12th Grade > Chemistry
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS MCQs
Total Questions : 30
| Page 1 of 3 pages
Answer: Option A. -> S>p>d>f
:
A
In a given shell the screening effect or shielding effect decreases from s to f.
:
A
In a given shell the screening effect or shielding effect decreases from s to f.
Answer: Option D. -> Na and Mg
:
D
The ionization energy increases normally from sodium to magnesium as Mg has a higher effective nuclear charge as compared to Na.
In the case of Be and B, and N and O, Be is more stable because of its electronic configuration.
:
D
The ionization energy increases normally from sodium to magnesium as Mg has a higher effective nuclear charge as compared to Na.
In the case of Be and B, and N and O, Be is more stable because of its electronic configuration.
Answer: Option D. -> (i), (ii), (iii)
:
D
Down the group ionization potential (ionization enthalpy) decreases with increase in size.
Across a period, ionization potential decreases and then increases at the noble gasses.
Elements of group 2(IIA) have I.E more than that of group 13(IIA) as they have completely filled 's' orbital. Be > B
Elements of group 15(VA) have more than that of group 16(VIA) as they have half filled 'P' subshell. N > O
Inert gas elements have the highest I.P in a given period due to a stable electronic configuration.
:
D
Down the group ionization potential (ionization enthalpy) decreases with increase in size.
Across a period, ionization potential decreases and then increases at the noble gasses.
Elements of group 2(IIA) have I.E more than that of group 13(IIA) as they have completely filled 's' orbital. Be > B
Elements of group 15(VA) have more than that of group 16(VIA) as they have half filled 'P' subshell. N > O
Inert gas elements have the highest I.P in a given period due to a stable electronic configuration.
Answer: Option C. -> Type of bonding in the crystal lattice
:
C
Electron is removed from an isolated neutral gaseous atom and so type of bonding in the crystalline lattice is not associated with ionization enthalpy.
:
C
Electron is removed from an isolated neutral gaseous atom and so type of bonding in the crystalline lattice is not associated with ionization enthalpy.
Answer: Option A. -> N < C < S < P
:
A
In a group, the size of an atom increases as one proceeds from top to bottom.
This is due to the successive addition of shells.
In a period, the size of an atom decreases from left to right.
This is because the effective nuclear charge increases from left to right in the same period, thereby bringing the outermost shell closer to the nucleus.
So, the correct order of atomic size are as follows:
N < C < S < P
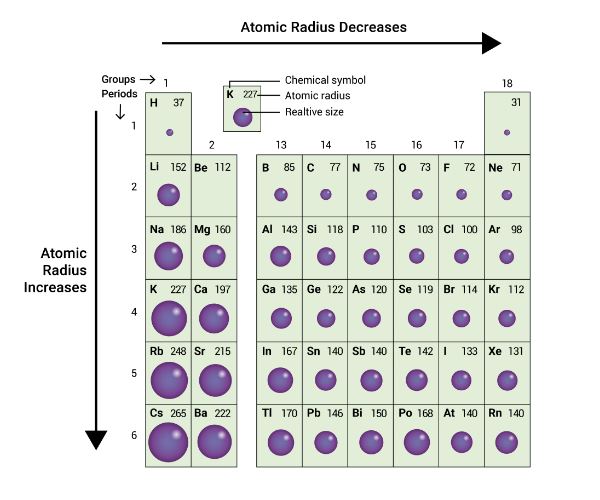
:
A
In a group, the size of an atom increases as one proceeds from top to bottom.
This is due to the successive addition of shells.
In a period, the size of an atom decreases from left to right.
This is because the effective nuclear charge increases from left to right in the same period, thereby bringing the outermost shell closer to the nucleus.
So, the correct order of atomic size are as follows:
N < C < S < P
Answer: Option D. -> S
:
D
In general, the electropositive character of the oxide's central atom will determine whether the oxide will be acidic or basic. The more electropositive the central atom the more basic the oxide. The more electronegative the central atom, the more acidic the oxide. Electropositive character increases from right to left across the periodic table and increases down the column. The trend of acid-base behaviour is from strongly basic oxides on the left-hand side to strongly acidic ones on the right, via an amphoteric oxide (aluminium oxide) in the middle.
:
D
In general, the electropositive character of the oxide's central atom will determine whether the oxide will be acidic or basic. The more electropositive the central atom the more basic the oxide. The more electronegative the central atom, the more acidic the oxide. Electropositive character increases from right to left across the periodic table and increases down the column. The trend of acid-base behaviour is from strongly basic oxides on the left-hand side to strongly acidic ones on the right, via an amphoteric oxide (aluminium oxide) in the middle.
Answer: Option D. -> M2+(g) → M3+(g)
:
D
More energy is required to remove an electron from acation with a higher positive charge.
:
D
More energy is required to remove an electron from acation with a higher positive charge.
Answer: Option A. -> Fifth
:
A
sp3 - hybridised carbon has 25% s character , 75% p character.
sp2 → 33.3% s character, 66.6% p character
sp → 50% s and 50% p
More the s character, more is the electronegativity.
H C1 ≡C2 - C3H =C4H - C5H3
1 & 2→ sp
5th carbon issp3
3 & 4 → sp2
:
A
sp3 - hybridised carbon has 25% s character , 75% p character.
sp2 → 33.3% s character, 66.6% p character
sp → 50% s and 50% p
More the s character, more is the electronegativity.
H C1 ≡C2 - C3H =C4H - C5H3
1 & 2→ sp
5th carbon issp3
3 & 4 → sp2
Answer: Option B. -> 69% Mg+ + 31 % Mg+
:
B
Energy absorbed for converting Mg(g) → Mg(g)+ = 750 kJ
Energy left unconsumed = 1200 = 750 = 450 kJ.
This energy will be required to convertMg(g)+ toMg(g)+2
Thus % ofMg(g)+2 = 4501450 × 100 = 31%
% ofMg(g)+ = 100 - 31 = 69%
:
B
Energy absorbed for converting Mg(g) → Mg(g)+ = 750 kJ
Energy left unconsumed = 1200 = 750 = 450 kJ.
This energy will be required to convertMg(g)+ toMg(g)+2
Thus % ofMg(g)+2 = 4501450 × 100 = 31%
% ofMg(g)+ = 100 - 31 = 69%
Answer: Option B. -> Si
:
B
Among the Ionization Potentials given there is a huge jump from IP4to IP5, which shows that element attains stable inert gas configuration after losing 4 electrons.
It should be an element from 14thgroup (IVA). Among the given elements, the answer will be Si.
:
B
Among the Ionization Potentials given there is a huge jump from IP4to IP5, which shows that element attains stable inert gas configuration after losing 4 electrons.
It should be an element from 14thgroup (IVA). Among the given elements, the answer will be Si.
















