12th Grade > Chemistry
S BLOCK ELEMENTS MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option B. -> KO2
:
B
Whenever potassium is heated strongly in a good supply of air or oxygen, it forms KO2. KO2 is superoxide.
K2O is obtained by heating potassium nitrate with potassium.
Controlled oxidation of potassium in excess air or oxygen at 300
:
B
Whenever potassium is heated strongly in a good supply of air or oxygen, it forms KO2. KO2 is superoxide.
K2O is obtained by heating potassium nitrate with potassium.
Controlled oxidation of potassium in excess air or oxygen at 300
Answer: Option D. -> All of the above
:
D
The tendency to form hydrates decreases in the group. All the options reflect the fact that the chlorides do form hydrates.
:
D
The tendency to form hydrates decreases in the group. All the options reflect the fact that the chlorides do form hydrates.
Answer: Option C. -> sp, linear
:
C
It becomes monomer above 1200∘C. The monomer is a linear molecule with sp hybridization.
:
C
It becomes monomer above 1200∘C. The monomer is a linear molecule with sp hybridization.
Answer: Option A. -> Lewis acid and Lewis base
:
A
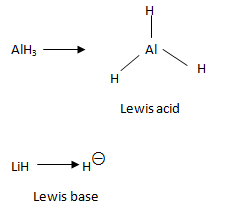
As shown in the figure, the central metal atom in AlH3 has only six valence electrons. Hence, it could accept a pair of electrons (Lewis acid) to complete its octet. On the other hand, H− is a Lewis base because it has two valence electrons thus having a completely filled shell. Further, since the ion readily shares or donates electrons - it acts as a Lewis base.
:
A

As shown in the figure, the central metal atom in AlH3 has only six valence electrons. Hence, it could accept a pair of electrons (Lewis acid) to complete its octet. On the other hand, H− is a Lewis base because it has two valence electrons thus having a completely filled shell. Further, since the ion readily shares or donates electrons - it acts as a Lewis base.
Answer: Option B. -> Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is Not a correct explanation for Statement-1
:
B
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light. The second statement describes the solvated cations (positively charged species) whereas the colour is due to the solvated electrons. Do note howeverthat both the statements are accurate.
:
B
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light. The second statement describes the solvated cations (positively charged species) whereas the colour is due to the solvated electrons. Do note howeverthat both the statements are accurate.
Answer: Option B. -> LiH>NaH>KH>RbH>CsH
:
B
The stability of alkali metal hydrides decreases with increase in the size of the metal cation. In other words, as we go down the group - the stabilityof the hydrides decreases.
:
B
The stability of alkali metal hydrides decreases with increase in the size of the metal cation. In other words, as we go down the group - the stabilityof the hydrides decreases.
Answer: Option A. -> Alkaline solution
:
A
NaH+H2O→NaOH+H2(g)
As you can see - we get NaOH which is very strongly basic.
:
A
NaH+H2O→NaOH+H2(g)
As you can see - we get NaOH which is very strongly basic.
Answer: Option A. -> Alkaline solution
:
A
As we go down a group - density increases generally. However, there is a notable exception in potassium, which is less dense than sodium. Simply put, in the case of potassium the increase in shell size outweighs the pull of the core on the outer shell electron and so potassium is less dense than sodium.
:
A
As we go down a group - density increases generally. However, there is a notable exception in potassium, which is less dense than sodium. Simply put, in the case of potassium the increase in shell size outweighs the pull of the core on the outer shell electron and so potassium is less dense than sodium.
Answer: Option A. -> Paramagnetic, paramagnetic
:
A
X is NO2& Y is O2 .Both the species have unpaired electrons in their electronic configurations (For O2 you will have to use MOT).
Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, both NO2 and O2 are paramagnetic.
:
A
X is NO2& Y is O2 .Both the species have unpaired electrons in their electronic configurations (For O2 you will have to use MOT).
Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, both NO2 and O2 are paramagnetic.
Answer: Option D. -> Making an amalgam
:
D
Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na(Hg), is analloyofmercuryandsodium.
Na(Hg) is less reactive than Na. It will decrease the rate of reaction.
Sodium is highly reactive with water and decreasing the temperature does not decrease the rate of the reaction if we consider Le Chatelier's principle.
Sodium reacts with alcohol and acetic acid also. They will not affect the rate of reaction of sodium with water.
:
D
Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na(Hg), is analloyofmercuryandsodium.
Na(Hg) is less reactive than Na. It will decrease the rate of reaction.
Sodium is highly reactive with water and decreasing the temperature does not decrease the rate of the reaction if we consider Le Chatelier's principle.
Sodium reacts with alcohol and acetic acid also. They will not affect the rate of reaction of sodium with water.
















