MCQs
Heat Radiation, Thermal Properties Of Matter, Dual Nature Of Matter
Total Questions : 247
| Page 3 of 25 pages
Answer: Option C. -> 400p0
:
C
λ∝1p⇒Δpp=−Δλλ⇒∣∣Δpp∣∣=∣∣Δλλ∣∣⇒p0p=0.25100=1400⇒p=400p0.
Note: The above method is applicable only whenthe changes in wavelength or momenta are small.
:
C
λ∝1p⇒Δpp=−Δλλ⇒∣∣Δpp∣∣=∣∣Δλλ∣∣⇒p0p=0.25100=1400⇒p=400p0.
Note: The above method is applicable only whenthe changes in wavelength or momenta are small.
Answer: Option B. -> False
:
B
There are various ways to transfer the sufficient energy to free electrons in a metal and make them leave the surface.
(a) Thermionic emission: The metal surface is heated until the electrons gain sufficient energy to come out.

(b) Field emission: High electric field is applied across the metal to pull out the electrons
(c) Secondary emission: A high energy electron is made to hit the plate thereby transferring sufficient energy to other electrons to come out.

(d) Photo electric emission is another way in which light with sufficient energy is shone on a plate and the electrons absorb this energy to eject out of the metal surface.
:
B
There are various ways to transfer the sufficient energy to free electrons in a metal and make them leave the surface.
(a) Thermionic emission: The metal surface is heated until the electrons gain sufficient energy to come out.

(b) Field emission: High electric field is applied across the metal to pull out the electrons
(c) Secondary emission: A high energy electron is made to hit the plate thereby transferring sufficient energy to other electrons to come out.

(d) Photo electric emission is another way in which light with sufficient energy is shone on a plate and the electrons absorb this energy to eject out of the metal surface.
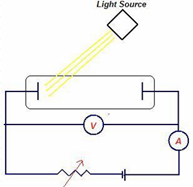
Answer: Option B. -> The emitter plate
:
B
In the diagram, light is falling on the left, which is the emitter plate, and the photoelectrons would be collected by the plate on the right, the collector plate. Electrons being negatively charged, will be repelled and slowed down if the collector plate is made negative. or if the emitter plate itself is made positive, electrons coming out will be attracted back to the left, and could, possibly, never make it to the collector plate - thus achieving stopping potential. Hence, (b) is correct.
:
B
In the diagram, light is falling on the left, which is the emitter plate, and the photoelectrons would be collected by the plate on the right, the collector plate. Electrons being negatively charged, will be repelled and slowed down if the collector plate is made negative. or if the emitter plate itself is made positive, electrons coming out will be attracted back to the left, and could, possibly, never make it to the collector plate - thus achieving stopping potential. Hence, (b) is correct.
Answer: Option B. -> I2=0.25 I1
:
B
As we have seen earlier, the intensity from a point source decreases as the square of the distance from the source. If intensityI1 was received at a distance r1,andI2atr2 -
Iα1r2⇒I1I2=r22r21=(2r1)2r21=4⇒I2=14I1⇒I2=0.25I1
:
B
As we have seen earlier, the intensity from a point source decreases as the square of the distance from the source. If intensityI1 was received at a distance r1,andI2atr2 -
Iα1r2⇒I1I2=r22r21=(2r1)2r21=4⇒I2=14I1⇒I2=0.25I1
Answer: Option A. -> 5∘C
:
A
Same amount of heat is supplied to copper and water.
mcccΔTc=mwcwΔTw
ΔTw=mcccΔTcmwcw
ΔTw=50×10−3×420×1010×10−3×4200
ΔTw=5∘C
:
A
Same amount of heat is supplied to copper and water.
mcccΔTc=mwcwΔTw
ΔTw=mcccΔTcmwcw
ΔTw=50×10−3×420×1010×10−3×4200
ΔTw=5∘C
Answer: Option D. -> all of the above
:
D
Let us look at some real life examples.
(1)Density of water is seen to be 1 kg/m3 only at 40C. At 800C, it is seen to get reduced to 0.971 kg/m3.
(2)A plastic bottle half-filled with water often shrinks when kept inside the refrigerator.
(3)If you keep heating a car tyre, which is made of a certain sturdy rubber, it will explode at some point.
Although it is unscientific to make general statements based on singular observations, we are inclined, at this point, to make the following guesses -
(1)Density of water decreases with increasing temperature
(2)Decreasing temperature shrinks a plastic bottle
(3)Since we can assume the tyre is sturdy and will not leak easily, an explosion will only be due to an increase in the pressure of air inside.
Thus, all the properties listed from (a) to (c) seem to explicitly depend on temperature.
:
D
Let us look at some real life examples.
(1)Density of water is seen to be 1 kg/m3 only at 40C. At 800C, it is seen to get reduced to 0.971 kg/m3.
(2)A plastic bottle half-filled with water often shrinks when kept inside the refrigerator.
(3)If you keep heating a car tyre, which is made of a certain sturdy rubber, it will explode at some point.
Although it is unscientific to make general statements based on singular observations, we are inclined, at this point, to make the following guesses -
(1)Density of water decreases with increasing temperature
(2)Decreasing temperature shrinks a plastic bottle
(3)Since we can assume the tyre is sturdy and will not leak easily, an explosion will only be due to an increase in the pressure of air inside.
Thus, all the properties listed from (a) to (c) seem to explicitly depend on temperature.
Answer: Option B. -> 336 W
:
B
Work done by man = Heat absorbed by ice = mL = 60 × 80 = 4800 calorie = 20160 J
∴Power=Wt=2016060=336W
:
B
Work done by man = Heat absorbed by ice = mL = 60 × 80 = 4800 calorie = 20160 J
∴Power=Wt=2016060=336W
Answer: Option A. -> 0.001∘C−1
:
A
Given: Initial density, d1=1.1gc.c−1
Final density, d2=1gc.c−1
Initial tempereature, t1=20∘C
Final temperature, t2=120∘C
Volumetric expansion of solids can be expressed as,
V2=V1(1+γ(t2−t1))
where, V1 is the initial volume, V2 is the final volume, t1 is the initial temperature, t2 is the final temperature and γ is the coefficient of cubical expansion of solid.
We know volume=massdensity
Let d1 be the density at volume V1 and d2 be the density at volume V2
Since mass of the substance, m remains same, we have,
or, md2=md1(1+γ(t2−t1))
or,γ=d1−d2d2(t2−t1)
or,γ=1.1−11(120−20)=0.1100=0.001
∴γ=0.001∘C−1
:
A
Given: Initial density, d1=1.1gc.c−1
Final density, d2=1gc.c−1
Initial tempereature, t1=20∘C
Final temperature, t2=120∘C
Volumetric expansion of solids can be expressed as,
V2=V1(1+γ(t2−t1))
where, V1 is the initial volume, V2 is the final volume, t1 is the initial temperature, t2 is the final temperature and γ is the coefficient of cubical expansion of solid.
We know volume=massdensity
Let d1 be the density at volume V1 and d2 be the density at volume V2
Since mass of the substance, m remains same, we have,
or, md2=md1(1+γ(t2−t1))
or,γ=d1−d2d2(t2−t1)
or,γ=1.1−11(120−20)=0.1100=0.001
∴γ=0.001∘C−1
Answer: Option C. -> 98∘
:
C
Temperature on any scale can be converted into other scale by X−LFPUFP−LFP = Constant for all scales
∴ X−20∘150∘−20∘=C−0∘100∘−0o ⇒ X = C×130∘100∘+20∘ = 60∘×130∘100∘+20∘=98∘
:
C
Temperature on any scale can be converted into other scale by X−LFPUFP−LFP = Constant for all scales
∴ X−20∘150∘−20∘=C−0∘100∘−0o ⇒ X = C×130∘100∘+20∘ = 60∘×130∘100∘+20∘=98∘
Answer: Option C. -> The water gets slightly warmer after taking heat from the surrounding air.
:
C
Let us assume the room is perfectly closed and no heat is being gained from or lost to the environment outside.
Here we have three bodiesthermally interacting inside the room - the glass of water (initially at room temperature of 23 degree Celsius), the air in the room, and the hot mug of coffee.
Asthe coffee cools down, it slightly increases the hotness of the air in the room. Thus, the room temperature itself increases after some time.This means the glass of water is now slightlycooler than the air around it.
Due to this temperature difference, the water will get slightly warmer until it has the same temperature as the air through whichexchange of heat occur.
:
C
Let us assume the room is perfectly closed and no heat is being gained from or lost to the environment outside.
Here we have three bodiesthermally interacting inside the room - the glass of water (initially at room temperature of 23 degree Celsius), the air in the room, and the hot mug of coffee.
Asthe coffee cools down, it slightly increases the hotness of the air in the room. Thus, the room temperature itself increases after some time.This means the glass of water is now slightlycooler than the air around it.
Due to this temperature difference, the water will get slightly warmer until it has the same temperature as the air through whichexchange of heat occur.