12th Grade > Physics
VECTORS MCQs
Total Questions : 26
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option D. -> zero magnitude and no specific direction
:
D
If vectors A and B are equal, i.e. A = B, then their difference (A – B) is defined as a null vector. It has a zeromagnitude and no specific direction.
Hence the correct choice is (d).
:
D
If vectors A and B are equal, i.e. A = B, then their difference (A – B) is defined as a null vector. It has a zeromagnitude and no specific direction.
Hence the correct choice is (d).
Answer: Option B. -> (C) & (B)
:
B
For 2 vectors to be equal their magnitude and direction has to be same.
Option A: says vector A and E surely they are pointed in the same direction but if we see magnitude wise the vector A has a magnitude of 2 units or it is only 2 boxes long, while vector E has magnitude of 3 units, so vector A & E can't be same.
Option B: says vector C & B, they are surely pointing in the same direction are their magnitudes also same.
Vector C has a unit of 2√2units and so does vector B.
So option B is correct.
Here we conclude that we can translate a vector anywhere on the 3D space, it wouldn't change it as long as I keep the magnitude of the vector same and keep it pointing in the same direction.
:
B
For 2 vectors to be equal their magnitude and direction has to be same.
Option A: says vector A and E surely they are pointed in the same direction but if we see magnitude wise the vector A has a magnitude of 2 units or it is only 2 boxes long, while vector E has magnitude of 3 units, so vector A & E can't be same.
Option B: says vector C & B, they are surely pointing in the same direction are their magnitudes also same.
Vector C has a unit of 2√2units and so does vector B.
So option B is correct.
Here we conclude that we can translate a vector anywhere on the 3D space, it wouldn't change it as long as I keep the magnitude of the vector same and keep it pointing in the same direction.
Answer: Option A. -> A||B = 3√3;A⊥B=3
:
A
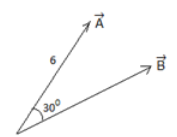
So, we need to resolve the vector A along the direction of B and perpendicular to it.
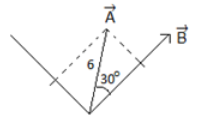
Angle between A & B is 30∘
So component along the direction B is using trigonometric ration
6cos30∘ = compound of A along B = 3√3 component of A perpendicular to B = 6 sin30∘ = 3
:
A

So, we need to resolve the vector A along the direction of B and perpendicular to it.

Angle between A & B is 30∘
So component along the direction B is using trigonometric ration
6cos30∘ = compound of A along B = 3√3 component of A perpendicular to B = 6 sin30∘ = 3
Answer: Option C. -> The magnitude of the vector is doubled and its direction is reversed
:
C
Multiplication of a vector by a real negative number – n makes its magnitude n times and also reverses thedirection of the vector.
Hence the correct choice is (c).
:
C
Multiplication of a vector by a real negative number – n makes its magnitude n times and also reverses thedirection of the vector.
Hence the correct choice is (c).
Answer: Option C. -> 120∘
:
C
R2=A2+B2+2ABcosθ. It is given that R=A=B. Putting these values we have A2=A2+A2+2A2cosθ
or cosθ=−12 which gives θ=120∘
Hence the correct choice is (c)
:
C
R2=A2+B2+2ABcosθ. It is given that R=A=B. Putting these values we have A2=A2+A2+2A2cosθ
or cosθ=−12 which gives θ=120∘
Hence the correct choice is (c)
Answer: Option C. -> →A×→B=→C
:
C
As explained above, choices (a) and (b) are not possible. Since vector C is perpendicular to both vectors A and B,choice (c) is possible. Choice (d) is not possible because vector B is not perpendicular to vector A.
:
C
As explained above, choices (a) and (b) are not possible. Since vector C is perpendicular to both vectors A and B,choice (c) is possible. Choice (d) is not possible because vector B is not perpendicular to vector A.
Answer: Option C. -> A||B = -5; A⊥B=5√3
:
C
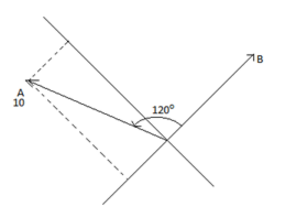
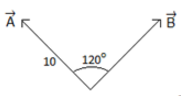
So component of A along direction of B is Acos120∘=−Asin30=−5
[∵cos(90+θ)=−sinθ]
Here we can see if just measure the shadow you will get a cos60=a2=5
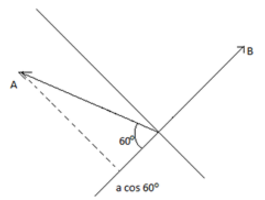
But since this 5 is in the opposite direction of vector B so we say that the component of A along the
direction B is -5.
Now component in the perpendicular direction of B is
Asin(120∘)=Acos30=5√3
[∵sin(90+θ)=cosθ]
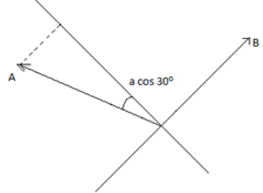
Just the shadow measurement is a cos 30∘ and it's in the perpendicular direction, so no need to
change sign.
So component along the direction is always acosθ and in perpendicular direction is asinθ. This will take care of sign so don't worry.
:
C

So component of A along direction of B is Acos120∘=−Asin30=−5
[∵cos(90+θ)=−sinθ]
Here we can see if just measure the shadow you will get a cos60=a2=5

But since this 5 is in the opposite direction of vector B so we say that the component of A along the
direction B is -5.
Now component in the perpendicular direction of B is
Asin(120∘)=Acos30=5√3
[∵sin(90+θ)=cosθ]

Just the shadow measurement is a cos 30∘ and it's in the perpendicular direction, so no need to
change sign.
So component along the direction is always acosθ and in perpendicular direction is asinθ. This will take care of sign so don't worry.
Answer: Option B. -> A + B = - (B + A)
:
B
Vector addition is commutative, i.e. A + B = B + A. Vector addition is also associative,
i.e. (A + B) + C = A + (B + C) = (A + C) + B.
Hence choice (b) is false.
:
B
Vector addition is commutative, i.e. A + B = B + A. Vector addition is also associative,
i.e. (A + B) + C = A + (B + C) = (A + C) + B.
Hence choice (b) is false.