9th Grade > Mathematics
TRIANGLES MCQs
Total Questions : 56
| Page 1 of 6 pages
:
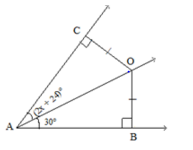
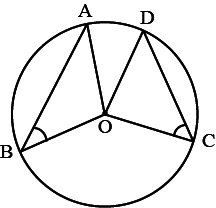
InΔAOCandΔAOB,OC=OB(Given)∠OBC=∠OCA(Both angles are right angles)AndAOis common side.Hence,ΔAOC≅ΔAOB(RHS congruence)∴∠CAO=∠BAO(CPCT)⇒2x+24=30⇒x=3⇒x−3=0
Answer: Option C. -> ∠NVY+ 2∠VYN = 180∘
:
C
Given, in △NVY, NV = VY.

Then, ∠VYN=∠YNV.
[angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal]
Using angle sum property of a triangle, we get:
∠NVY+∠VYN+∠YNV=180∘
So, ∠NVY+2∠VYN=180∘.
It is also given that VY≠YN. Hence the options ∠NVY=∠VYN and∠NVY=∠YNV are not correct.
:
C
Given, in △NVY, NV = VY.

Then, ∠VYN=∠YNV.
[angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal]
Using angle sum property of a triangle, we get:
∠NVY+∠VYN+∠YNV=180∘
So, ∠NVY+2∠VYN=180∘.
It is also given that VY≠YN. Hence the options ∠NVY=∠VYN and∠NVY=∠YNV are not correct.
Answer: Option C. -> Statement 1 is correct but 2 is false
:
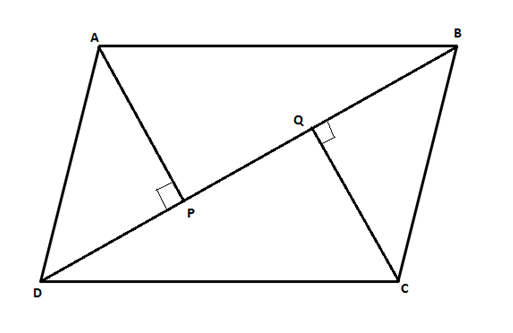
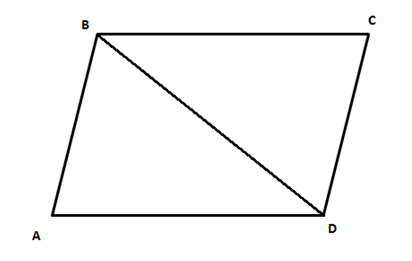
C
InΔAPBandΔCQD,AB=CD(opposite sides of a parallelogram).∠ABP=∠CDQ(alternate angles).∠APB=∠CQD(both are right angles).∴ΔAPB≅ΔCQD
(using AAS criterion)
Hence, statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is false
:
C
InΔAPBandΔCQD,AB=CD(opposite sides of a parallelogram).∠ABP=∠CDQ(alternate angles).∠APB=∠CQD(both are right angles).∴ΔAPB≅ΔCQD
(using AAS criterion)
Hence, statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is false
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
The given statement is false. Even when two triangles have all angles same, they can still have sides of different lengths. However, the ratio of lengths of corresponding sides will be same. But in this case, they will be called 'similar' triangles, not congruent.
Congruent triangles are a special case of similar triangles.
For example, in the image below, both triangles are equilateral and have all angles equal but they are not congruent.
:
B
The given statement is false. Even when two triangles have all angles same, they can still have sides of different lengths. However, the ratio of lengths of corresponding sides will be same. But in this case, they will be called 'similar' triangles, not congruent.
Congruent triangles are a special case of similar triangles.
For example, in the image below, both triangles are equilateral and have all angles equal but they are not congruent.

Answer: Option A. -> True
:
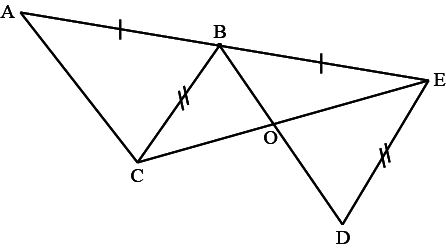
A
Since ΔABC≅ΔBED,∠DBE=∠CAB=25∘(CPCT)And,∠DEB=∠CBA(CPCT)Now,∠BDE+∠DBE+∠BED=180∘⇒∠BDE+25∘+115∘=180∘⇒∠BDE=40∘Also,∠CBA+∠CBD+∠DBE=180∘(Linear set of angles)⇒∠CBA+25∘+115∘=180∘⇒∠CBA=40∘⇒∠BDE=∠CBDand they are alternate angles, soBC||ED.
:
A
Since ΔABC≅ΔBED,∠DBE=∠CAB=25∘(CPCT)And,∠DEB=∠CBA(CPCT)Now,∠BDE+∠DBE+∠BED=180∘⇒∠BDE+25∘+115∘=180∘⇒∠BDE=40∘Also,∠CBA+∠CBD+∠DBE=180∘(Linear set of angles)⇒∠CBA+25∘+115∘=180∘⇒∠CBA=40∘⇒∠BDE=∠CBDand they are alternate angles, soBC||ED.
Answer: Option C. -> 16∘
:
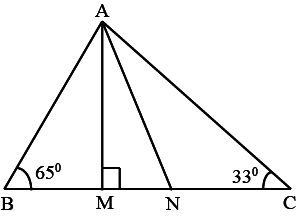
C
In given figure,
∠BAC+∠ABC+∠ACB=180∘(Angles of same triangle)⇒∠BAC+65∘+33∘=180∘⇒∠BAC=82∘
∠CAN=∠BAC2=41∘(Given that AN is an angle bisector).Now,∠CAN+∠ANC+∠ACN=180∘(Angles of same triangle)⇒41∘+∠ANC+33∘=180∘⇒∠ANC=106∘
∠ANC+∠ANM=180∘(Linear pair)⇒106∘+∠ANM=180∘⇒∠ANM=74∘
∠ANM+∠AMN+∠MAN=180∘⇒74∘+90∘+∠MAN=180∘⇒∠MAN=16∘.
:
C
In given figure,
∠BAC+∠ABC+∠ACB=180∘(Angles of same triangle)⇒∠BAC+65∘+33∘=180∘⇒∠BAC=82∘
∠CAN=∠BAC2=41∘(Given that AN is an angle bisector).Now,∠CAN+∠ANC+∠ACN=180∘(Angles of same triangle)⇒41∘+∠ANC+33∘=180∘⇒∠ANC=106∘
∠ANC+∠ANM=180∘(Linear pair)⇒106∘+∠ANM=180∘⇒∠ANM=74∘
∠ANM+∠AMN+∠MAN=180∘⇒74∘+90∘+∠MAN=180∘⇒∠MAN=16∘.
Answer: Option B. -> Isosceles but not right angled
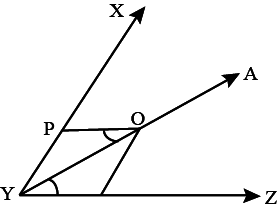
:
B
∠ POY = ∠ OYZ(alternate angles)
∠Y is bisected, so∠ POY =∠ PYO
Hence, PY = PO
So,△YPO is isosceles
Also, it is given that∠XYZ is acute, so any angle which is half of it (bisected by OY) is less than 45∘.
or∠ PYO +∠OYZ < 90∘
Hence, the third angle of the△YPO i.e.∠ YPO will be obtuse to satisfy angle-sum property of a triangle.
Hence,△YPO is isosceles but not rightangled.
:
B
∠ POY = ∠ OYZ(alternate angles)
∠Y is bisected, so∠ POY =∠ PYO
Hence, PY = PO
So,△YPO is isosceles
Also, it is given that∠XYZ is acute, so any angle which is half of it (bisected by OY) is less than 45∘.
or∠ PYO +∠OYZ < 90∘
Hence, the third angle of the△YPO i.e.∠ YPO will be obtuse to satisfy angle-sum property of a triangle.
Hence,△YPO is isosceles but not rightangled.