12th Grade > Chemistry
STEREOCHEMISTRY MCQs
Total Questions : 11
| Page 1 of 2 pages
:
When we have a 50:50 mixture of a pair of enantiomers, it is called a racemic mixture or recemate. A racemic mixture does not show any optical activity although it is made up of two enantiomers which are optically active.
If we have a mixture in any other ratio, then the resultant sample is always optically active. In this scenario it is said that there is an enantiomeric excess.
Enantiomeric excess is the percentage or ratio by which one enantiomer is greater in quantity than the other enantiomer present in the same sample.
Since there is no difference between the quantities of the two enantiomers present in a racemic solution, the enantiomeric excess is '0'.
Answer: Option B. -> Nicol
:
B
The type of prism used in Biot’s experiment is called a Nicol prism. This is a special material which is able to polarise light passing through it.
You know that light normally vibrates in all possible planes when coming out of a source. But when passed through special devices like this Nicol prism it comes out vibrating in just one direction. This allows us to test for optical activity.
:
B
The type of prism used in Biot’s experiment is called a Nicol prism. This is a special material which is able to polarise light passing through it.
You know that light normally vibrates in all possible planes when coming out of a source. But when passed through special devices like this Nicol prism it comes out vibrating in just one direction. This allows us to test for optical activity.
:
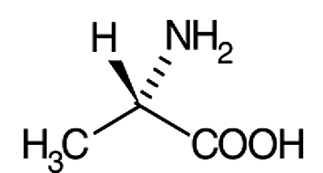
First step while writing the R - S nomenclature is to identify the atoms and their atomic number.
Here we have - H - 1
F - 9
Cl - 17
Br - 35
Now, we need to place the order of priority accordingly. So, the order of priority would be
Br > Cl > F > H
Now, we need to place the atom with the lowest priority at the back, i.e., facing away from you when you look at the carbon. Let’s do that now.
Here we have H above the plane and F below the plane.
If I need H to be away, I need to look at this molecule in this way.

I hope you can visualize this.
Let’s draw this like this and number it.
Another way is to convert this to Fischer projection. You will learn that soon.
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
Looks tricky doesn’t it?
Let us run through the definition of a meso compound. It has to have at least 2 tetrahedral stereogenic centers. Further, it has to be achiral due to a plane of symmetry.
Let us see if we can fit the given compound into the above framework.
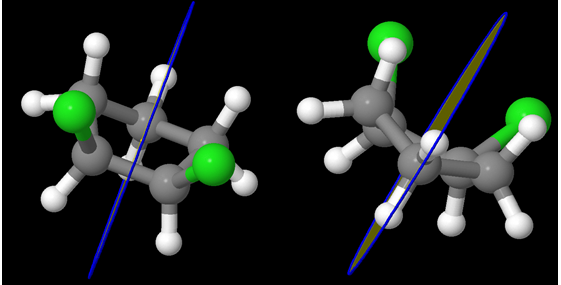
trans-1,3-dichlorocyclobutane (Chlorine atoms are in green; Carbon in grey)

Can you think of a plane that bisects the molecule into two mirror images of each other? As you can see, the 4 carbons are not planar – and the Chlorine atoms are on the opposite sides. Let us shift to a different view:

It becomes immediately clear that the 4 carbons are not in a plane. It is almost as if the compound is like:

One Chlorine is axial and the other is equatorial! But the question remains – id there a plane of symmetry?
Interestingly, there is one isn’t there?
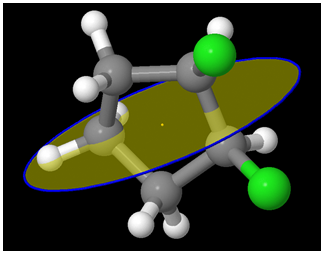
A different view:
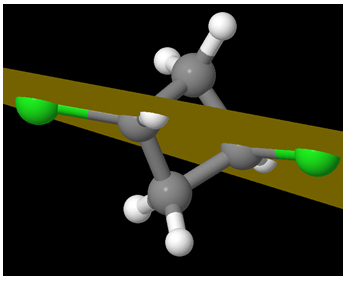
A view from another perspective:
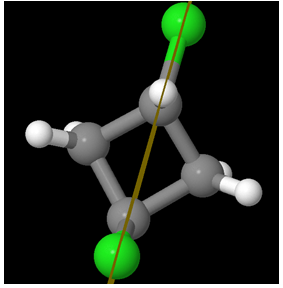
So the molecule is Achiral. But hey! Are there at least two chiral centers?
Ha Ha! There are NO chiral centers!
You might be tempted to think there are – but there aren’t!
Look at the carbon atoms attached to the Chlorine atoms. They are attached to two equivalent (CH2) groups. In the above diagram, start from the Carbon at the top. As we go through the left part of the cyclic compound, we first encounter a single bon CH2and then reach a CHCl, followed by a CH2group again and finish with the topmost carbon.
Do the same exercise but in the right part of the chain (clockwise). Start with the carbon at the top. Go right to the single bond CH2group. From there we find a CHCl group and then again a CH2group and then finish with the topmost carbon! So there is no point of difference!
Hence, there are NO chiral centers for trans-1,3-dichlorocyclobutane. Thus it is not a meso compound.
:
B
Looks tricky doesn’t it?
Let us run through the definition of a meso compound. It has to have at least 2 tetrahedral stereogenic centers. Further, it has to be achiral due to a plane of symmetry.
Let us see if we can fit the given compound into the above framework.
trans-1,3-dichlorocyclobutane (Chlorine atoms are in green; Carbon in grey)

Can you think of a plane that bisects the molecule into two mirror images of each other? As you can see, the 4 carbons are not planar – and the Chlorine atoms are on the opposite sides. Let us shift to a different view:

It becomes immediately clear that the 4 carbons are not in a plane. It is almost as if the compound is like:

One Chlorine is axial and the other is equatorial! But the question remains – id there a plane of symmetry?
Interestingly, there is one isn’t there?

A different view:

A view from another perspective:

So the molecule is Achiral. But hey! Are there at least two chiral centers?
Ha Ha! There are NO chiral centers!
You might be tempted to think there are – but there aren’t!
Look at the carbon atoms attached to the Chlorine atoms. They are attached to two equivalent (CH2) groups. In the above diagram, start from the Carbon at the top. As we go through the left part of the cyclic compound, we first encounter a single bon CH2and then reach a CHCl, followed by a CH2group again and finish with the topmost carbon.
Do the same exercise but in the right part of the chain (clockwise). Start with the carbon at the top. Go right to the single bond CH2group. From there we find a CHCl group and then again a CH2group and then finish with the topmost carbon! So there is no point of difference!
Hence, there are NO chiral centers for trans-1,3-dichlorocyclobutane. Thus it is not a meso compound.
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
C
Let’s draw according to the question. Remember that wedge and dash should be adjacent. Although this need not be true in reality, this is the convention we follow.
So, chlorine above the plane, a dash.
Hydrogen below the plane, a wedge.

Rest? They will be in the plane right?
:
C
Let’s draw according to the question. Remember that wedge and dash should be adjacent. Although this need not be true in reality, this is the convention we follow.
So, chlorine above the plane, a dash.

Hydrogen below the plane, a wedge.

Rest? They will be in the plane right?

Answer: Option B. -> S
:
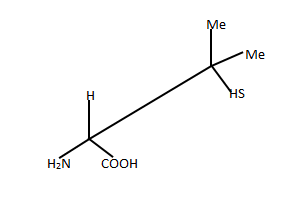
B
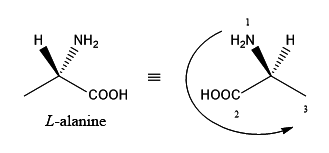
In the given projection formula, there is only one stereogenic center.
It is the carbon attached to the −COOH group! Apart from the carboxylicacid group, there is an −NH2 group, a −H and a CSH(Me)_2. Since there are four different groups on the carbon, it is a chiral centre.
The carbon attached to two methyl groups is clearly not chiral.
Let us convert the projection into a wedge-dash format and take itfrom there:
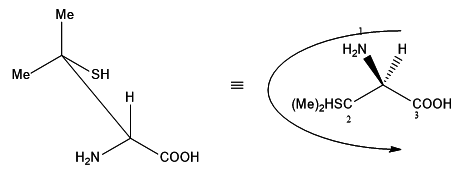
As we know hydrogen has the least atomic number, 'H' takes number '4' and in the wedge-dash notation shown above, hydrogen is below the plane. The carbon attached to the sulphur(SCC) takes number '2'. It has higher precedence than the carboxylic acidcarbon (OOO) which will take number '3'. Now we can see that the numbers are making an arc in the anti-clockwise direction. Hence given compound is in S configuration.
:
B
In the given projection formula, there is only one stereogenic center.
It is the carbon attached to the −COOH group! Apart from the carboxylicacid group, there is an −NH2 group, a −H and a CSH(Me)_2. Since there are four different groups on the carbon, it is a chiral centre.
The carbon attached to two methyl groups is clearly not chiral.
Let us convert the projection into a wedge-dash format and take itfrom there:

As we know hydrogen has the least atomic number, 'H' takes number '4' and in the wedge-dash notation shown above, hydrogen is below the plane. The carbon attached to the sulphur(SCC) takes number '2'. It has higher precedence than the carboxylic acidcarbon (OOO) which will take number '3'. Now we can see that the numbers are making an arc in the anti-clockwise direction. Hence given compound is in S configuration.
Answer: Option A. -> 60
:
A
Watch the video for the solution.
:
A
Watch the video for the solution.