an independent and integrated judiciary. The lower and district courts are at the bottom levels, the high courts are at the state levels and at the topmost position is the Supreme Court of India. All courts are subordinate to the Supreme Court.
Statement 2 is Incorrect:
Unitary Features of the Indian Union
- The flexibility of the constitution – the constitution is a blend of flexibility and rigidity. Certain provisions of the constitution can be easily amended. In case the amendments seek to change aspects of federalism in India, the provision to bring about such amendments is not easy.
Hence statement 2 is not correct
- More power vests with the Centre – the constitution guarantees more powers with the Union List. On the Concurrent List, the parliament can make laws that can override the laws made by a state legislature on some matters. The parliament can also make laws regarding certain subjects in the State List.
- Unequal representation of states in the Rajya Sabha
Answer: Option C. -> Kesavananda Bharati case
:
C
Explanation:
One thing that has had a long lasting effect on the evolution of the Indian Constitution is the theory of the basic structure of the Constitution. The Judiciary advanced this theory in the famous case of Kesavananda Bharati. This ruling has contributed to the evolution of the Constitution in the following ways:
:
C
Explanation:
One thing that has had a long lasting effect on the evolution of the Indian Constitution is the theory of the basic structure of the Constitution. The Judiciary advanced this theory in the famous case of Kesavananda Bharati. This ruling has contributed to the evolution of the Constitution in the following ways:
- It has set specific limits to Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution. It says that no amendment can violate the basic structure of the Constitution;
- It allows Parliament to amend any and all parts of theConstitution (within this limitation); and
- It places the Judiciary as the final authority in deciding if an amendment violates basic structure and what constitutes the basic structure.
Answer: Option C. -> Proved misbehaviour or incapacity
:
C
Explanation:
The removal of judges of the Supreme Court and the High Courts is difficult. A judge of the Supreme Court or High Court can be removed only on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity. A motion containing the charges against the judge must be approved by a special majority in both Houses of theParliament.
:
C
Explanation:
The removal of judges of the Supreme Court and the High Courts is difficult. A judge of the Supreme Court or High Court can be removed only on the ground of proved misbehaviour or incapacity. A motion containing the charges against the judge must be approved by a special majority in both Houses of theParliament.
Answer: Option D. -> 1, 2, 3 and 4
:
D
Explanation:
Twenty-nine subjects, which were earlier in the State list of subjects, are identified and listed in the EleventhSchedule of the Constitution. These subjects are to be transferred to the Panchayati Raj institutions. These Subjects were mostly linked to development and welfare functions at the local level. The actual transfer of these functions depends upon the State legislation. Each State Decides how many of these twenty-nine subjects would be transferred to the local bodies.
List of subjects in 11th Schedule:
:
D
Explanation:
Twenty-nine subjects, which were earlier in the State list of subjects, are identified and listed in the EleventhSchedule of the Constitution. These subjects are to be transferred to the Panchayati Raj institutions. These Subjects were mostly linked to development and welfare functions at the local level. The actual transfer of these functions depends upon the State legislation. Each State Decides how many of these twenty-nine subjects would be transferred to the local bodies.
List of subjects in 11th Schedule:
- Agriculture, including agricultural extension.
- Land improvement, implementation of land reforms, landconsolidation and soil conservation.
- Minor irrigation, water management and watershed development.
- Animal husbandry, dairying and poultry.
- Fisheries.
- Social forestry and farm forestry.
- Minor forest produce.
- Small scale industries, including food processing industries.
- Khadi, village and cottage industries.
- Rural housing.
- Drinking water.
- Fuel and fodder.
- Roads, culverts, bridges, ferries, waterways and other means ofcommunication.
- Rural electrification, including distribution of electricity.
- Non-conventional energy sources.
- Poverty alleviation programme.
- Education, including primary and secondary schools.
- Technical training and vocational education.
- Adult and non-formal education.
- Libraries.
- Cultural activities
- Markets and fairs.
- Health and sanitation, including hospitals, primary health centresand dispensaries.
- Family welfare.
- Women and child development.
- Social welfare, including welfare of the handicapped and mentallyretarded.
- Welfare of the weaker sections, and in particular, of the ScheduledCastes and the Scheduled Tribes.
- Public distribution system.
- Maintenance of community assets.
Question 55. Q. With reference to the President's rule, consider the following statements:
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
- The Governor gets power to recommend dismissal or suspension of the State Government.
- It can be extended upto 1 year in a State.
- The constitutional validity of the decision to impose President's rule can be judicially reviewed.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
Answer: Option A. -> 1 and 3 only
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: One of the most controversial articles in the Constitution is Article 356, which provides for President’s rule in any State. This provision is to be applied, when ‘a situation has arisen in which the Government of the State cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution.’ It results in the takeover of the State government by the Union government. The Governor has the power to recommend the dismissal of the State government and suspension or dissolution of the State assembly.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: The President’s proclamation has to be ratified by Parliament. President’s rule can be extended till three years.
Statement 3 is correct: In some cases, State governments were dismissed even when they had a majority in the legislature, as had happened in Kerala in 1959 or without testing their majority, as happened in several other States after 1967.Some cases went to the Supreme Court and the Court has ruled that the constitutional validity of the decision to impose President’s rule can be examined by the judiciary.
:
A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: One of the most controversial articles in the Constitution is Article 356, which provides for President’s rule in any State. This provision is to be applied, when ‘a situation has arisen in which the Government of the State cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution.’ It results in the takeover of the State government by the Union government. The Governor has the power to recommend the dismissal of the State government and suspension or dissolution of the State assembly.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: The President’s proclamation has to be ratified by Parliament. President’s rule can be extended till three years.
Statement 3 is correct: In some cases, State governments were dismissed even when they had a majority in the legislature, as had happened in Kerala in 1959 or without testing their majority, as happened in several other States after 1967.Some cases went to the Supreme Court and the Court has ruled that the constitutional validity of the decision to impose President’s rule can be examined by the judiciary.
Answer: Option D. -> Supreme Court
:
D
Explanation:
The Supreme Court of India is the country’s highest judicial court. It is the final court of appeal in the country. It upholds the rule of law and also guarantees and protects citizens’ rights and liberties as given in the Constitution. Therefore, the Supreme Court is also known as the Guardian of the Constitution.
:
D
Explanation:
The Supreme Court of India is the country’s highest judicial court. It is the final court of appeal in the country. It upholds the rule of law and also guarantees and protects citizens’ rights and liberties as given in the Constitution. Therefore, the Supreme Court is also known as the Guardian of the Constitution.
Question 57. Q. With reference to the Right to Freedom of Religion in Constitution , consider the following Statements:
Which of the above given statements is/are incorrect?
- It seeks to nurture the State's philosophy of Secularism.
- States can restrict the Right citing threat to public order,Security of State or sovereignty of India.
- The government can interfere in religious matters for rooting out certain social evils.
Which of the above given statements is/are incorrect?
Answer: Option B. -> 2 only
:
B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: According to our Constitution, everyone enjoys the right to follow the religion of his or her choice. This freedom is considered as a hallmark of democracy.Being a country which is home to several religions, it is necessary that the government must extend equal treatment to different religions. Negatively, it means that the government will not favour any particular religion. India does not have any official religion.The institutions run by the state will not preach any religion or give religious education nor will they favour persons of any religion. The objective of these provisions is to sustain and nurture the principle of secularism.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: Freedom of religion is subject to certain limitations. The government can impose restrictions on the practice of freedom of religion in order to protect:
This means that the freedom of religion is not an unlimited right.
Statement 3 is correct: As stated above, the Government can impose restrictions on the practice of freedom of religion in order to protect public order,morality and health. This means that the freedom of religion is not an unlimited right. The government can interfere in religious matters for rooting out certain social evils. For example in the past, thegovernment has taken steps banning practices like sati, bigamy or human sacrifice.
:
B
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: According to our Constitution, everyone enjoys the right to follow the religion of his or her choice. This freedom is considered as a hallmark of democracy.Being a country which is home to several religions, it is necessary that the government must extend equal treatment to different religions. Negatively, it means that the government will not favour any particular religion. India does not have any official religion.The institutions run by the state will not preach any religion or give religious education nor will they favour persons of any religion. The objective of these provisions is to sustain and nurture the principle of secularism.
Statement 2 is Incorrect: Freedom of religion is subject to certain limitations. The government can impose restrictions on the practice of freedom of religion in order to protect:
- Public order
- Morality and
- Health
This means that the freedom of religion is not an unlimited right.
Statement 3 is correct: As stated above, the Government can impose restrictions on the practice of freedom of religion in order to protect public order,morality and health. This means that the freedom of religion is not an unlimited right. The government can interfere in religious matters for rooting out certain social evils. For example in the past, thegovernment has taken steps banning practices like sati, bigamy or human sacrifice.
Answer: Option A. -> 1, 2 and 4 only
:
A
Explanation:
India follows First Past The Post system of Elections to the Lok Sabha and Legislative Assembly of the State. While, In the system of Proportional Representation (PR) a party gets the same proportion of seats as it’s proportion of votes. In India, we have adopted a PR system on a limited scale for indirect elections. The Constitution prescribes PR system for the election of President, Vice President, and for the election to the Rajya Sabha and Vidhan Parishads(Legislative Council).
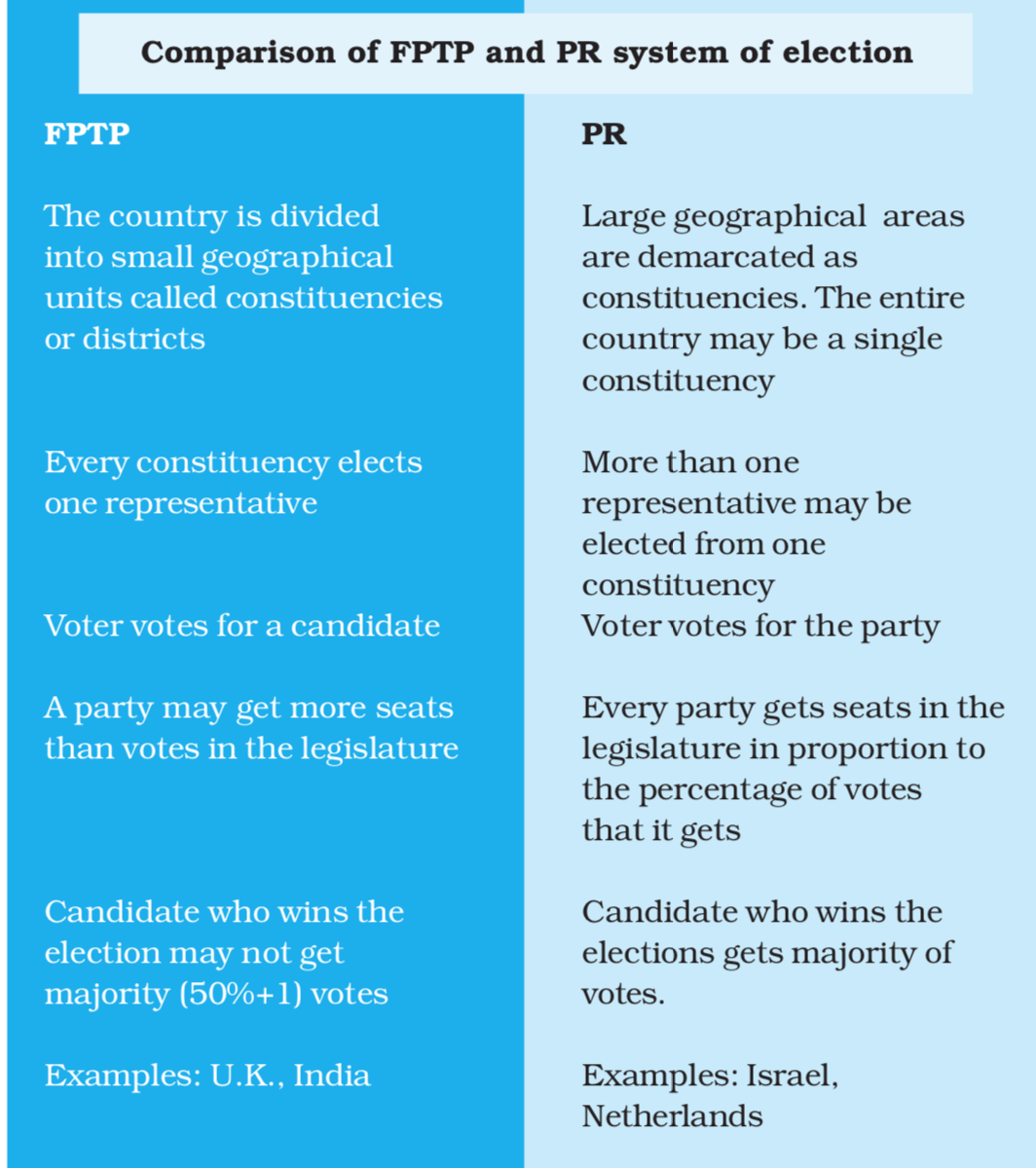
:
A
Explanation:
India follows First Past The Post system of Elections to the Lok Sabha and Legislative Assembly of the State. While, In the system of Proportional Representation (PR) a party gets the same proportion of seats as it’s proportion of votes. In India, we have adopted a PR system on a limited scale for indirect elections. The Constitution prescribes PR system for the election of President, Vice President, and for the election to the Rajya Sabha and Vidhan Parishads(Legislative Council).

Answer: Option D. -> 1, 2, and 3 only
:
D
Explanation:
The Constitution has some special provisions for some States given their peculiar social and historical circumstances. Most of the special provision pertain to the north eastern States (Assam, Nagaland,Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, etc.) largely due to a sizeableindigenous tribal population with a distinct history and culture, which they wish to retain (Art 371). However, these provisions have not been able to stem alienation and the insurgency in parts of the region. Special provisions also exist for hilly States like Himachal Pradesh and some other States like Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra Sikkim and Telangana.
:
D
Explanation:
The Constitution has some special provisions for some States given their peculiar social and historical circumstances. Most of the special provision pertain to the north eastern States (Assam, Nagaland,Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, etc.) largely due to a sizeableindigenous tribal population with a distinct history and culture, which they wish to retain (Art 371). However, these provisions have not been able to stem alienation and the insurgency in parts of the region. Special provisions also exist for hilly States like Himachal Pradesh and some other States like Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra Sikkim and Telangana.
Answer: Option A. -> Rajya Sabha
:
A
Explanation:
There may be occasions when the situation may demand that the central government needs to legislate on matters from the State list. This is possible if the move is ratified by the Rajya Sabha. The Constitution clearly states that executive powers of the centre are superior to the executive powers of the States.
:
A
Explanation:
There may be occasions when the situation may demand that the central government needs to legislate on matters from the State list. This is possible if the move is ratified by the Rajya Sabha. The Constitution clearly states that executive powers of the centre are superior to the executive powers of the States.
















