12th Grade > Physics
SOUND MCQs
Total Questions : 31
| Page 1 of 4 pages
Answer: Option B. -> 36%
:
B
Intensity after passing through one slab
I′=[I−20100×I]=[I−15]=415
So, intensity after passing through two slabs
I"=[I−20100×I′]=4I′5=16125∴%decrease=[(I=−1615)I]×100=36%
:
B
Intensity after passing through one slab
I′=[I−20100×I]=[I−15]=415
So, intensity after passing through two slabs
I"=[I−20100×I′]=4I′5=16125∴%decrease=[(I=−1615)I]×100=36%
Answer: Option A. -> 0
:
A
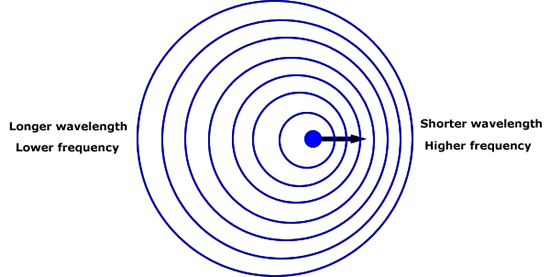
The frequency of direct and reflected sound is same.
:
A
The frequency of direct and reflected sound is same.
Answer: Option A. -> 711 Hz
:
A
As the source and the observer are approaching one another, so n’ would be larger.
f=(v+v15v−v10)600=711Hz
:
A
As the source and the observer are approaching one another, so n’ would be larger.
f=(v+v15v−v10)600=711Hz
Answer: Option A. -> The minimum value of apparent frequency is 889 Hz.
:
A
This frequency–time curve corresponds to a source moving at an angle to a stationary observer.
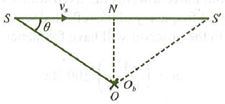
In the region SN, the source is moving towards the observer, i.e., the apparent frequency
n′=n0(vv−vscosθ)
n′=n0(300300−30cosθ)
Whenθ=π2. i.e., at N,
n′=n0=1000Hz, i.e., natural frequency of source. In the region NS’ the source is moving away from the observer, i.e., apparent frequency
n′=n0(300300−30cosθ)
Whenθ=0,i.e.,cosθ=1,
nmax=n0vv−vs=(1000Hz)(300m/s)(300m/s−30m/s)
=109×1000Hz=1111Hz
nmin=n0vv+vs=1000×300330=909Hz
:
A
This frequency–time curve corresponds to a source moving at an angle to a stationary observer.

In the region SN, the source is moving towards the observer, i.e., the apparent frequency
n′=n0(vv−vscosθ)
n′=n0(300300−30cosθ)
Whenθ=π2. i.e., at N,
n′=n0=1000Hz, i.e., natural frequency of source. In the region NS’ the source is moving away from the observer, i.e., apparent frequency
n′=n0(300300−30cosθ)
Whenθ=0,i.e.,cosθ=1,
nmax=n0vv−vs=(1000Hz)(300m/s)(300m/s−30m/s)
=109×1000Hz=1111Hz
nmin=n0vv+vs=1000×300330=909Hz
Answer: Option A. -> 1.2f and λ
:
A
Given that velocity of source vS = 0(because it is stationary). Velocity of observer v0=(15)v=0.2v (where v is the velocity of sound). Actual frequency of source is f and actual wavelength of source is λ. We know from the Doppler’s effect that the apparent frequency recorded, when the observer is moving towards the stationary source, is given by
n′=(v+v0v−vs)×n=(v+0.2vv−0)×n=1.2vv×n=1.2n=1.2f
Since the source is stationary, therefore the apparent wavelength remains unchanged, i.e., λ
:
A
Given that velocity of source vS = 0(because it is stationary). Velocity of observer v0=(15)v=0.2v (where v is the velocity of sound). Actual frequency of source is f and actual wavelength of source is λ. We know from the Doppler’s effect that the apparent frequency recorded, when the observer is moving towards the stationary source, is given by
n′=(v+v0v−vs)×n=(v+0.2vv−0)×n=1.2vv×n=1.2n=1.2f
Since the source is stationary, therefore the apparent wavelength remains unchanged, i.e., λ
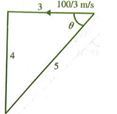
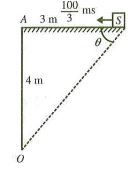
Question 7. A source of sound S is travelling at 1003 m/s along a road, towards a point A. When the source is 3 m away from A, a person standing at a point O on a road perpendicular to AS hears a sound of frequency v’. The distance of O from A at that time is 4m. If the original frequency is 640 Hz, then the value of v’ is (velocity of sound is 340 m/s)

Question 8. A source of sound is travelling with a velocity of 30 m/s towards a stationary observer. If actual frequency of source is 1000 Hz and the wind is blowing with velocity 20 m/s in a direction at 60∘ with the direction of motion of source, then the apparent frequency heard by observer is (speed of sound is 340 m/s)
Answer: Option C. -> 1094 Hz
:
C
f=(v+vmv+vm−vsource)1000
=(340+20cos60∘340+20cos60∘−30)1000
=1094 Hz
:
C
f=(v+vmv+vm−vsource)1000
=(340+20cos60∘340+20cos60∘−30)1000
=1094 Hz
Answer: Option B. -> 2.5 m/s
:
B
Apparent frequency due to source A is
n′=v−uv×n
Apparent frequency due to source B is
n"=v+uv×n
∴n"−n′=2uv×n=10
∴u=10v2n=10×3402×680=2.5m/s
:
B
Apparent frequency due to source A is
n′=v−uv×n
Apparent frequency due to source B is
n"=v+uv×n
∴n"−n′=2uv×n=10
∴u=10v2n=10×3402×680=2.5m/s
Answer: Option B. -> 30 m/s
:
B
v′=vv−vsv,v"=vv+vsvv′v′′=v+vzv−vsor65=330+v330−v11vs=330⇒vs=30m/s
:
B
v′=vv−vsv,v"=vv+vsvv′v′′=v+vzv−vsor65=330+v330−v11vs=330⇒vs=30m/s