12th Grade > Biology
GROWTH & REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS MCQs
Plant Growth And Development, Reproduction In Animals, Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
Total Questions : 111
| Page 5 of 12 pages
Answer: Option A. -> Self pollinated
:
A
When some physical barrier is present between male and female reproductive parts of a flower which prevents self-pollination, it is called herkogamy. Some flowers, do not expose their sex organs. Such flowers are called cleistogamous and the phenomenon as cleistogamy. Here self-pollination takes place. Dichogamy refers to maturation of male and female sex organs at different times.
:
A
When some physical barrier is present between male and female reproductive parts of a flower which prevents self-pollination, it is called herkogamy. Some flowers, do not expose their sex organs. Such flowers are called cleistogamous and the phenomenon as cleistogamy. Here self-pollination takes place. Dichogamy refers to maturation of male and female sex organs at different times.
Answer: Option C. -> Geitonogamy
:
C
Geitonogamy involves transfer of the pollen from one flower of a plant to the stigma of another flower of the same plant. As the pollen has to move from one flower to another flower, it requires a pollinating agent. Yet it is genetically similar to autogamy, as both the flowers of the plant, share the same genotype of the plant.
:
C
Geitonogamy involves transfer of the pollen from one flower of a plant to the stigma of another flower of the same plant. As the pollen has to move from one flower to another flower, it requires a pollinating agent. Yet it is genetically similar to autogamy, as both the flowers of the plant, share the same genotype of the plant.
Answer: Option A. -> Cleistogamy
:
A
Herkogamy is the adaptation which facilitates cross pollination where the anthers and the stigma are placed at different positions in such a way that the anthers cannot reach the stigma of the flower. Dichogamy refers to maturation of male and female sex organs at different times.Some flowers, do not expose their sex organs. Such flowers are called cleistogamous and the phenomenon is called cleistogamy and here self-pollination takes place.
:
A
Herkogamy is the adaptation which facilitates cross pollination where the anthers and the stigma are placed at different positions in such a way that the anthers cannot reach the stigma of the flower. Dichogamy refers to maturation of male and female sex organs at different times.Some flowers, do not expose their sex organs. Such flowers are called cleistogamous and the phenomenon is called cleistogamy and here self-pollination takes place.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Auxin directed growth of the hypocotyl towards light to form the shoot and gibberellin directed growth of the epicotyl causing the radicle to move downwards towards the gravity are called growth movements in plants.
:
A
Auxin directed growth of the hypocotyl towards light to form the shoot and gibberellin directed growth of the epicotyl causing the radicle to move downwards towards the gravity are called growth movements in plants.
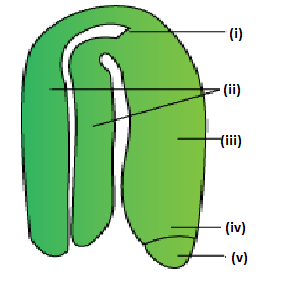
Answer: Option A. -> (i)-Plumule, (ii)-Cotyledons, (iii)-Hypocotyl, (iv)-Radicle, (v)-Root cap
:
A
A dicot embryo consists of two cotyledons and an embryonic axis. The region above the cotyledons is called epicotyl which terminates at the plumule. Hypocotyl is the region below the cotyledons and terminates at the radicle. The tip of the radicle is covered with a root cap.
:
A
A dicot embryo consists of two cotyledons and an embryonic axis. The region above the cotyledons is called epicotyl which terminates at the plumule. Hypocotyl is the region below the cotyledons and terminates at the radicle. The tip of the radicle is covered with a root cap.
Answer: Option C. -> geitonogamy
:
C
Geitonogamy is a type of pollination in which pollen grains of one flower are transformed to stigma of another flower belonging to either the same plant or genetically similar plant.
:
C
Geitonogamy is a type of pollination in which pollen grains of one flower are transformed to stigma of another flower belonging to either the same plant or genetically similar plant.
Answer: Option B. -> Sporopollenin
:
B
Exine of pollen grains is made up of a stable polymer termed sporopollenin.
:
B
Exine of pollen grains is made up of a stable polymer termed sporopollenin.
Answer: Option C. -> Xenogamy
:
C
In xenogamy, male and female gametes are derived from different parents. Hence, it results in cross fertilisation. Cross pollination enables the fusion of characters of two genetically distinct plants of the same species therefore it introduces genetic recombination and variations in plants. Autogamy and geitonogamy do not exhibit cross fertilisation.
:
C
In xenogamy, male and female gametes are derived from different parents. Hence, it results in cross fertilisation. Cross pollination enables the fusion of characters of two genetically distinct plants of the same species therefore it introduces genetic recombination and variations in plants. Autogamy and geitonogamy do not exhibit cross fertilisation.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
In a typicalflower, the reproductive parts or essential organs, i.e., the androecium and the gynoecium are protected by the non-essential or non-reproductive parts, i.e., the calyx and corolla. It is important to protect the reproductive structures from external environmental conditions as they are involved in gamete formation and other processes in sexual reproduction.
:
A
In a typicalflower, the reproductive parts or essential organs, i.e., the androecium and the gynoecium are protected by the non-essential or non-reproductive parts, i.e., the calyx and corolla. It is important to protect the reproductive structures from external environmental conditions as they are involved in gamete formation and other processes in sexual reproduction.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
In monocot embryo, the lower part of embryonal axis has the radicle and root cap enclosed in an undifferentiated sheath called coleorhiza. The shoot apex or plumule is enclosed in a hollow foliar structure called coleoptile.
:
A
In monocot embryo, the lower part of embryonal axis has the radicle and root cap enclosed in an undifferentiated sheath called coleorhiza. The shoot apex or plumule is enclosed in a hollow foliar structure called coleoptile.