12th Grade > Physics
SEMICONDUCTORS MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
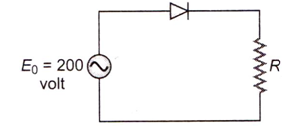
Answer: Option C. -> 200√2
:
C
If half wave rectifier the output voltage is the RMS voltage
=Vo√2=200√2
:
C
If half wave rectifier the output voltage is the RMS voltage
=Vo√2=200√2
Answer: Option B. -> 50 Hz
:
B
In half wave rectifier, we get the output only in one half cycle of input AC therefore, the frequency of the ripple of the output is same as that of input AC ie, 50 Hz.
:
B
In half wave rectifier, we get the output only in one half cycle of input AC therefore, the frequency of the ripple of the output is same as that of input AC ie, 50 Hz.
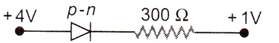
Answer: Option B. -> 10−2 A
:
B
If=4−1300=1100=10−2A
:
B
If=4−1300=1100=10−2A
Answer: Option B. -> produced when boron is added as an impurity
:
B
Boron has valency three. When boron is doped in a pure semiconductor, then p-type semiconductor is formed.
:
B
Boron has valency three. When boron is doped in a pure semiconductor, then p-type semiconductor is formed.
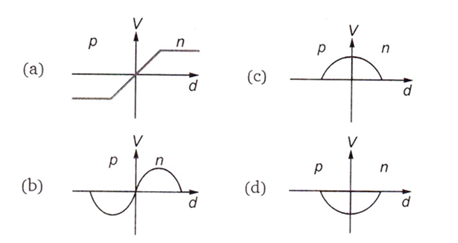
Answer: Option A. -> a
:
A
V-d curve near the junction will be as shown by curve (a).
:
A
V-d curve near the junction will be as shown by curve (a).
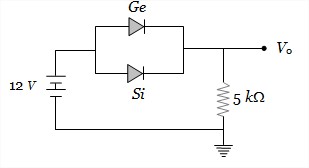
Answer: Option B. -> 0.4 V
:
B
Consider the case when Ge and Si diodes are connected as show in the given figure.
Equivalent voltage drop across the combination Ge and Si diode = 0.3 V
⇒ Current i=12−0.35kΩ=2.34mA
∴ Out put voltage V0=Ri=5kΩ×2.34mA=11.7V
Now consider the case when diode connection are reversed. In this case voltage drop across the diode's combination = 0.7 V
⇒ current i=12−0.75kΩ=2.26mA
∴V0=iR=2.26mA×5kΩ=11.3V
Hence charge in the value of v0 =11.7 - 11.3=0.4V
:
B
Consider the case when Ge and Si diodes are connected as show in the given figure.
Equivalent voltage drop across the combination Ge and Si diode = 0.3 V
⇒ Current i=12−0.35kΩ=2.34mA
∴ Out put voltage V0=Ri=5kΩ×2.34mA=11.7V
Now consider the case when diode connection are reversed. In this case voltage drop across the diode's combination = 0.7 V
⇒ current i=12−0.75kΩ=2.26mA
∴V0=iR=2.26mA×5kΩ=11.3V
Hence charge in the value of v0 =11.7 - 11.3=0.4V
Answer: Option B. -> zener voltage
:
B
In reverse bias of p-n junction when a high voltage is applied, electric breakdown of junction takes place, resulting in a large increase in reverse current. This high voltage applied is called zener voltage.
:
B
In reverse bias of p-n junction when a high voltage is applied, electric breakdown of junction takes place, resulting in a large increase in reverse current. This high voltage applied is called zener voltage.
Question 8. A working transistor with its three legs marked P, Q and R is tested using a multi-meter. No conduction is found between P and Q. By connecting the common (negative) terminal of the multimeter to R and the other (positive) terminal to P or Q, some resistance is seen on the multi-meter. Which of the following is true for the transistor?
Answer: Option B. -> It is an n-p-n transistor with R as base
:
B
When a multimeter is connected between P and Q there is no conduction between P and Q, then P and Q are of same type of semiconductor, ie, either both are on n-type or of p-type. It means emitter and collector of a transistor are P and Q. When R is connected to negative terminal of multimeter and positive terminal to P or Q, then emitter-base junction will conduct to some extent due to reverse biasing.
The similar is the case of collector – base junction. Thus the transistor is n-p-n transistor with R as base.
:
B
When a multimeter is connected between P and Q there is no conduction between P and Q, then P and Q are of same type of semiconductor, ie, either both are on n-type or of p-type. It means emitter and collector of a transistor are P and Q. When R is connected to negative terminal of multimeter and positive terminal to P or Q, then emitter-base junction will conduct to some extent due to reverse biasing.
The similar is the case of collector – base junction. Thus the transistor is n-p-n transistor with R as base.
Answer: Option C. -> 89 mA
:
C
Ic=Ie−Ib = 90 - 1 = 89mA.
:
C
Ic=Ie−Ib = 90 - 1 = 89mA.
Answer: Option D. -> potential at p is less than that at n
:
D
Option (d)
At the barrier, there are electron concentration on p side.
:
D
Option (d)
At the barrier, there are electron concentration on p side.