12th Grade > Chemistry
GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESS OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS MCQs
Total Questions : 11
| Page 1 of 2 pages
Answer: Option C. -> A molten mixture of Al2O3 & Na3AlF6
:
C
In the electrolytic extraction of Aluminium, purified alumina is mixed with Na3AlF6 and CaF2. Cryolite (Na3AlF6) helps dissolve Alumina and lowers the melting point of this mix to about 1050 ∘C. Pure Alumina melts at about 2100 ∘C. CaF2 is added to enhance the conductivity.
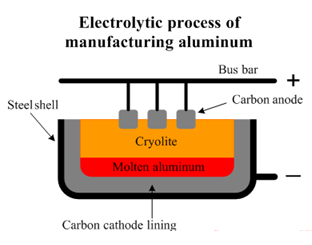
As shown in the above image, the surface on the inside of the steel case is coated with a graphite lining, which acts as the cathode. The electrolyte is a molten mixture of cryolite, molten Alumina and CaF2.
:
C
In the electrolytic extraction of Aluminium, purified alumina is mixed with Na3AlF6 and CaF2. Cryolite (Na3AlF6) helps dissolve Alumina and lowers the melting point of this mix to about 1050 ∘C. Pure Alumina melts at about 2100 ∘C. CaF2 is added to enhance the conductivity.

As shown in the above image, the surface on the inside of the steel case is coated with a graphite lining, which acts as the cathode. The electrolyte is a molten mixture of cryolite, molten Alumina and CaF2.
Answer: Option A. -> Ag, Cu, Pb
:
A
Let us look at the chief ores of the given metals:
Copper: CuFeS2 (chalcopyrites).
Silver: Ag2S (Argentite)
Lead: PbS (Galena)
:
A
Let us look at the chief ores of the given metals:
Copper: CuFeS2 (chalcopyrites).
Silver: Ag2S (Argentite)
Lead: PbS (Galena)
:
A spontaneous process is one that needs no intervention from outside. It is also called a irreversible reaction. It releases free energy and moves to a lower, thermodynamically more stable state.The change in free energy is negative.
Answer: Option C. -> Zr & Ti
:
C
van Arkel Method: The impure metal (Zr and Ti) are converted to a volatile compound, impurities being unaffected. Theformed pure volatile compound is decomposed to get the pure metal. Hence this is a method to obtain ultra pure metal by refining. Hf & Si can also be purified by van Arkel method.
:
C
van Arkel Method: The impure metal (Zr and Ti) are converted to a volatile compound, impurities being unaffected. Theformed pure volatile compound is decomposed to get the pure metal. Hence this is a method to obtain ultra pure metal by refining. Hf & Si can also be purified by van Arkel method.
Answer: Option C. -> Al, CO2
:
C
Alumina reacts with carbon or coke to form Aluminium and carbon dioxide.
2Al2O3+3C→4Al+3CO2
This is not used to extract aluminium as the (very high) temperature makes the process economically unviable. Also, at such elevated temperatures (2000 0C), aluminium could react with coke (carbon) to form aluminium carbide.
:
C
Alumina reacts with carbon or coke to form Aluminium and carbon dioxide.
2Al2O3+3C→4Al+3CO2
This is not used to extract aluminium as the (very high) temperature makes the process economically unviable. Also, at such elevated temperatures (2000 0C), aluminium could react with coke (carbon) to form aluminium carbide.
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
The underlying principle behind the process is differential wettability of ore and matrix. In other words, if by adding suitable reagents, ore and gangue can be wetted differentially, then this method can be applied to non-sulphide ores as well.
For example,
The activator Na2S is added to Malachite CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 so that a coating of CuS is formed around ore particles, such that the ore is now conducive for froth floatation. Na2S can also be added to anglesite PbSO4 so that the ore can be dressed using froth floatation.
:
A
The underlying principle behind the process is differential wettability of ore and matrix. In other words, if by adding suitable reagents, ore and gangue can be wetted differentially, then this method can be applied to non-sulphide ores as well.
For example,
The activator Na2S is added to Malachite CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 so that a coating of CuS is formed around ore particles, such that the ore is now conducive for froth floatation. Na2S can also be added to anglesite PbSO4 so that the ore can be dressed using froth floatation.
Answer: Option D. -> It is used when either ore or impurities are magnetic in nature.
:
D
Electromagnetic separation is applicable when either the ore particles or the impurities are magnetic (attracted by a magnet) in nature. Electromagnets present in a rotor attracts magnetic particles forming a separate heap from non-magnetic particles.
:
D
Electromagnetic separation is applicable when either the ore particles or the impurities are magnetic (attracted by a magnet) in nature. Electromagnets present in a rotor attracts magnetic particles forming a separate heap from non-magnetic particles.
Answer: Option A. -> Silica which is an acidic flux
:
A
FeO (Basic gangue) impurity is mixed with SiO2 (acidic flux) to form a fusible slag
FeO +SiO2 → FeSiO3
(slag)
:
A
FeO (Basic gangue) impurity is mixed with SiO2 (acidic flux) to form a fusible slag
FeO +SiO2 → FeSiO3
(slag)
Answer: Option C. -> Ni(CO)4 Δ−→ Ni+4CO
:
C
Mond’s / Carbonyl process is a technique created by Ludwig Mond in 1890 to extract and purify Nickel.
NiO(s) +H2 200∘C−−−−→ Ni(s) +H2O(g)
(Impurities)
Ni(s) +4CO(g) 50−60∘C−−−−−→ Ni(CO)4(g)
(impurities)
Ni(CO)4(g) 220−250∘C−−−−−−−→ Ni(s)+4CO(g)
:
C
Mond’s / Carbonyl process is a technique created by Ludwig Mond in 1890 to extract and purify Nickel.
NiO(s) +H2 200∘C−−−−→ Ni(s) +H2O(g)
(Impurities)
Ni(s) +4CO(g) 50−60∘C−−−−−→ Ni(CO)4(g)
(impurities)
Ni(CO)4(g) 220−250∘C−−−−−−−→ Ni(s)+4CO(g)
Answer: Option A. -> True
:
A
Gravity separation also known as hydraulic washing is based on the differences in weight between the gangue and the metal. In general, the metal particles of the ore are heavier than the impurities. So we use the principle of gravity separation to separate the two.
Finely pulverized (powdered) ore is treated with a stream of water such that the lighter gangue particles are washed away leaving behind the heavier ore particles. This is particularly applicable for heavier ore like Cassiterite and Haematite.
:
A
Gravity separation also known as hydraulic washing is based on the differences in weight between the gangue and the metal. In general, the metal particles of the ore are heavier than the impurities. So we use the principle of gravity separation to separate the two.
Finely pulverized (powdered) ore is treated with a stream of water such that the lighter gangue particles are washed away leaving behind the heavier ore particles. This is particularly applicable for heavier ore like Cassiterite and Haematite.
















